Pull up a chair!
Discussions is your place to get to know your peers, tackle the bigger challenges together, and have fun along the way.
- Want to see the latest updates? Follow the Highlights!
- Looking for techniques improve your MATLAB or Simulink skills? Tips & Tricks has you covered!
- Sharing the perfect math joke, pun, or meme? Look no further than Fun!
- Think there's a channel we need? Tell us more in Ideas
Updated Discussions
function ans = your_fcn_name(n)
n;
j=sum(1:n);
a=zeros(1,j);
for i=1:n
a(1,((sum(1:(i-1))+1)):(sum(1:(i-1))+i))=i.*ones(1,i);
end
disp
Check out the LLMs with MATLAB project on File Exchange to access Large Language Models from MATLAB.
Along with the latest support for GPT-4o mini, you can use LLMs with MATLAB to generate images, categorize data, and provide semantic analyis.
Don't use / What are Projects?
27%
1–10
31%
11–20
15%
21–30
8%
31–50
7%
51+ (comment below)
11%
추천 수: 2556
Hello, everyone! I’m Mark Hayworth, but you might know me better in the community as Image Analyst. I've been using MATLAB since 2006 (18 years). My background spans a rich career as a former senior scientist and inventor at The Procter & Gamble Company (HQ in Cincinnati). I hold both master’s & Ph.D. degrees in optical sciences from the College of Optical Sciences at the University of Arizona, specializing in imaging, image processing, and image analysis. I have 40+ years of military, academic, and industrial experience with image analysis programming and algorithm development. I have experience designing custom light booths and other imaging systems. I also work with color and monochrome imaging, video analysis, thermal, ultraviolet, hyperspectral, CT, MRI, radiography, profilometry, microscopy, NIR, and Raman spectroscopy, etc. on a huge variety of subjects.
I'm thrilled to participate in MATLAB Central's Ask Me Anything (AMA) session, a fantastic platform for knowledge sharing and community engagement. Following Adam Danz’s insightful AMA on staff contributors in the Answers forum, I’d like to discuss topics in the area of image analysis and processing. I invite you to ask me anything related to this field, whether you're seeking recommendations on tools, looking for tips and tricks, my background, or career development advice. Additionally, I'm more than willing to share insights from my experiences in the MATLAB Answers community, File Exchange, and my role as a member of the Community Advisory Board. If you have questions related to your specific images or your custom MATLAB code though, I'll invite you to ask those in the Answers forum. It's a more appropriate forum for those kinds of questions, plus you can get the benefit of other experts offering their solutions in addition to me.
For the coming weeks, I'll be here to engage with your questions and help shed light on any topics you're curious about.
Gabriel's horn is a shape with the paradoxical property that it has infinite surface area, but a finite volume.
Gabriel’s horn is formed by taking the graph of 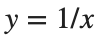 with the domain
with the domain  and rotating it in three dimensions about the
and rotating it in three dimensions about the 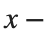 axis.
axis.
There is a standard formula for calculating the volume of this shape, for a general function 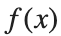 .Wwe will just state that the volume of the
.Wwe will just state that the volume of the  solid between a and b is:
solid between a and b is:
The surface area of the solid is given by:
One other thing we need to consider is that we are trying to find the value of these integrals between 1 and ∞. An integral with a limit of infinity is called an improper integral and we can't evaluate it simply by plugging the value infinity into the normal equation for a definite integral. Instead, we must first calculate the definite integral up to some finite limit b and then calculate the limit of the result as b tends to ∞:
Volume
We can calculate the horn's volume using the volume integral above, so
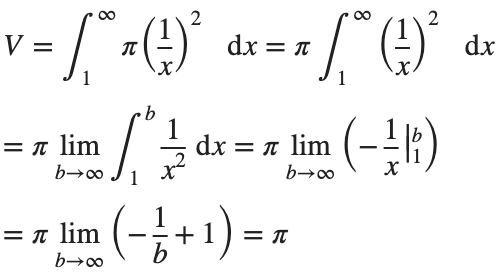
The total volume of this infinitely long trumpet isπ.
Surface Area
To determine the surface area, we first need the function’s derivative:
Now plug it into the surface area formula and we have:
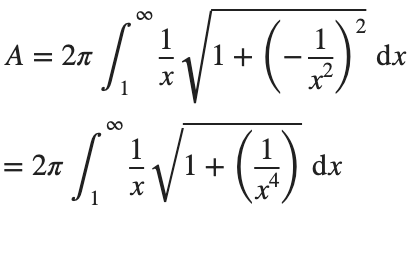
This is an improper integral and it's hard to evaluate, but since in our interval 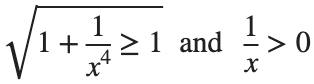
So, we have :
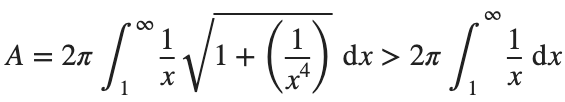
Now,we evaluate this last integral
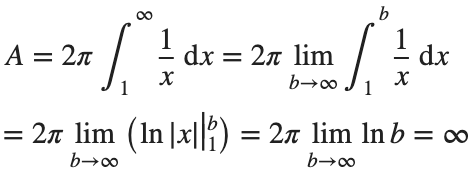
So the surface are is infinite.
% Define the function for Gabriel's Horn
gabriels_horn = @(x) 1 ./ x;
% Create a range of x values
x = linspace(1, 40, 4000); % Increase the number of points for better accuracy
y = gabriels_horn(x);
% Create the meshgrid
theta = linspace(0, 2 * pi, 6000); % Increase theta points for a smoother surface
[X, T] = meshgrid(x, theta);
Y = gabriels_horn(X) .* cos(T);
Z = gabriels_horn(X) .* sin(T);
% Plot the surface of Gabriel's Horn
figure('Position', [200, 100, 1200, 900]);
surf(X, Y, Z, 'EdgeColor', 'none', 'FaceAlpha', 0.9);
hold on;
% Plot the central axis
plot3(x, zeros(size(x)), zeros(size(x)), 'r', 'LineWidth', 2);
% Set labels
xlabel('x');
ylabel('y');
zlabel('z');
% Adjust colormap and axis properties
colormap('gray');
shading interp; % Smooth shading
% Adjust the view
view(3);
axis tight;
grid on;
% Add formulas as text annotations
dim1 = [0.4 0.7 0.3 0.2];
annotation('textbox',dim1,'String',{'$$V = \pi \int_{1}^{a} \left( \frac{1}{x} \right)^2 dx = \pi \left( 1 - \frac{1}{a} \right)$$', ...
'', ... % Add an empty line for larger gap
'$$\lim_{a \to \infty} V = \lim_{a \to \infty} \pi \left( 1 - \frac{1}{a} \right) = \pi$$'}, ...
'Interpreter','latex','FontSize',12, 'EdgeColor','none', 'FitBoxToText', 'on');
dim2 = [0.4 0.5 0.3 0.2];
annotation('textbox',dim2,'String',{'$$A = 2\pi \int_{1}^{a} \frac{1}{x} \sqrt{1 + \left( -\frac{1}{x^2} \right)^2} dx > 2\pi \int_{1}^{a} \frac{dx}{x} = 2\pi \ln(a)$$', ...
'', ... % Add an empty line for larger gap
'$$\lim_{a \to \infty} A \geq \lim_{a \to \infty} 2\pi \ln(a) = \infty$$'}, ...
'Interpreter','latex','FontSize',12, 'EdgeColor','none', 'FitBoxToText', 'on');
% Add Gabriel's Horn label
dim3 = [0.3 0.9 0.3 0.1];
annotation('textbox',dim3,'String','Gabriel''s Horn', ...
'Interpreter','latex','FontSize',14, 'EdgeColor','none', 'HorizontalAlignment', 'center');
hold off
daspect([3.5 1 1]) % daspect([x y z])
view(-27, 15)
lightangle(-50,0)
lighting('gouraud')
The properties of this figure were first studied by Italian physicist and mathematician Evangelista Torricelli in the 17th century.
Acknowledgment
I would like to express my sincere gratitude to all those who have supported and inspired me throughout this project.
First and foremost, I would like to thank the mathematician and my esteemed colleague, Stavros Tsalapatis, for inspiring me with the fascinating subject of Gabriel's Horn.
