다음에 대한 결과:

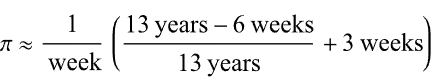
- The first argument becomes 12.885 yrs / 13 yrs or 0.99115
- Add three weeks: 0.99115 + 3 weeks = 21.991 days
- The reduced fraction becomes 21.991 days / 7 days
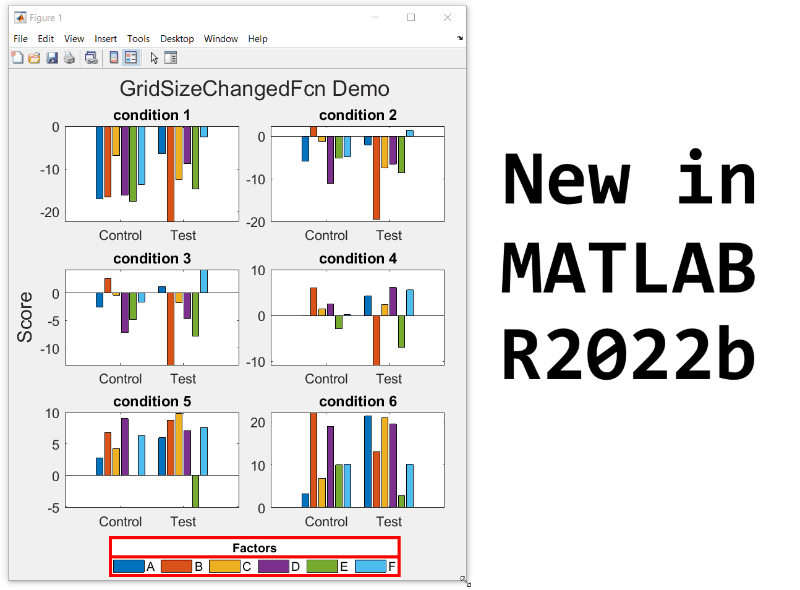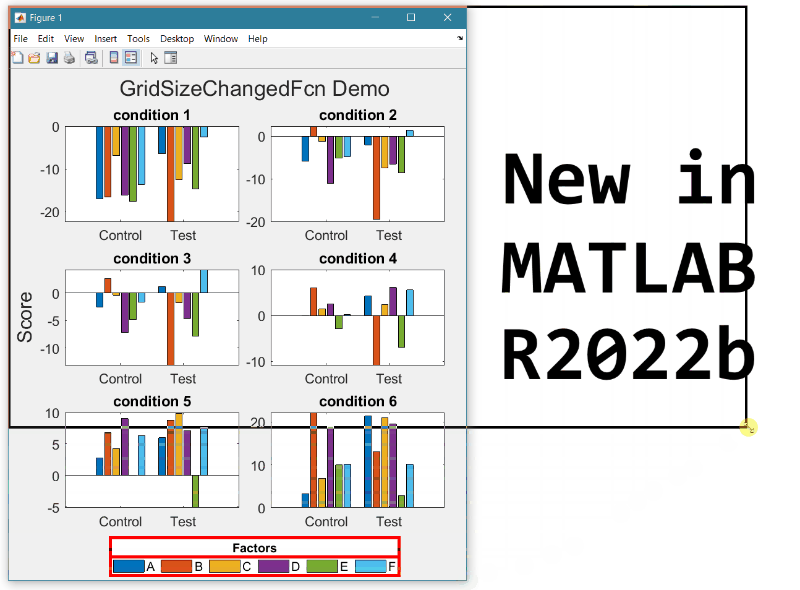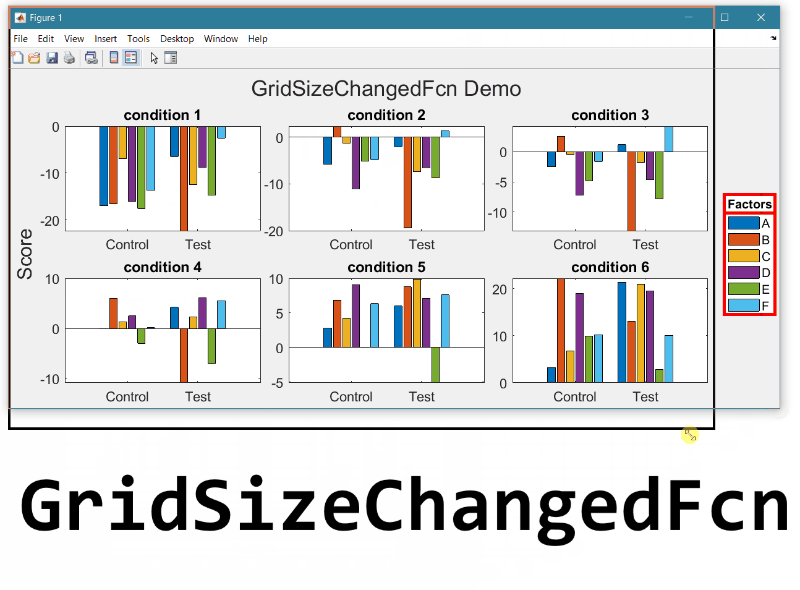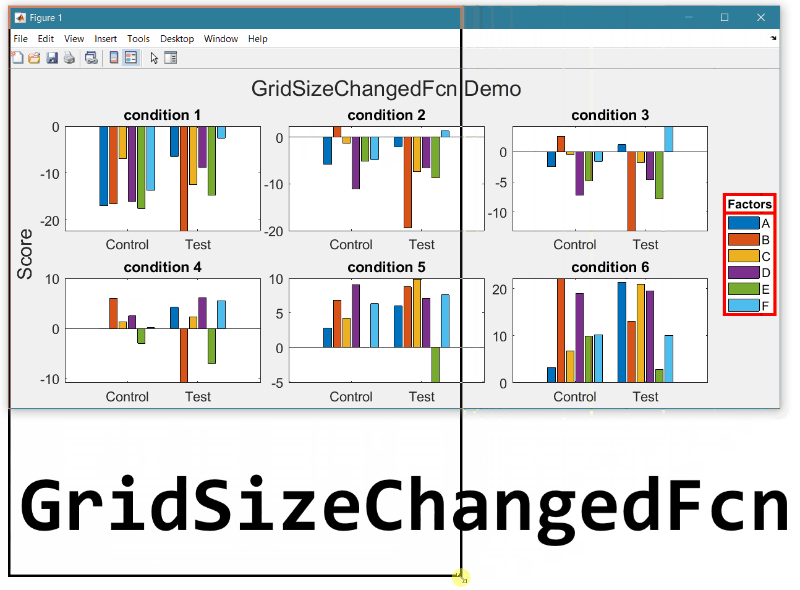
- Replace the legend with a colorbar to update the location and orientation of the colorbar.
- Define a GridSizeChangedFcn within the loop so that it is called every time a tile is added.
- Create a figure with many tiles (~20) and dynamically set a color to each row of axes.
- Assign xlabels only to the bottom row of tiles and ylabels to only the left column of tiles.

- What happens when all elements of v are equal?
- Can you produce a vector with uniform spacing without using colons or linspace?
- What additional steps would be needed to use isuniform with circular data?
- isuniform - documentation
- Floating point numbers - documentation
- Floating point numbers - Cleve's Corner (blog)
20 minutes makes a difference
I struggled to learn MATLAB at first. A colleague at my university gave me about 20 minutes of his time to show me some basic features, how to reference the documentation, and how to debug code. That was enough for me to start using MATLAB independently. After a few semesters of developing analyses and visualizations, I started answering questions in the forum when I had time. I became addicted to volunteering and learning from the breadth of analytical problems the forum exposed me to.
Have you ever solved a problem using a MathWorks product?
If your answer is YES, you may be the right person to help someone looking for guidance to solve a similar problem. Some answers in the MATLAB Central community forum maintain 1000s of views per month and some files on the File Exchange have 1000s of downloads. Volunteering a moment of your time to answer a question or to share content to the File Exchange may benefit countless individuals in the near and distant future and you will likely learn a lot by contributing too!
- 3616 questions were asked last month in the forum and in that time, 747 volunteers answered at least one question!
- 62% of those volunteers were first-time contributors!
- 335 volunteer contributors shared content in the File Exchange last month!
- 1: the number of contributions it takes to make a difference.
This week is National Volunteer Week in the USA (April 17-23). Challenge yourself and your colleagues by committing to help a stranger break barriers in their path to learning MATLAB.
How to volunteer and contribute to the MATLAB Central Community
Here are two easy ways to accept the volunteer challenge.
Contribute to the MATLAB Answers Forum
- Go to the MATLAB Answers repository. This page shows all unanswered questions starting with the most recent question. Use the filters on the left to see answered questions or questions belonging to a specific category. Alternatively, search for questions using keywords in the search field or visit the landing page.
- Open a few questions that interest you based on the question titles and tags.
