이 페이지는 기계 번역을 사용하여 번역되었습니다. 영어 원문을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.
RoadRunner HD Map을 사용하여 교차로 및 정적 객체가 있는 RoadRunner 장면 구축
이 예에서는 교차로의 위도-경도 좌표가 포함된 KML(Keyhole Markup Language) 파일에서 RoadRunner HD Map을 생성하는 방법을 보여줍니다. RoadRunner HD Map 데이터를 RoadRunner로 가져와 이를 사용하여 도로 교차로와 나무, 건물 등 주변의 정적 객체를 포함하는 3D 장면을 구축할 수 있습니다. 도로에 대한 데이터 파일을 가져오려면 Mapping Toolbox™ 라이선스가 있어야 합니다.
KML 파일 가져오기
이 예에서는 KML 파일을 사용하여 도로 교차로의 점 모양과 건물과 나무의 다각형 모양을 가져옵니다. 이 예에서는 미국 뉴저지의 Whitesville Road 주변 지역에 대한 지도 데이터(© 2022 by Google)를 사용합니다.
모양, 이름, 설명만 읽는 readgeotable 함수를 사용하여 KML 파일에서 데이터를 읽습니다.
kmlRoadData = readgeotable("RoadIntersection.kml"); kmlTreeData = readgeotable("Trees.kml"); kmlBuildingData = readgeotable("Buildings.kml");
도로 좌표를 플롯하고, 건물을 표시하고, 나무 위치에 대한 다각형을 렌더링합니다.
geoplot(kmlRoadData) hold on geoplot(kmlTreeData) geoplot(kmlBuildingData) geobasemap topographic
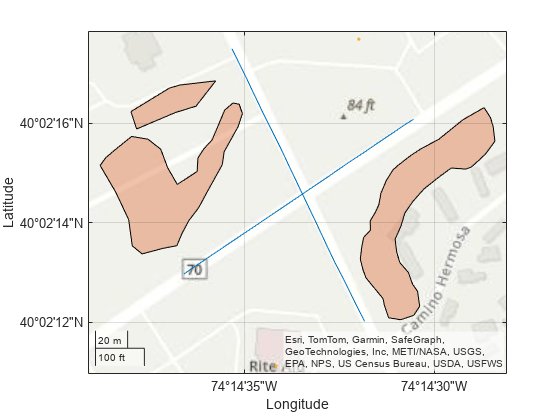
지리공간 테이블을 도로 중심 테이블로 변환하여 교차로에서 만나는 두 도로의 위도 및 경도 좌표를 얻습니다.
T1 = geotable2table(kmlRoadData,["Latitude","Longitude"]); [lat1,lon1] = polyjoin(T1.Latitude(1),T1.Longitude(1)); % Road centers of the first road meeting at the intersection [lat2,lon2] = polyjoin(T1.Latitude(2),T1.Longitude(2)); % Road centers of the second road meeting at the intersection
지리 공간 테이블을 다각형 정점 테이블로 변환하여 다각형과 건물 내부의 나무에 대한 위도 및 경도 좌표를 얻습니다.
T2 = geotable2table(kmlTreeData,["Latitude","Longitude"]); [lat3,lon3] = polyjoin(T2.Latitude(1),T2.Longitude(1)); % Polygon geometry to form trees inside of polygon [lat4,lon4] = polyjoin(T2.Latitude(2),T2.Longitude(2)); % Polygon geometry to form trees inside of polygon [lat5,lon5] = polyjoin(T2.Latitude(3),T2.Longitude(3)); % Polygon geometry to form trees inside of polygon T3 = geotable2table(kmlBuildingData,["Latitude","Longitude"]); lat6 = T3.Latitude; % Geometry for buildings lon6 = T3.Longitude; % Geometry for buildings
RoadRunner HD Map 만들기
빈 RoadRunner HD Map을 만듭니다.
rrMap = roadrunnerHDMap;
지리적 참조 원점을 경계 사각형의 중심으로 계산합니다.