I am also deeply thankful to Mr. @Star Strider for his invaluable assistance in completing the final code.
References:
figure out what my old code does
18%
write code comments for future me
11%
address a code analyzer warning
3%
reflect on the skills I've gained
8%
get food on my mouse and keyboard
38%
All of the above
22%
추천 수: 15467
I am trying to earn my Intro to MATLAB badge in Cody, but I cannot click the Roll the Dice! problem. It simply is not letting me click it, therefore I cannot earn my badge. Does anyone know who I should contact or what to do?
cities
15%
beaches, islands, or cruises
22%
rivers, lakes, or mountains
33%
National Parks or historical sites
14%
wherever my family lives
12%
somewhere else
5%
추천 수: 12757
Base case:
Suppose you need to do a computation many times. We are going to assume that this computation cannot be vectorized. The simplest case is to use a for loop:
number_of_elements = 1e6;
test_fcn = @(x) sqrt(x) / x;
tic
for i = 1:number_of_elements
x(i) = test_fcn(i);
end
t_forward = toc;
disp(t_forward + " seconds")
Preallocation:
This can easily be sped up by preallocating the variable that houses results:
tic
x = zeros(number_of_elements, 1);
for i = 1:number_of_elements
x(i) = test_fcn(i);
end
t_forward_prealloc = toc;
disp(t_forward_prealloc + " seconds")
In this example, preallocation speeds up the loop by a factor of about three to four (running in R2024a). Comment below if you get dramatically different results.
disp(sprintf("%.1f", t_forward / t_forward_prealloc))
Run it in reverse:
Is there a way to skip the explicit preallocation and still be fast? Indeed, there is.
clear x
tic
for i = number_of_elements:-1:1
x(i) = test_fcn(i);
end
t_backward = toc;
disp(t_backward + " seconds")
By running the loop backwards, the preallocation is implicitly performed during the first iteration and the loop runs in about the same time (within statistical noise):
disp(sprintf("%.2f", t_forward_prealloc / t_backward))
Do you get similar results when running this code? Let us know your thoughts in the comments below.
Beneficial side effect:
Have you ever had to use a for loop to delete elements from a vector? If so, keeping track of index offsets can be tricky, as deleting any element shifts all those that come after. By running the for loop in reverse, you don't need to worry about index offsets while deleting elements.
Several of the colormaps are great for a 256 color surface plot, but aren't well optimized for extracting m colors for plotting several independent lines. The issue is that many colormaps have start/end colors that are too similar or are suboptimal colors for lines. There are certainly many workarounds for this, but it would be a great quality of life to adjust that directly when calling this.
Example:
x = linspace(0,2*pi,101)';
y = [1:6].*cos(x);
figure; plot(x,y,'LineWidth',2); grid on; axis tight;
And now if I wanted to color these lines, I could use something like turbo(6) or gray(6) and then apply it using colororder.