- Decide how you'd like to contribute. Sometimes a question needs refinement or requires a bit of work to address. Decide whether to leave a comment that guides the user in the right direction, answer the question, or skip to the next question. The decision tree below is how some experienced contributors approach these decisions.
Pro tips
- Newer questions have more traffic and are often answered within an hour or minutes.
- Multiple answers often add valuable alternative perspectives and solutions.
- Sometimes answers aren't accepted or the asker disappears. Be not discouraged. Your answer holds much value.
Contribute to the File Exchange
- Choose a function, script, demo, or toolbox you created that may be helpful to the community.
- Go to the MathWorks File Exchange. Search for submissions that are similar to your idea and decide whether your idea adds value.
- Prepare your code for open-source sharing. The best submissions include brief documentation that explains the purpose of the code, inputs, expected outputs and limitations.
- Use the "Publish your code" button from the link above. This will guide you through the submission process.
Make a difference
No matter what level you are at as a MATLAB developer, you have skills that others around you could benefit from learning. Take the challenge and become a giant.
Let us know about your experience with MATLAB Central volunteers or your experience becoming a MATLAB Central volunteer in the comments below!
.
MATLAB R2022a provides app developers more control over user navigation through app components using the keyboard's Tab key.
Part 1. The new focus function: programmatically set keyboard focus to a UI component
Part 2. Modify focus order of components
Today we'll review Part 2. See yesterday's Community Highlight for Part 1.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Well-designed apps have an obvious flow through interactive fields and, as we learned yesterday, using the Tab key to move the focus to the next UI component is faster and more efficient than using a mouse. Here we'll learn how to read and set the tab order of UI components in an app.
Understanding tab and stacking order
By default, tab order in MATLAB apps is controlled by the stacking order in the Component Browser. Initially, the stacking order within the component browswer is based on the sequence in which the objects were added to the container object within the app. MATLAB R2020b gave us control to edit the stacking order by selecting a component and using either the Reorder tool from the Canvas toolstrip or by right-clicking the component and selecting Reorder from the context menu [1]. Tab order flows from bottom to top through the Component Browswer hierarchy for objects that are focusable. Sending a component backward within the stack sets its tab order to earlier relative to other components.
Setting tab focus order in R2022a
Three additional tab order features were added in MATLAB R2022a that make it easier to control app navigation with the Tab key.
1. Sort and Filter by Tab Order : Instead of using the Reorder tool which lists components in reverse tab-order and includes components that are not focusable, filter the list by focusable components and sort them by tab-order using the View dropdown menu within the Component Browser (label 1 in image below). From here, you can drag and drop components to set their tab (and stacking) order.
2. Auto Tab Order : To automatically sort focusable components within your app so that the tab order is from left-to-right and then top-to-bottom, in App Designer, from Design View, select the Canvas tab > Tab Order button > Apply Auto Tab Order (label 2 in image below). Alternatively, you can apply auto tab order to components within a container such as a uipanel or uitab by right-clicking on the container within the Component Browser and selecting Apply Auto Tab Order.
3. Visualize Tab Order : You no longer have to read and interpret the handle names in the component browser to understand the current tab order of UI components. Instead, view an animation of tab order within App Designer. From Design View, select the Canvas tab > Tab Order button > Visualize Tab Order (label 3 in image below).
.
Contextual focus control: the power of combining focus() with setting tab order
Yesterday's Community Highlight showed how to programmatically set UI component focus using the focus(c) function. This, combined with control of tab order, allows app developers to implement contextual focus control. For example, when a radio button is selected in the GIF below, the corresponding UI Tab is selected programmatically and the keyboard focus is set to the first component within the UI Tab thus allowing the user to smoothly continue keyboard navigation. This is achieved by a callback function that responds to changes in the Button Group that sets the SelectedTab property of the TabGroup and uses the new focus() function. For details, see the attached focusAndTabOrderDemo.mlapp.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Stay tuned
Follow Community Highlights to get notifications for new content.
Let us know what interests you in the new MATLAB R2022a release in the comment section below.
See also
- MATLAB documentation: Modify Tab Focus Order of Components
- Release notes: Modify tab focus order
- R2021a Highlight: keyboard shortcuts for UI Components
- Download the latest release of MATLAB
Footnotes
[1] R202b release notes: change the stacking order of UI components
This Community Highlight is attached as a live script.
.
MATLAB R2022a provides app developers more control over user navigation through app components using the keyboard's Tab key.
Part 1. The new focus function: programmatically set keyboard focus to a UI component
Part 2. Modify focus order of components
Today we'll review Part 1. Come back tomorrow for Part 2.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Programmatically set UI component focus
Did you know that you can save ~2 seconds every time you use a keyboard shortcut rather than reaching for your mouse [1,2]?