[latlim,lonlim] = geoquadline([lat1; lat2],[lon1; lon2]); lat0 = mean(latlim); lon0 = mean(lonlim);
관심 지역에 대한 지리적 참조를 설정합니다.
rrMap.GeoReference = [lat0 lon0];
위도-경도 좌표를 xy 지도 좌표로 투영
RoadRunner HD Map에서 횡축 메르카토르 투영 CRS를 읽어보세요.
p = readCRS(rrMap);
위도와 경도 좌표를 xy 좌표로 투영합니다.
% Road geometry data [x1,y1] = projfwd(p,lat1,lon1); [x2,y2] = projfwd(p,lat2,lon2); % Trees geometry data [x3,y3] = projfwd(p,lat3,lon3); [x4,y4] = projfwd(p,lat4,lon4); [x5,y5] = projfwd(p,lat5,lon5); % Buildings geometry data [x6,y6] = projfwd(p,lat6,lon6);
차선 및 차선 경계에 대한 지오메트리 계산
교차로의 두 도로에 대한 선 방정식을 만듭니다.
coefficients1 = polyfit([x1(1) x1(2)],[y1(1) y1(2)],1); coefficients2 = polyfit([x2(1) x2(2)],[y2(1) y2(2)],1);
선 방정식을 사용하여 차선 지오메트리를 계산합니다.
m1 = coefficients1(1); c1 = coefficients1(2); % Specify lane widths, estimated using the measurement tool of Google Earth leftLanesWidth = [0 -3.659 -3.686 -3.643 -2.988]; rightLanesWidth = [2.820 3.764 3.698]; % Find cumulative width of all lanes to compute the geometries of parallel lanes leftLanesWidth = cumsum(leftLanesWidth); rightLanesWidth = cumsum(rightLanesWidth); rightLanesWidth = flip(rightLanesWidth); d1 = [rightLanesWidth leftLanesWidth]; m2 = coefficients2(1); c2 = coefficients2(2); % Specify lane widths, estimated using the measurement tool of Google Earth leftLanesWidth2 = [0 -3.614 -3.610 -3.661]; rightLanesWidth2 = [3.621 3.685]; % Find cumulative width of all lanes to compute the geometries of parallel lanes leftLanesWidth2 = cumsum(leftLanesWidth2); rightLanesWidth2 = cumsum(rightLanesWidth2); rightLanesWidth2 = flip(rightLanesWidth2); d2 = [rightLanesWidth2 leftLanesWidth2]; d = [d1 d2]; numLanes = size(d,2); x = cell(numLanes,1); [x{1:8}] = deal(x1); [x{9:14}] = deal(x2); m(1:8) = deal(m1); m(9:14) = deal(m2); c(1:8) = deal(c1); c(9:14) = deal(c2); y = cell(numLanes,1); for i = 1:numLanes y{i} = m(i)*x{i} + c(i) + d(i)*sqrt(1+m(i)^2); end
도로 교차로 만들기
계산된 데이터를 사용하여 RoadRunner HD Map 도로 네트워크를 생성하고 다중 차선과 다중 차선 경계로 구성된 실제 도로와 유사하도록 도로를 수정합니다. 그런 다음 실제 장면과 마찬가지로 차선 경계에 적절한 차선 표시를 적용합니다. 성능을 향상시키려면 지도의 객체 수가 증가함에 따라 HD 지도의 Lanes 및 LaneBoundaries 속성을 초기화하세요.
rrMap.Lanes(12,1) = roadrunner.hdmap.Lane; rrMap.LaneBoundaries(14,1) = roadrunner.hdmap.LaneBoundary;
Lanes 속성에 값을 할당합니다.