colororder(turbo(6))
But my issue is that the ends of the colormap are too similar. For other colormaps, you may get lines that are too light to be visible against the white background. There are plenty of workarounds, with my preference being to create extra colors and truncate that before using colororder.
cmap = turbo(8); cmap = cmap(2:end-1,:); % Truncate the end colors
figure; plot(x,y,'LineWidth',2); grid on; axis tight;
colororder(cmap)
I think it would be really awesome to add some name-argument input pair to these colormaps that can specify the range you want so this could even be done inside the colororder calling if desired. An example of my proposed solution would look something like this:
cmap = turbo(6,'Range',[0.1 0.8]); % Proposed idea to add functionality
Where in this scenario, the resulting colormap would be 6 equally spaced colors that range from 10% to 80% of the total color range. This would be especially nice because you could more quickly modify the range of colors, or you could set the limits regardless of whether you need to plot 3, 6, or 20 lines.
I've noticed is that the highly rated fonts for coding (e.g. Fira Code, Inconsolata, etc.) seem to overlook one issue that is key for coding in Matlab. While these fonts make 0 and O, as well as the 1 and l easily distinguishable, the brackets are not. Quite often the curly bracket looks similar to the curved bracket, which can lead to mistakes when coding or reviewing code.
So I was thinking: Could Mathworks put together a team to review good programming fonts, and come up with their own custom font designed specifically and optimized for Matlab syntax?
Chord diagrams are very common in Python and R, but there are no related functions in MATLAB before. It is not easy to draw chord diagrams of the same quality as R language, But I created a MATLAB tool that could almost do it.
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑
Here is the help document:
1 Data Format
The data requirement is a numerical matrix with all values greater than or equal to 0, or a table array, or a numerical matrix and cell array for names. First, give an example of a numerical matrix:
1.1 Numerical Matrix
dataMat=randi([0,5],[5,4]);
% 绘图(draw)
CC=chordChart(dataMat);
CC=CC.draw();
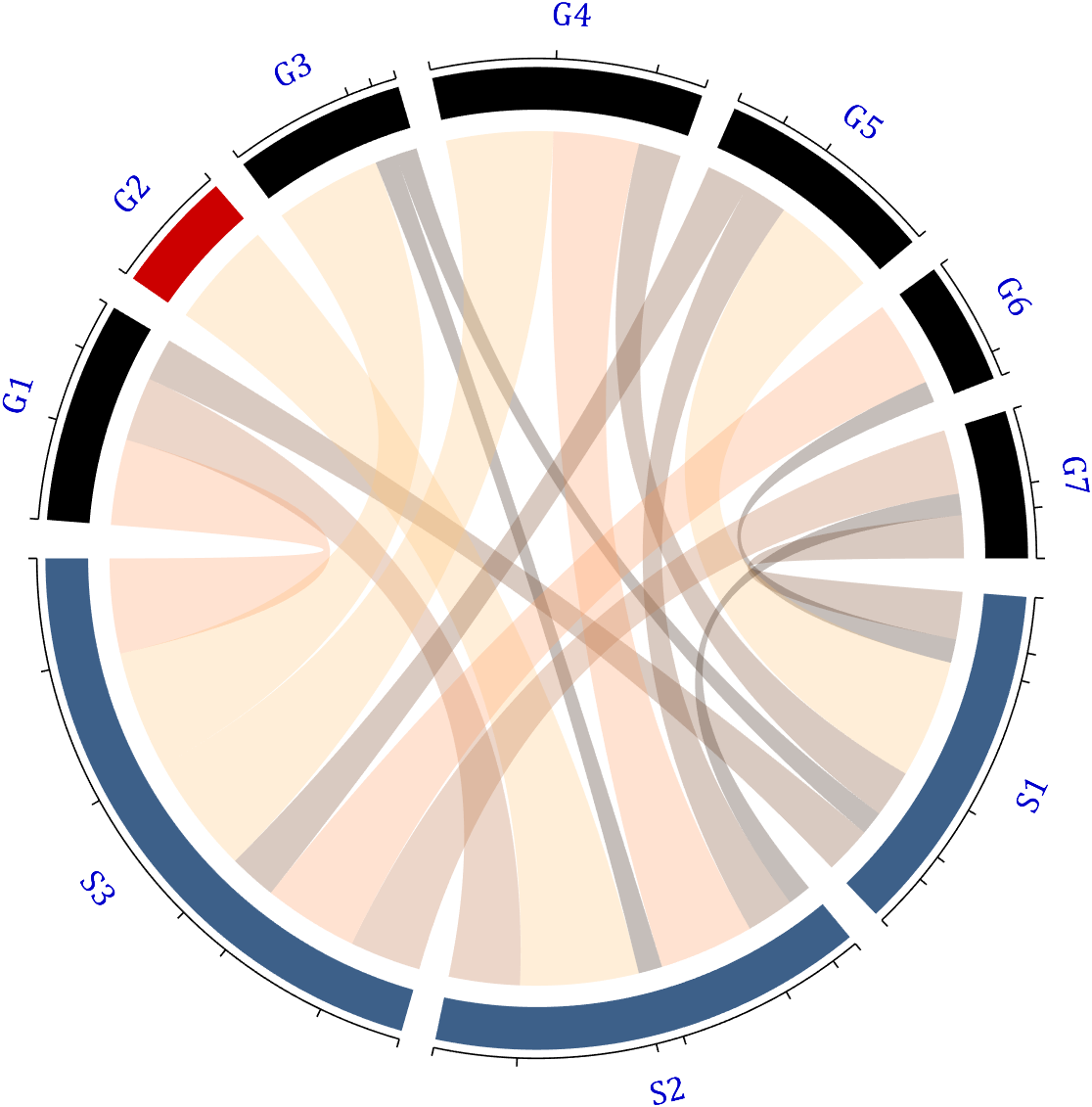
Since each object is not named, it will be automatically named Rn and Cn
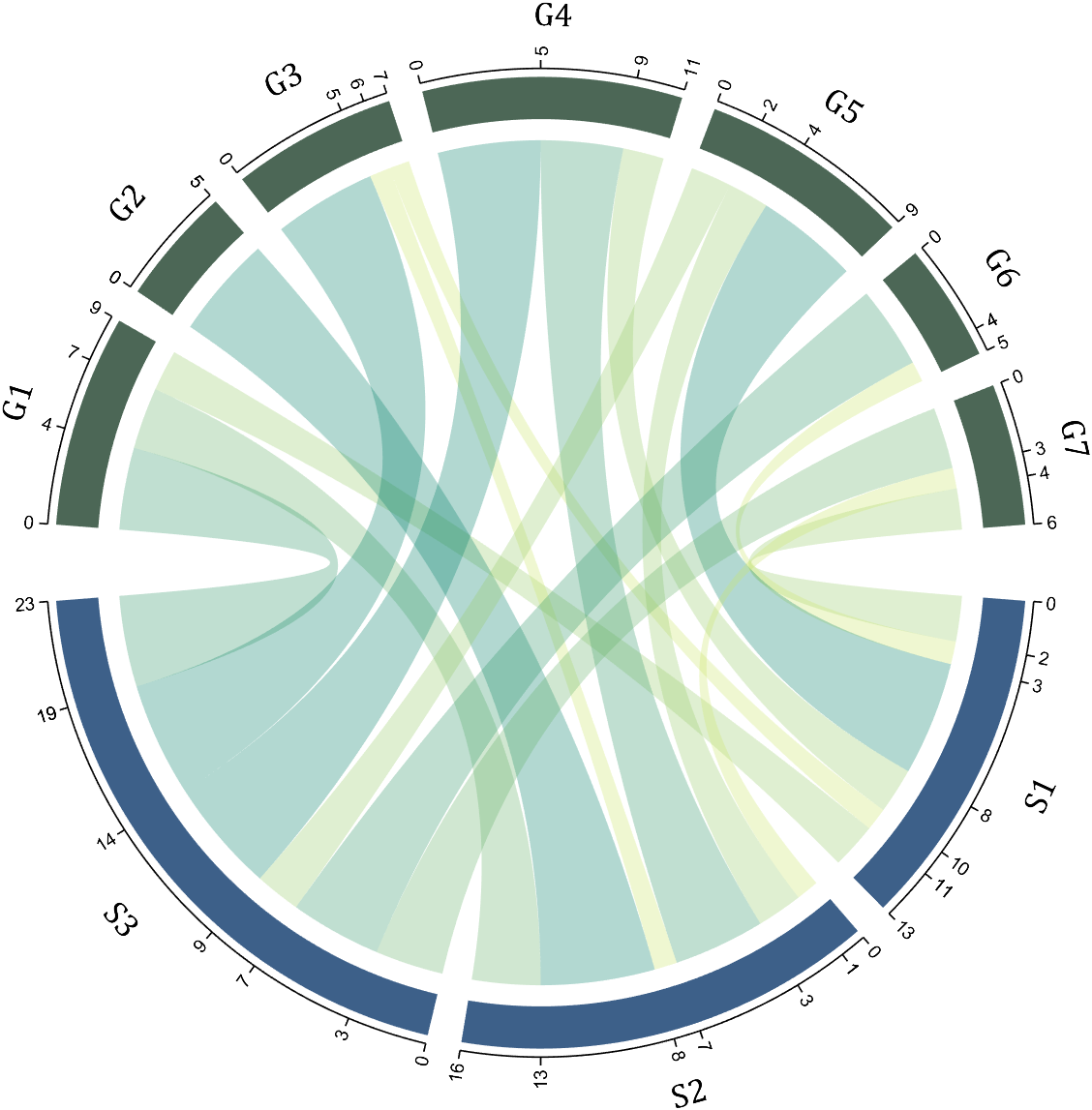
1.2 Numerical Matrix and Cell Array for Names
dataMat=[2 0 1 2 5 1 2;
3 5 1 4 2 0 1;
4 0 5 5 2 4 3];
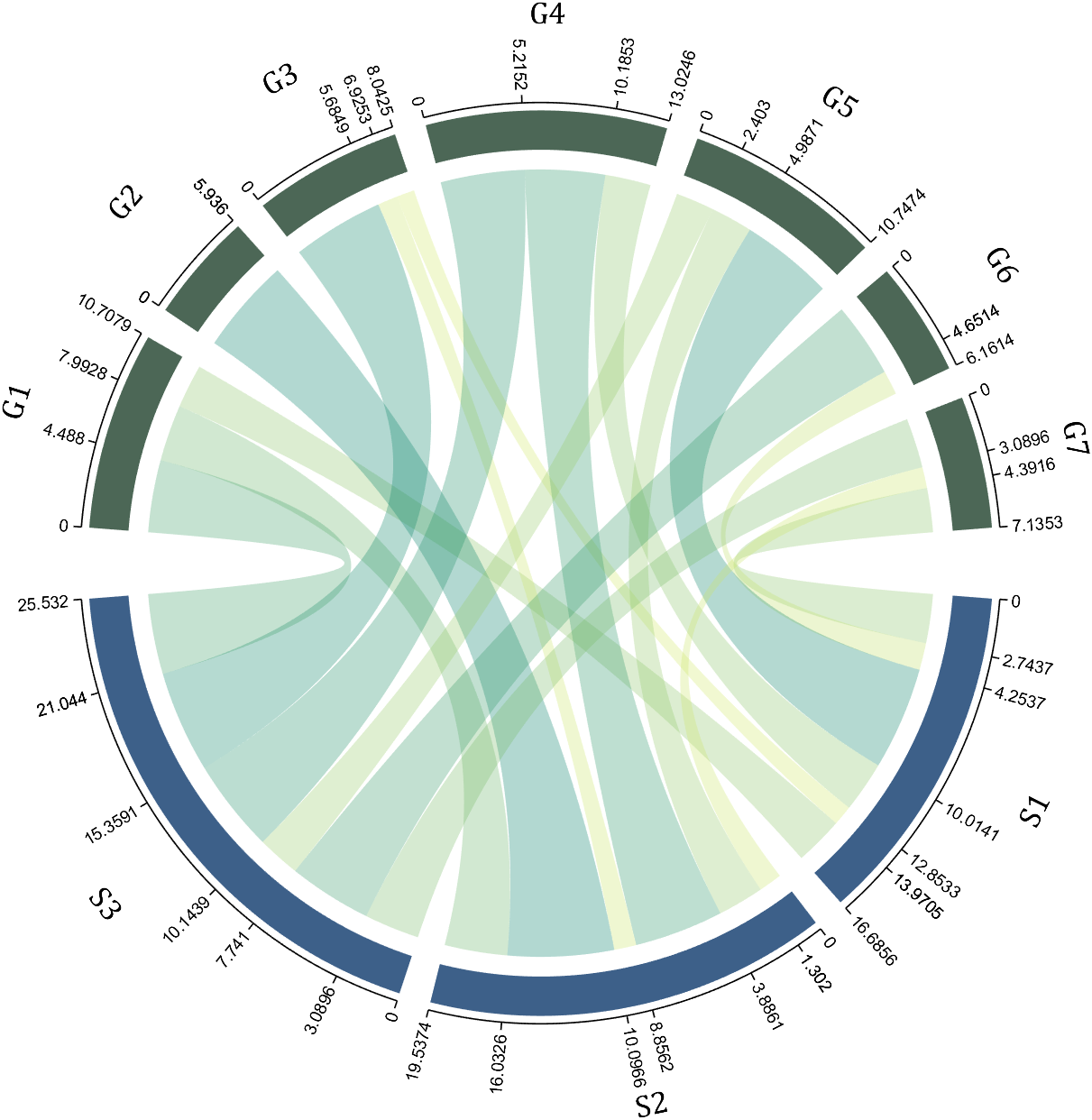
colName={'G1','G2','G3','G4','G5','G6','G7'};
rowName={'S1','S2','S3'};
CC=chordChart(dataMat,'rowName',rowName,'colName',colName);
CC=CC.draw();
RowName should be the same size as the rows of the matrix
ColName should be the same size as the columns of the matrix
For this example, if the value in the second row and third column is 1, it indicates that there is an energy flow from S2 to G3, and a chord with a width of 1 is needed between these two.