I need you to focus here: starting in MATLAB R2022a, use the new focus function to set keyboard focus to a specific UI component.
By specifying the component handle ( c ) in focus(c),
- The figure containing the component is displayed
- A blue frame appears around the component
- The user can directly interact with the component.
.
Which components are focusable?
Focusable components are those that a user can interact with using the keyboard. So an object set to Enable='off' or Visible='off' cannot be in focus. See the documentation for more details.
What will you do with all of that extra time saved?
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Stay tuned
Tomorrow we'll learn how to apply the new focus function with control of tab order to create contextual flow of UI component focus. Follow Community Highlights to get notifications.
Let us know what interests you in the new MATLAB R2022a release in the comment section below.
See also
- Release notes: focus
- R2021a Highlight: keyboard shortcuts for UI Components
- Download the latest release of MATLAB
Footnotes
[1] Lane et. al. (2005). International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction, 18(2).
[2] Michels (2018). median.com
This Community Highlight is attached as a live script.
Starting in MATLAB R2022a, use the append option in exportgraphics to create GIF files from animated axes, figures, or other visualizations.
This basic template contains just two steps:
% 1. Create the initial image file gifFile = 'myAnimation.gif'; exportgraphics(obj, gifFile);
% 2. Within a loop, append the gif image for i = 1:20
% % % % % % %
% Update the figure/axes %
% % % % % % % exportgraphics(obj, gifFile, Append=true); end
Note, exportgraphics will not capture UI components such as buttons and knobs and requires constant axis limits.
To create animations of images or more elaborate graphics, learn how to use imwrite to create animated GIFs .
Share your MATLAB animated GIFs in the comments below!
See Also
This Community Highlight is attached as a live script
You've spent hours designing the perfect figure and now it's time to add it to a presentation or publication but the font sizes in the figure are too small to see for the people in the back of the room or too large for the figure space in the publication. You've got titles, subtitles, axis labels, legends, text objects, and other labels but their handles are inaccessible or scattered between several blocks of code. Making your figure readable no longer requires digging through your code and setting each text object's font size manually.
Starting in MATLAB R2022a, you have full control over a figure's font sizes and font units using the new fontsize function (see release notes ).
Use fontsize() to
- Set FontSize and FontUnits properties for all text within specified graphics objects
- Incrementally increase or decrease font sizes
- Specify a scaling factor to maintain relative font sizes
- Reset font sizes and font units to their default values . Note that the default font size and units may not be the same as the font sizes/units set directly with your code.
When specifying an object handle or an array of object handles, fontsize affects the font sizes and font units of text within all nested objects.
While you're at it, also check out the new fontname function that allows you to change the font name of objects in a figure!
Give the new fontsize function a test drive using the following demo figure in MATLAB R2022a or later and try the following commands:
% Increase all font sizes within the figure by a factor of 1.5 fontsize(fig, scale=1.5)
% Set all font sizes in the uipanel to 16 fontsize(uip, 16, "pixels")
% Incrementally increase the font sizes of the left two axes (x1.1) % and incrementally decrease the font size of the legend (x0.9) fontsize([ax1, ax2], "increase") fontsize(leg, "decrease")
% Reset the font sizes within the entire figure to default values fontsize(fig, "default")
% Create fake behavioral data
rng('default')
fy = @(a,x)a*exp(-(((x-8).^2)/(2*3.^2)));
x = 1 : 0.5 : 20;
y = fy(32,x);
ynoise = y+8*rand(size(y))-4;
selectedTrial = 13;
% Plot behavioral data
fig = figure('Units','normalized','Position',[0.1, 0.1, 0.4, 0.5]);
movegui(fig, 'center')
tcl = tiledlayout(fig,2,2);
ax1 = nexttile(tcl);
hold(ax1,'on')
h1 = plot(ax1, x, ynoise, 'bo', 'DisplayName', 'Response');
h2 = plot(ax1, x, y, 'r-', 'DisplayName', 'Expected');
grid(ax1, 'on')
title(ax1, 'Behavioral Results')
subtitle(ax1, sprintf('Trial %d', selectedTrial))
xlabel(ax1, 'Time (seconds)','Interpreter','Latex')
ylabel(ax1, 'Responds ($\frac{deg}{sec}$)','Interpreter','Latex')
leg = legend([h1,h2]);
% Plot behavioral error
ax2 = nexttile(tcl,3);
behavioralError = ynoise-y;
stem(ax2, x, behavioralError)
yline(ax2, mean(behavioralError), 'r--', 'Mean', ...