laneIds = ["Lane1","Lane2","Lane3","Lane4","Lane5","Lane6","Lane7","Lane8","Lane9","Lane10","Lane11","Lane12"]; travelDirection = ["Undirected","Forward","Forward","Backward","Backward","Backward","Undirected","Backward","Backward","Backward","Forward","Forward"]; for i = 1:size(rrMap.Lanes,1) rrMap.Lanes(i).ID = laneIds(i); rrMap.Lanes(i).TravelDirection = travelDirection(i); rrMap.Lanes(i).LaneType = "Driving"; if (i<8) % Assign coordinates to the Geometry properties of the lanes of the first road meeting at intersection rrMap.Lanes(i).Geometry = ([x{i} y{i}] + [x{i} y{i+1}])/2; elseif (i>8) % Assign coordinates to the Geometry properties of the lanes of the second road meeting at intersection rrMap.Lanes(i).Geometry = ([x{i} y{i+1}] + [x{i} y{i+2}])/2; end end
차선 경계에 ID와 해당 좌표를 할당합니다.
laneBoundaries = ["LB1","LB2","LB3","LB4","LB5","LB6","LB7","LB8","LB9","LB10","LB11","LB12","LB13","LB14"]; for i = 1:size(rrMap.LaneBoundaries,1) rrMap.LaneBoundaries(i).ID = laneBoundaries(i); rrMap.LaneBoundaries(i).Geometry = [x{i} y{i}]; end
차선 경계 ID를 사용하여 차선 경계를 해당 차선과 연결합니다.
for i = 1:size(rrMap.Lanes,1) if (i<8) % Associate lane boundaries of the first road meeting at intersection leftBoundary(rrMap.Lanes(i),"LB"+i,Alignment="Forward"); rightBoundary(rrMap.Lanes(i),"LB"+(i+1),Alignment="Forward"); else % Associate lane boundaries of the second road meeting at intersection leftBoundary(rrMap.Lanes(i),"LB"+(i+1),Alignment="Backward"); rightBoundary(rrMap.Lanes(i),"LB"+(i+2),Alignment="Backward"); end end
RoadRunner 차선 표시 에셋에 대한 파일 경로를 정의합니다.
% Define path to a dashed single white lane marking asset dashedSingleWhiteAsset = roadrunner.hdmap.RelativeAssetPath(AssetPath="Assets/Markings/DashedSingleWhite.rrlms"); % Define path to a solid white lane marking asset solidWhiteAsset = roadrunner.hdmap.RelativeAssetPath(AssetPath="Assets/Markings/SolidSingleWhite.rrlms"); % Define path to a solid double yellow lane marking asset doubleYellowAsset = roadrunner.hdmap.RelativeAssetPath(AssetPath="Assets/Markings/SolidDoubleYellow.rrlms"); rrMap.LaneMarkings(3,1) = roadrunner.hdmap.LaneMarking; [rrMap.LaneMarkings.ID] = deal("DashedSingleWhite","SolidWhite","DoubleYellow"); [rrMap.LaneMarkings.AssetPath] = deal(dashedSingleWhiteAsset,solidWhiteAsset,doubleYellowAsset);
표시가 차선 경계의 전체 길이에 걸쳐 있도록 지정합니다. 그런 다음 도로 가장자리 근처의 차선 경계에 흰색 실선 표시를 할당하고, 중간 차선 경계에 흰색 점선 차선 표시를 할당하고, 중앙 차선 경계에 이중 노란색 표시를 할당합니다.