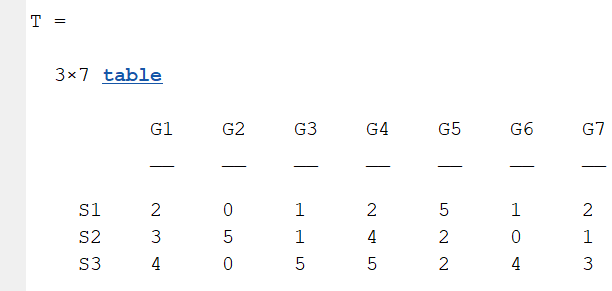
1.3 Table Array
A table array in the following format is required:
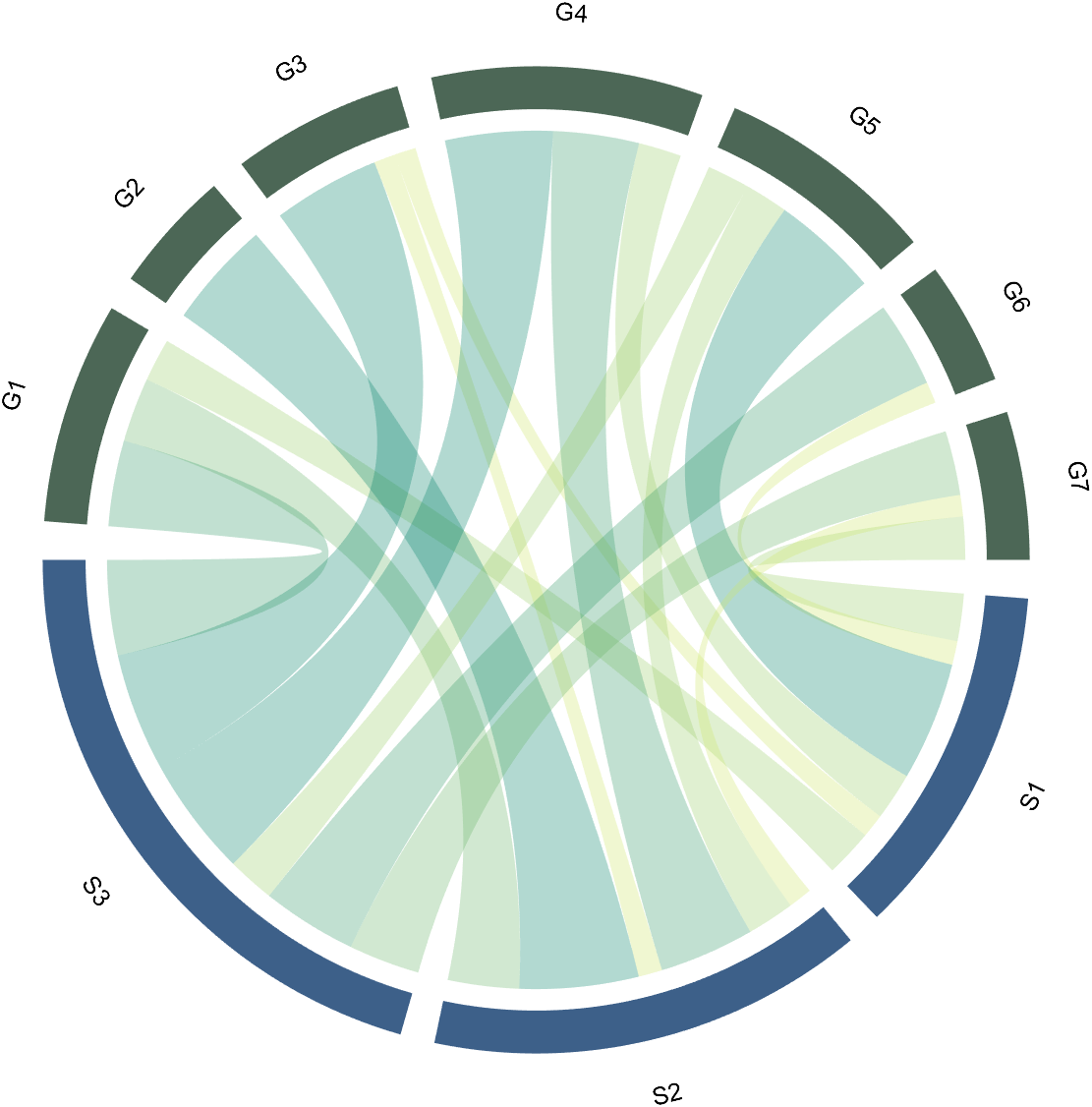
2 Decorate Chord
2.1 Batch modification of chords
Batch modification of chords can be done using the setChordProp function, and all properties of the Patch object can be modified. For example, modifying the color of the string, edge color, edge line sstyle, etc.:
CC.setChordProp('EdgeColor',[.3,.3,.3],'LineStyle','--',...
'LineWidth',.1,'FaceColor',[.3,.3,.3])
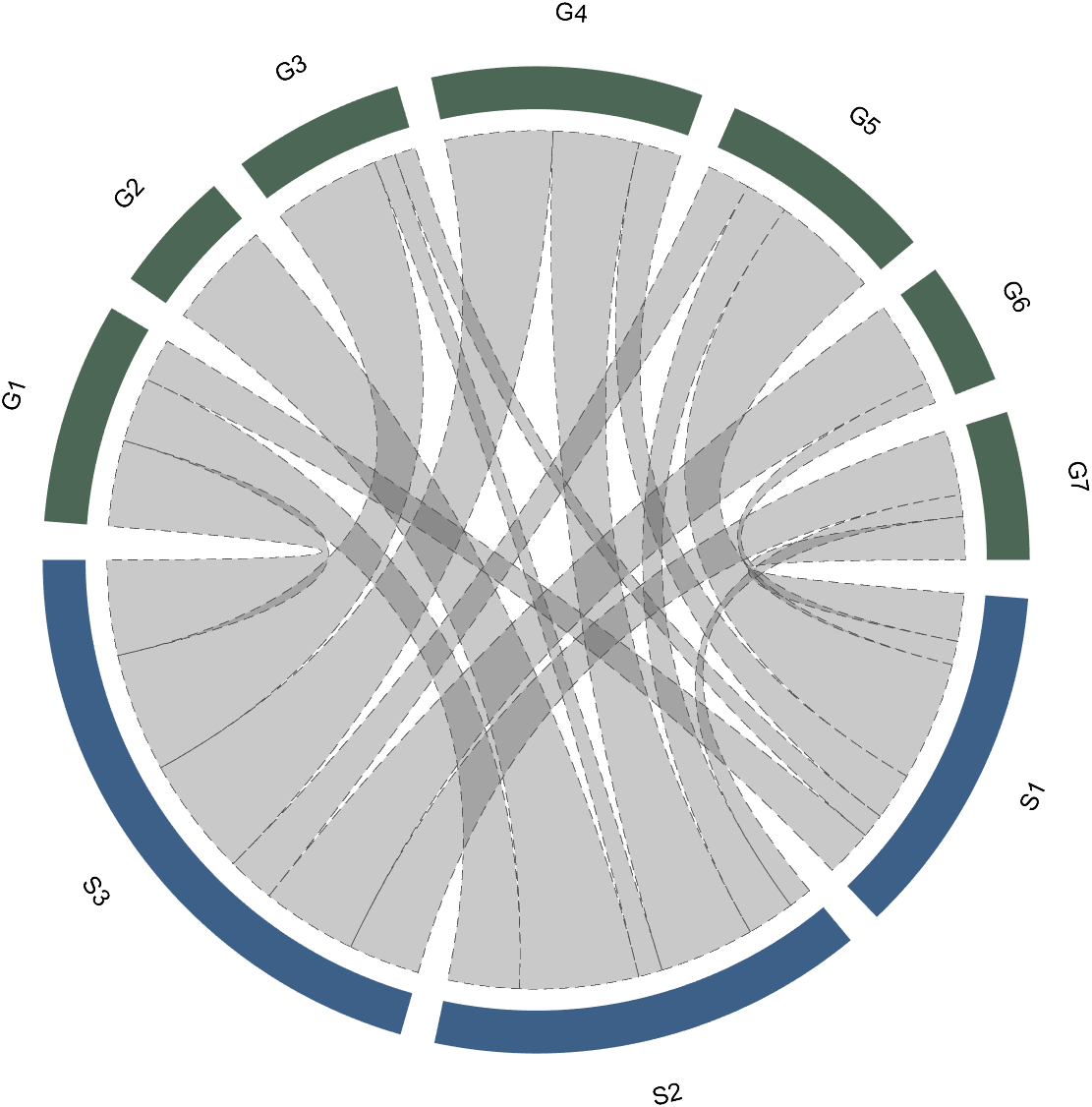
2.2 Individual Modification of Chord
The individual modification of chord can be done using the setChordMN function, where the values of m and n correspond exactly to the rows and columns of the original numerical matrix. For example, changing the color of the strings flowing from S2 to G4 to red:
CC.setChordMN(2,4,'FaceColor',[1,0,0])
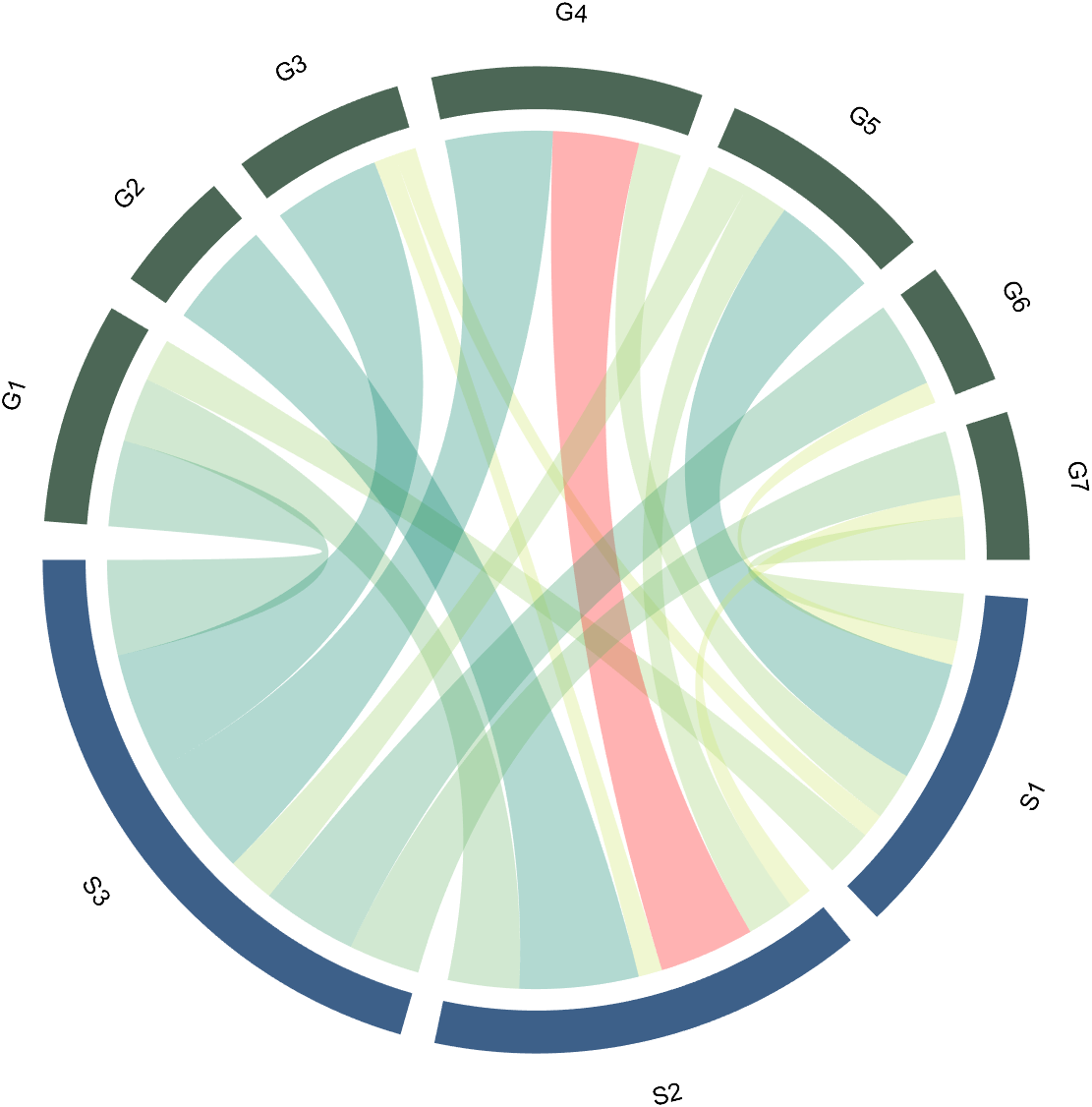