'LabelVerticalAlignment','bottom')
grid(ax2, 'on')
title(ax2, 'Behavioral Error')
subtitle(ax2, ax1.Subtitle.String)
xlabel(ax2, ax1.XLabel.String,'Interpreter','Latex')
ylabel(ax2, 'Response - Expected ($\frac{deg}{sec}$)','Interpreter','Latex')
% Simulate spike train data ntrials = 25; nSamplesPerSecond = 3; nSeconds = max(x) - min(x); nSamples = ceil(nSeconds*nSamplesPerSecond); xTime = linspace(min(x),max(x), nSamples); spiketrain = round(fy(1, xTime)+(rand(ntrials,nSamples)-.5)); [trial, sample] = find(spiketrain); time = xTime(sample);
% Spike raster plot
axTemp = nexttile(tcl, 2, [2,1]);
uip = uipanel(fig, 'Units', axTemp.Units, ...
'Position', axTemp.Position, ...
'Title', 'Neural activity', ...
'BackgroundColor', 'W');
delete(axTemp)
tcl2 = tiledlayout(uip, 3, 1);
pax1 = nexttile(tcl2);
plot(pax1, time, trial, 'b.', 'MarkerSize', 4)
yline(pax1, selectedTrial-0.5, 'r-', ...
['\leftarrow Trial ',num2str(selectedTrial)], ...
'LabelHorizontalAlignment','right', ...
'FontSize', 8);
linkaxes([ax1, ax2, pax1], 'x')
pax1.YLimitMethod = 'tight';
title(pax1, 'Spike train')
xlabel(pax1, ax1.XLabel.String)
ylabel(pax1, 'Trial #')
% Show MRI
pax2 = nexttile(tcl2,2,[2,1]);
[I, cmap] = imread('mri.tif');
imshow(I,cmap,'Parent',pax2)
hold(pax2, 'on')
th = 0:0.1:2*pi;
plot(pax2, 7*sin(th)+84, 5*cos(th)+90, 'r-','LineWidth',2)
text(pax2, pax2.XLim(2), pax2.YLim(1), 'ML22a',...
'FontWeight', 'bold', ...
'Color','r', ...
'VerticalAlignment', 'top', ...
'HorizontalAlignment', 'right', ...
'BackgroundColor',[1 0.95 0.95])
title(pax2, 'Area of activation')
% Overall figure title title(tcl, 'Single trial responses')
This Community Highlight is attached as a live script.
Starting in MATLAB R2021a axis tick labels will auto-rotate to avoid overlap when the user manually specifies ticks or tick labels ( release notes ). In custom visualization functions, the tick label density or tick label lengths may be variable and unknown. The new auto-rotation feature removes the burden of detecting the need to rotate manually-set labels and eliminates the need to manually rotate them.
Many properties and combinations of properties can cause tick labels to overlap if they are not rotated.
- Length of tick labels
- Number of tick labels
- Interval between tick labels
- Font size
- Font name
- Figure size
- Axes size
- Viewing angle of the axes
Demo: varying tick density and length of tick labels
These 9 axes vary by the number of x-ticks and length of x-tick-labels. MATLAB auto-rotates the labels when needed.
Demo: Changes to axis view angle and rotation
The auto-rotation feature updates the label angles as the axes change programmatically or during user interaction.
What if I don't want auto-rotation?
Auto-rotation mode is on by default for each X|Y|Z axis. When the tick label rotation angle is manually set from the X|Y|ZTickLabelRotation property of axes or by using xtickangle | ytickangle | ztickangle , auto-rotation is turned off. Auto-rotation can also be turned off by setting the X|Y|ZTickLabelRotationMode axis property to manual but it's important to also hold the axis properties so that the rotation mode does not revert to the default value, auto. If you're looking for a broader method of reverting to older behavior you can set the default label rotation mode to manual at the start of a function that produces multiple plots and then revert to the factory default rotation mode at the end of the file (consider using onCleanup).
set(groot,'defaultAxesXTickLabelRotationMode','manual') set(groot,'defaultAxesYTickLabelRotationMode','manual') set(groot,'defaultAxesZTickLabelRotationMode','manual')
% Revert to factory-default set(groot,'defaultAxesXTickLabelRotationMode','remove') set(groot,'defaultAxesYTickLabelRotationMode','remove') set(groot,'defaultAxesZTickLabelRotationMode','remove')
A copy of this Community Highlight is attached as a live script.