% Specify the span for markings as the entire lengths of their lane boundaries markingSpan = [0 1]; markingRefDSW = roadrunner.hdmap.MarkingReference(MarkingID=roadrunner.hdmap.Reference(ID="DashedSingleWhite")); markingAttribDSW = roadrunner.hdmap.ParametricAttribution(MarkingReference=markingRefDSW,Span=markingSpan); markingRefSY = roadrunner.hdmap.MarkingReference(MarkingID=roadrunner.hdmap.Reference(ID="DoubleYellow")); markingAttribSY = roadrunner.hdmap.ParametricAttribution(MarkingReference=markingRefSY,Span=markingSpan); markingRefSW = roadrunner.hdmap.MarkingReference(MarkingID=roadrunner.hdmap.Reference(ID="SolidWhite")); markingAttribSW = roadrunner.hdmap.ParametricAttribution(MarkingReference=markingRefSW,Span=markingSpan); % Assign the markings to lane boundaries [rrMap.LaneBoundaries.ParametricAttributes] = deal(markingAttribSW,markingAttribSW,markingAttribDSW,markingAttribSY,markingAttribDSW,markingAttribDSW,markingAttribSW,markingAttribSW, ... markingAttribSW,markingAttribDSW,markingAttribDSW,markingAttribSY,markingAttribDSW,markingAttribSW);
정적 객체의 지오메트리 계산
helperInsidePolygon 헬퍼 함수를 사용하여 나무의 각 다각형에 대한 정점 좌표를 계산합니다.
[X3,Y3] = helperInsidePolygon(x3,y3); [X4,Y4] = helperInsidePolygon(x4,y4); [X5,Y5] = helperInsidePolygon(x5,y5); X = [X3'; X4'; X5']; Y = [Y3'; Y4'; Y5']; numOfTrees = numel(X);
정적 객체 만들기
나무에 대한 정적 객체를 정의한 다음 모델에 나무를 추가하고 해당 속성을 정의합니다.
% Define tree static object type path = roadrunner.hdmap.RelativeAssetPath(AssetPath="Assets/Props/Trees/Eucalyptus_Sm01.fbx"); rrMap.StaticObjectTypes(1) = roadrunner.hdmap.StaticObjectType(ID="StaticObjectType1",AssetPath=path); rrMap.StaticObjects(numOfTrees,1) = roadrunner.hdmap.StaticObject; objectRef1 = roadrunner.hdmap.Reference(ID="StaticObjectType1"); % Specify the length, width, and height values of the trees, estimated using Google Earth. length = 9; width = 9; height = 23; for i = 1:numOfTrees x = X(i); y = Y(i); aGeoOrientedBoundingBox = roadrunner.hdmap.GeoOrientedBoundingBox; aGeoOrientedBoundingBox.Center = [x y 0]; aGeoOrientedBoundingBox.Dimension = [length width height/2]; geoAngle3 = mathworks.scenario.common.GeoAngle3; geoAngle3.roll = -2; geoAngle3.pitch = -2; geoAngle3.heading = 90; geoOrientation3 = mathworks.scenario.common.GeoOrientation3; geoOrientation3.geo_angle = geoAngle3; aGeoOrientedBoundingBox.GeoOrientation = [deg2rad(-2) deg2rad(-2) deg2rad(90)]; treeID = "Tree" + string(i); rrMap.StaticObjects(i) = roadrunner.hdmap.StaticObject(ID=treeID, ... Geometry=aGeoOrientedBoundingBox, ... ObjectTypeReference=objectRef1); end
건물에 대한 정적 객체를 정의한 다음 건물을 모델에 추가하고 해당 속성을 정의합니다.