2.3 Color Mapping of Chords
Just use function colormap to do so:
% version 1.7.0更新
% 可使用colormap函数直接修改颜色
% Colors can be adjusted directly using the function colormap(demo4)
colormap(flipud(pink))
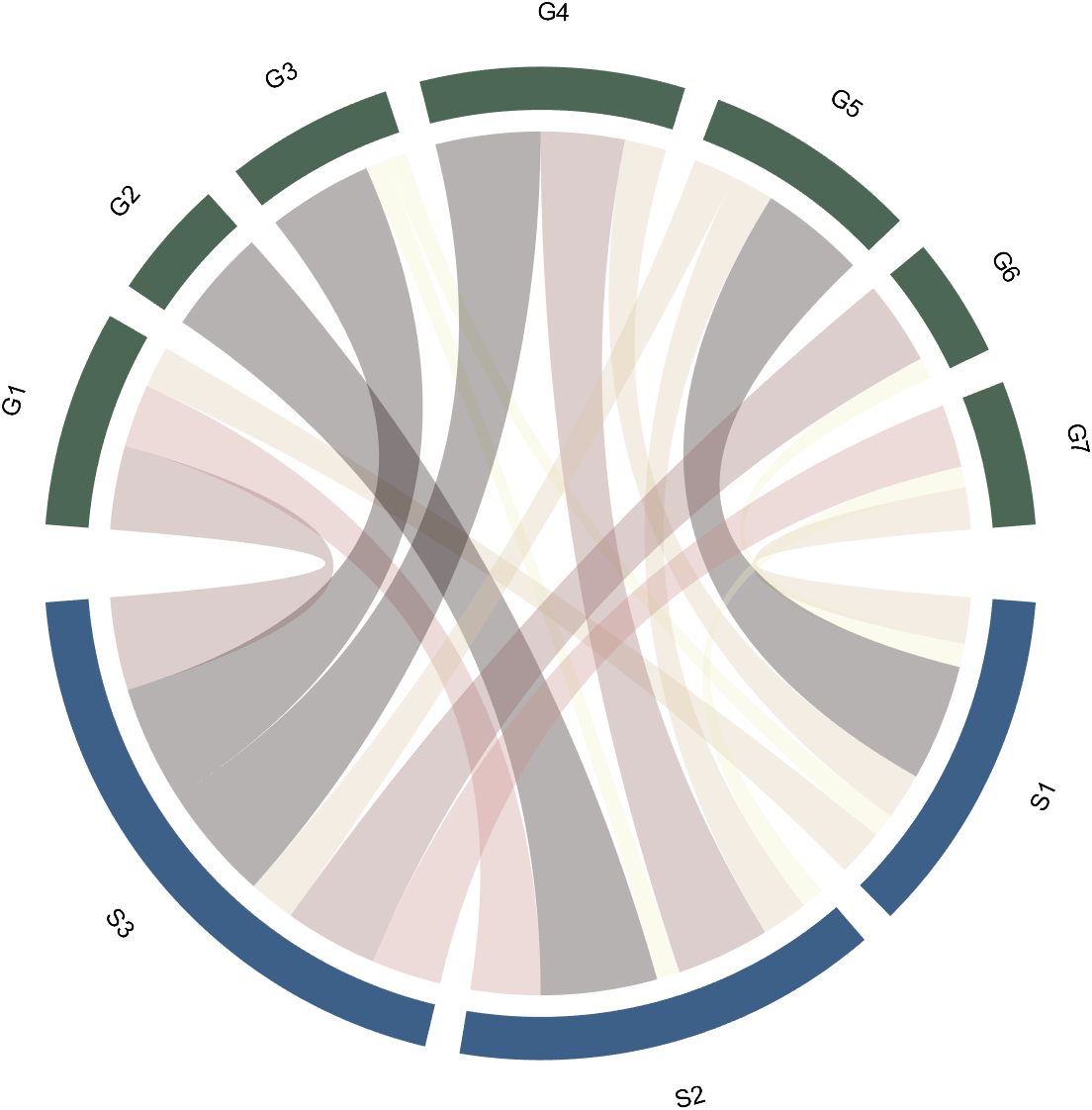
3 Arc Shaped Block Decoration
3.1 Batch Decoration of Arc-Shaped Blocks
use:
- setSquareT_Prop
- setSquareF_Prop
to modify the upper and lower blocks separately, and all attributes of the Patch object can be modified. For example, batch modify the upper blocks (change to black):
CC.setSquareT_Prop('FaceColor',[0,0,0])
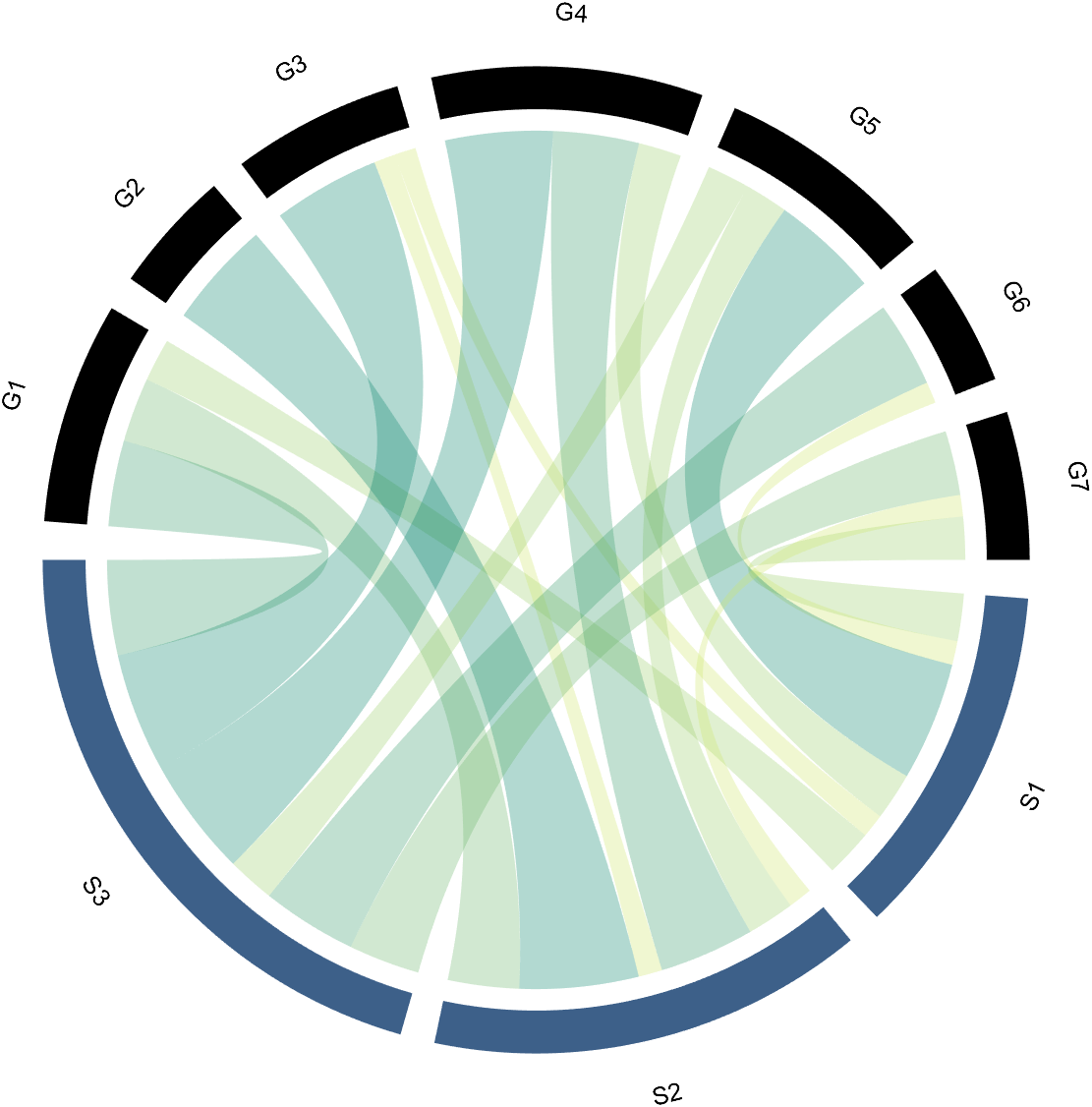
3.2 Arc-Shaped Blocks Individually Decoration
use:
- setSquareT_N
- setSquareF_N
to modify the upper and lower blocks separately. For example, modify the second block above separately (changed to red):
CC.setSquareT_N(2,'FaceColor',[.8,0,0])
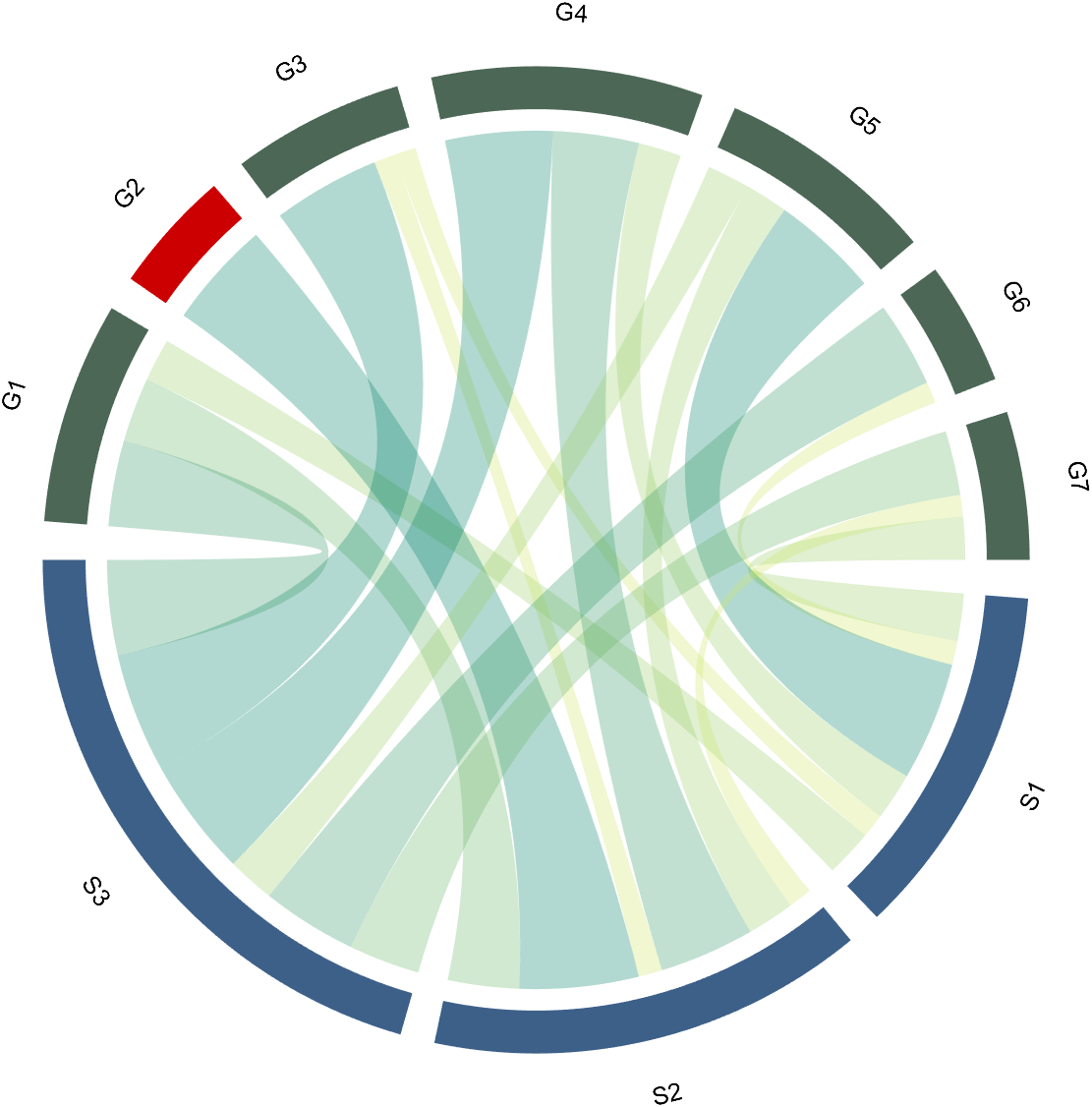
4 Font Adjustment
Use the setFont function to adjust the font, and all properties of the text object can be modified. For example, changing the font size, font, and color of the text:
CC.setFont('FontSize',25,'FontName','Cambria','Color',[0,0,.8])
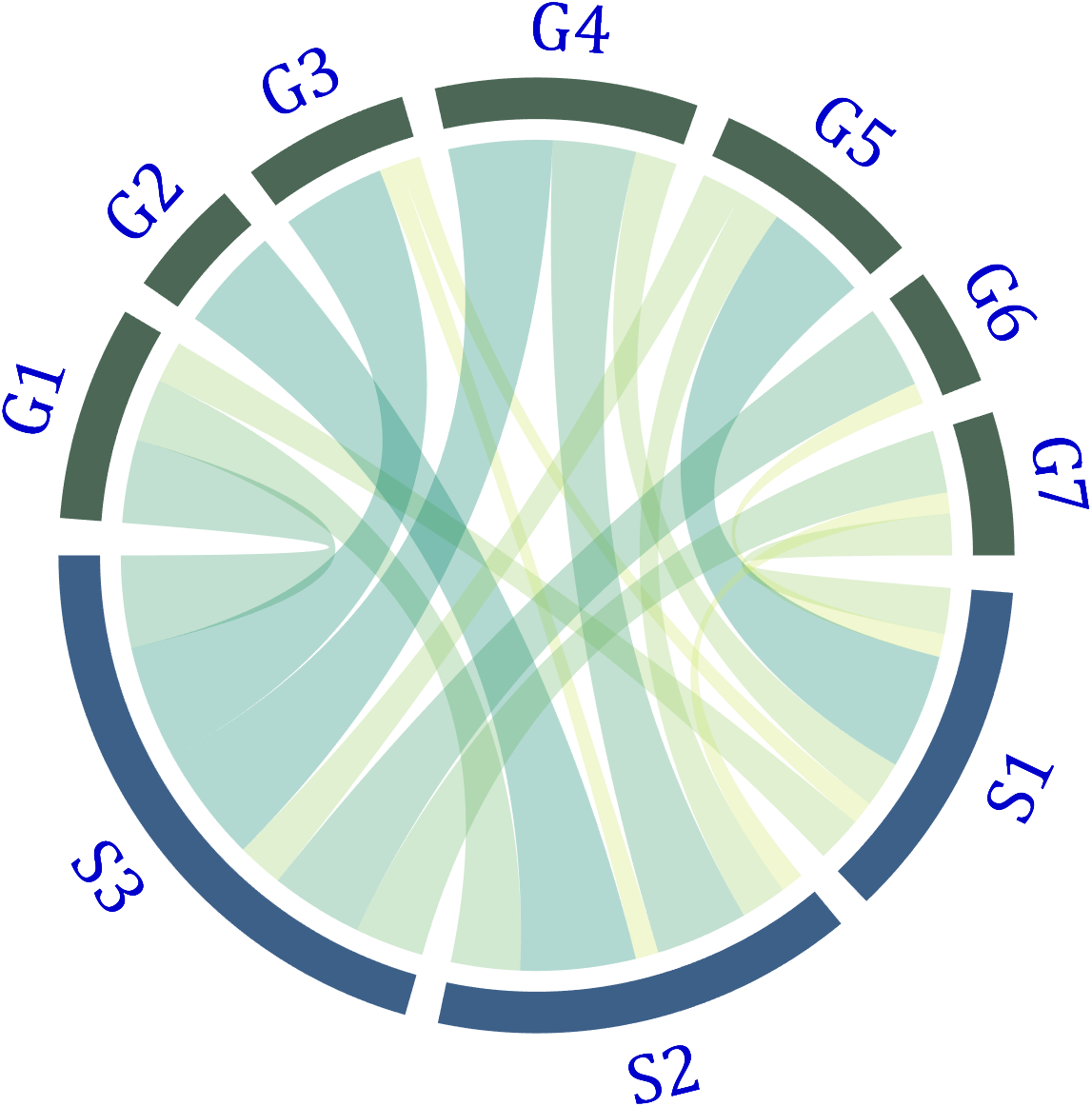
5 Show and Hide Ticks
Usage:
CC.tickState('on')
% CC.tickState('off')
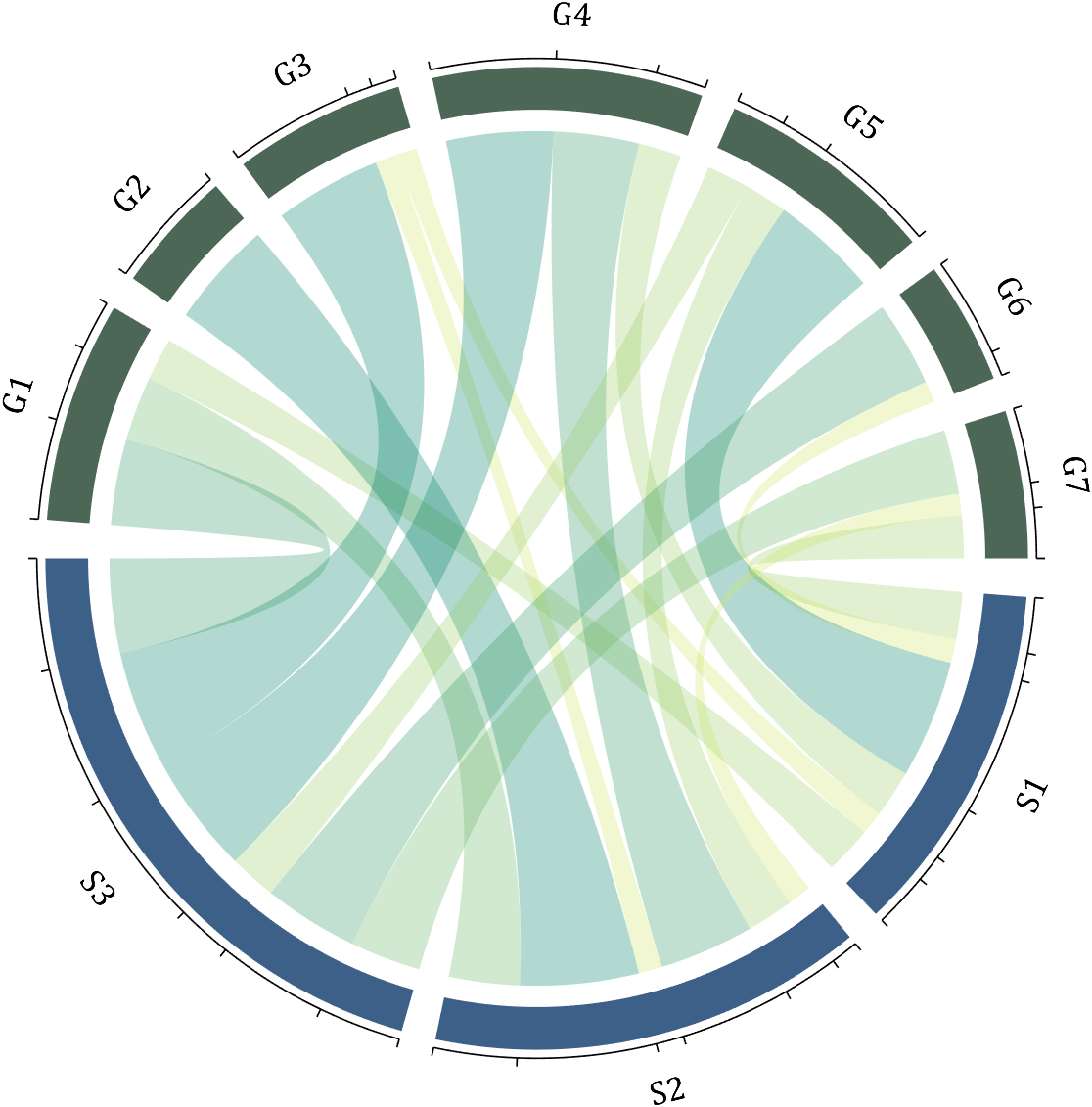
6 Attribute 'Sep' with Adjustable Square Spacing
If the matrix size is large, the drawing will be out of scale:
dataMat=randi([0,1],[20,10]);
CC=chordChart(dataMat);
CC=CC.draw();
% CC.tickState('on')
We can modify its Sep attribute:
dataMat=randi([0,1],[20,10]);
% use Sep to decrease space (separation)
% 使用 sep 减小空隙
CC=chordChart(dataMat,'Sep',1/120);
CC=CC.draw();
7 Modify Text Direction
dataMat=randi([0,1],[20,10]);
% use Sep to decrease space (separation)
% 使用 sep 减小空隙
CC=chordChart(dataMat,'Sep',1/120);
CC=CC.draw();
CC.tickState('on')
% version 1.7.0更新