numberOfBuildings = numel(x6); % Add static object type info path = roadrunner.hdmap.RelativeAssetPath(AssetPath="Assets/Buildings/Downtown_30mX30m_6storey.fbx"); % Define static object type rrMap.StaticObjectTypes(2) = roadrunner.hdmap.StaticObjectType(ID="StaticObjectType2",AssetPath=path); % Initialize elements in the StaticObjects property of the HD map object, for better performance as the number of objects in the map increases rrMap.StaticObjects(numberOfBuildings,1) = roadrunner.hdmap.StaticObject; objectRef2 = roadrunner.hdmap.Reference(ID="StaticObjectType2"); % Specify the length, width, and height values of the buildings, estimated using Google Earth. length = [26 26]; width = [26 46]; height = 28; ID = ["Building1","Building2"]; for i= 1:numberOfBuildings x = x6(i); y = y6(i); aGeoOrientedBoundingBox = roadrunner.hdmap.GeoOrientedBoundingBox; aGeoOrientedBoundingBox.Center = [x y 0]; aGeoOrientedBoundingBox.Dimension = [length(i) width(i) height/2]; geoAngle3 = mathworks.scenario.common.GeoAngle3; geoAngle3.roll = 0; geoAngle3.pitch = 0; geoAngle3.heading = 0.4697; geoOrientation3 = mathworks.scenario.common.GeoOrientation3; geoOrientation3.geo_angle = geoAngle3; aGeoOrientedBoundingBox.GeoOrientation = [deg2rad(-2) deg2rad(-2) deg2rad(90)]; rrMap.StaticObjects(i) = roadrunner.hdmap.StaticObject(ID=ID(i), ... Geometry=aGeoOrientedBoundingBox, ... ObjectTypeReference = objectRef2); end
지리적 경계 및 참조 설정
RoadRunner HD Map에 대한 지리적 경계 및 참조를 설정하면 가져온 도로의 중심에 장면이 배치되고 RoadRunner에서 World Settings Tool을 사용하지 않고도 장면에 도로를 삽입할 수 있습니다.
지도의 지리적 경계를 중심 경계의 최소 및 최대 좌표 값으로 설정합니다.
geometries = [x1 y1; x2 y2]; geoBounds = [min(geometries) 0; max(geometries) 0]; rrMap.GeographicBoundary = geoBounds;
차선 중앙과 차선 경계를 플롯합니다.
plot(rrMap,ShowStaticObjects=true) title("RoadRunner HD Map of Road Intersection Scene") xlabel("x (m)") ylabel("y (m)")
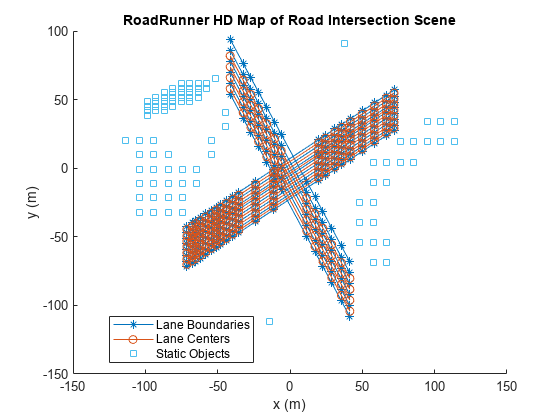
RoadRunner HD Map을 파일에 저장합니다.
write(rrMap,"RoadIntersection")HD Map 파일을 RoadRunner로 가져오고 장면 구축
MATLAB을 사용하여 RoadRunner를 열려면 프로젝트 경로를 지정하세요. 이 코드는 Windows®의 샘플 프로젝트 폴더를 보여줍니다. 프로젝트에 지정된 경로를 사용하여 RoadRunner를 엽니다.
rrProjectPath = "C:\RR\MyProjects";
rrApp = roadrunner(rrProjectPath);지정된 파일의 RoadRunner HD Map 데이터를 현재 열려 있는 장면으로 가져오고 맵을 구축합니다. 장면을 빌드하려면 활성 RoadRunner Scene Builder 라이선스가 있어야 합니다.
RoadRunner HD Map 파일을 RoadRunner 프로젝트에 복사합니다.
copyfile("RoadIntersection.rrhd","C:\RR\MyProjects\Assets")
RoadRunner HD Map에 대한 가져오기 옵션을 지정합니다.
importOptions = roadrunnerHDMapImportOptions(ImportStep="Load");RoadRunner HD Map을 RoadRunner로 가져옵니다.
importScene(rrApp,"RoadIntersection.rrhd","RoadRunner HD Map",importOptions)
장면 편집 캔버스에는 장면의 RoadRunner HD Map이 표시됩니다. 가져온 데이터를 확인하려면 장면 편집 캔버스에서 제어점, 차선, 차선 경계 및 정적 객체를 선택하고 특성 창에서 해당 특성을 볼 수 있습니다.
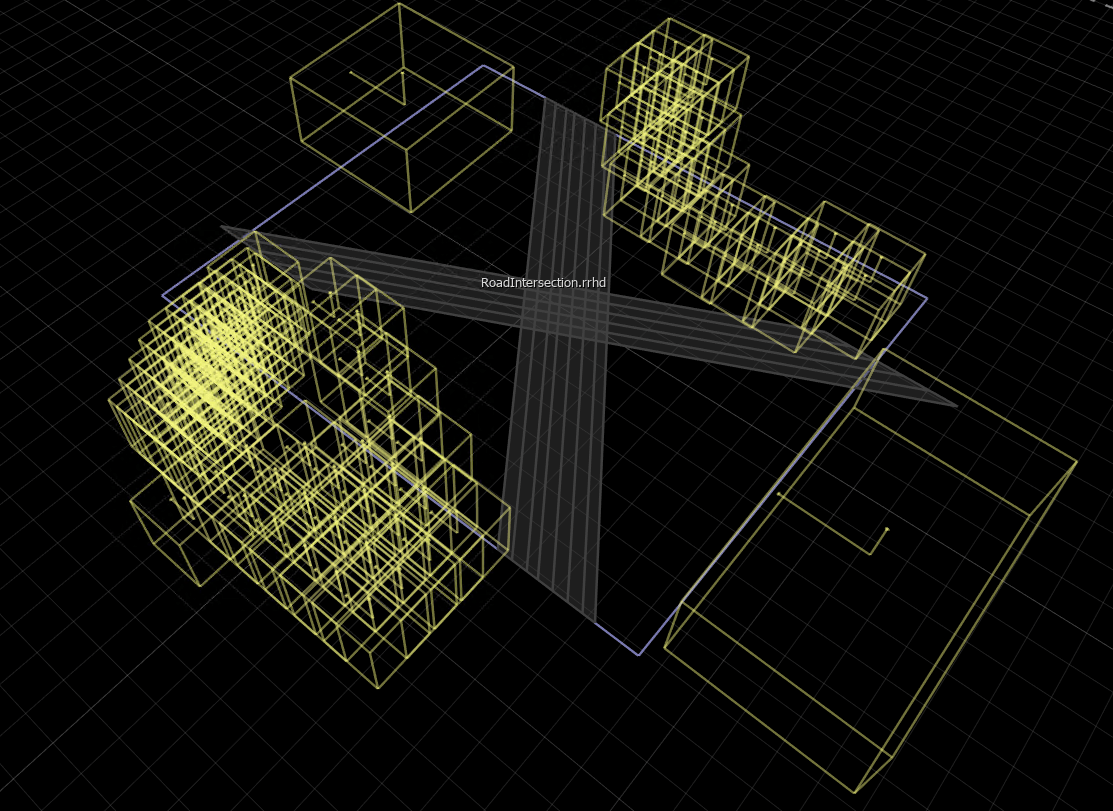
가져온 RoadRunner HD Map에서 장면을 구축하기 위한 옵션을 지정합니다. RoadRunner를 활성화하여 도로의 지오메트리 겹침에 자동 분기점을 생성하려면 겹침 그룹을 끄세요.
enableOverlapGroupsOptions = enableOverlapGroupsOptions(IsEnabled=0); buildOptions = roadrunnerHDMapBuildOptions(DetectAsphaltSurfaces=true,EnableOverlapGroupsOptions=enableOverlapGroupsOptions);
가져온 RoadRunner HD Map 데이터에서 장면을 구축하고 시각화합니다. 장면을 구축하려면 RoadRunner Scene Builder 라이선스가 있어야 합니다.
buildScene(rrApp,"RoadRunner HD Map",buildOptions)구축된 RoadRunner 장면에는 교차하는 도로는 물론 나무와 건물도 포함되어 있습니다. Junction Corner Tool을 사용하여 분기점 코너 반경을 조정하여 실제 분기점과 유사하도록 교차점을 수정합니다.