% 函数labelRatato用来旋转标签
% The function labelRatato is used to rotate the label
CC.labelRotate('on')
8 Add Tick Labels
dataMat=[2 0 1 2 5 1 2;
3 5 1 4 2 0 1;
4 0 5 5 2 4 3];
colName={'G1','G2','G3','G4','G5','G6','G7'};
rowName={'S1','S2','S3'};
CC=chordChart(dataMat,'rowName',rowName,'colName',colName);
CC=CC.draw();
CC.setFont('FontSize',17,'FontName','Cambria')
% 显示刻度和数值
% Displays scales and numeric values
CC.tickState('on')
CC.tickLabelState('on')
% 调节标签半径
% Adjustable Label radius
CC.setLabelRadius(1.3);
% figure()
% dataMat=[2 0 1 2 5 1 2;
% 3 5 1 4 2 0 1;
% 4 0 5 5 2 4 3];
% dataMat=dataMat+rand(3,7);
% dataMat(dataMat<1)=0;
%
% CC=chordChart(dataMat,'rowName',rowName,'colName',colName);
% CC=CC.draw();
% CC.setFont('FontSize',17,'FontName','Cambria')
%
% % 显示刻度和数值
% % Displays scales and numeric values
% CC.tickState('on')
% CC.tickLabelState('on')
%
% % 调节标签半径
% % Adjustable Label radius
% CC.setLabelRadius(1.4);
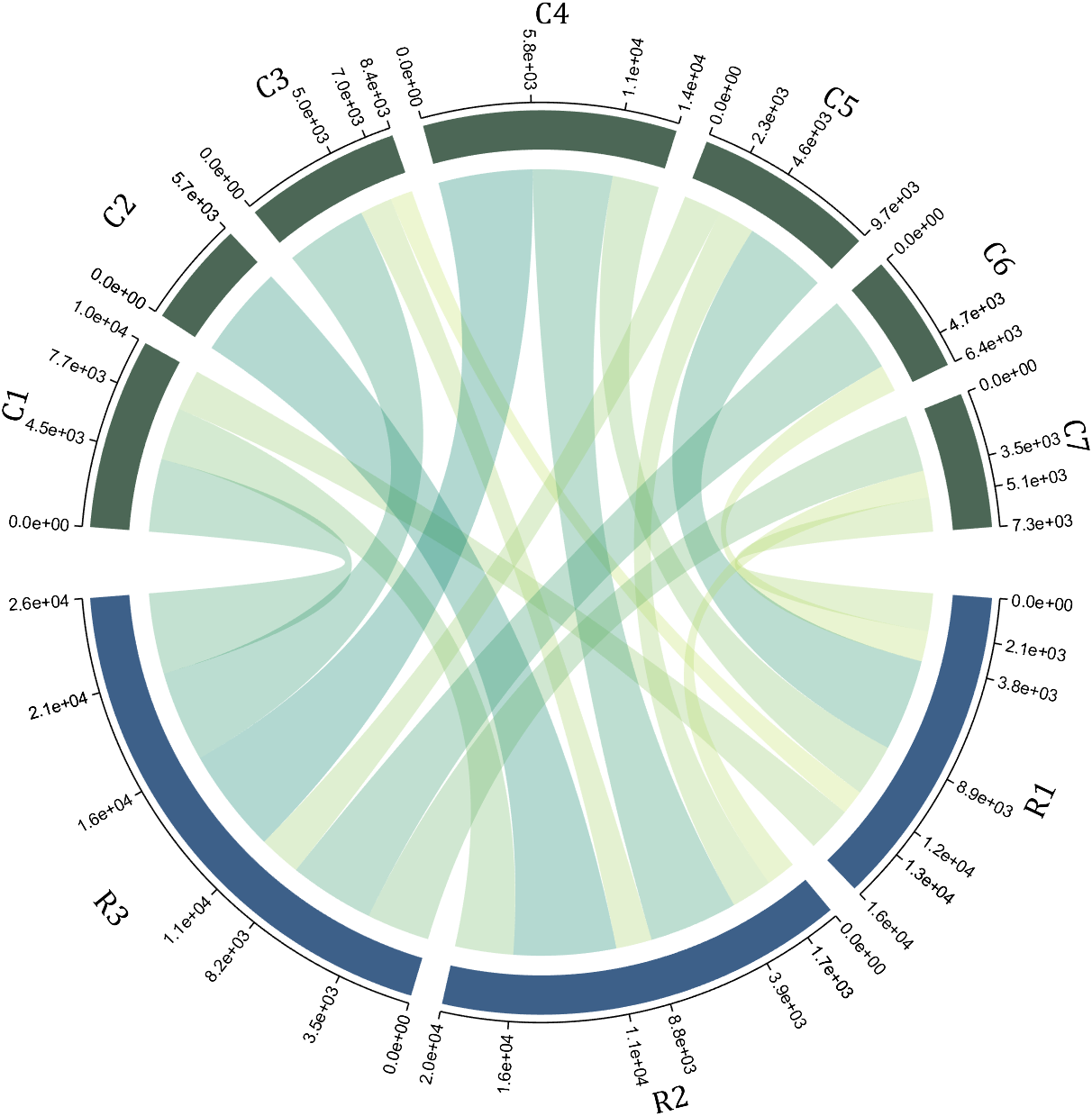
9 Custom Tick Label Format
A function handle is required to input numeric output strings. The format can be set through the setTickLabelFormat function, such as Scientific notation:
dataMat=[2 0 1 2 5 1 2;
3 5 1 4 2 0 1;
4 0 5 5 2 4 3];
dataMat=dataMat+rand(3,7);
dataMat(dataMat<1)=0;
dataMat=dataMat.*1000;
CC=chordChart(dataMat);
CC=CC.draw();
CC.setFont('FontSize',17,'FontName','Cambria')
% 显示刻度和数值
% Displays scales and numeric values
CC.tickState('on')
CC.tickLabelState('on')
% 调节标签半径
% Adjustable Label radius
CC.setLabelRadius(1.4);
% 调整数值字符串格式
% Adjust numeric string format
CC.setTickLabelFormat(@(x)sprintf('%0.1e',x))
10 A Demo
rng(2)
dataMat=randi([1,7],[11,5]);
colName={'Fly','Beetle','Leaf','Soil','Waxberry'};
rowName={'Bartomella','Bradyrhizobium','Dysgomonas','Enterococcus',...
'Lactococcus','norank','others','Pseudomonas','uncultured',...
'Vibrionimonas','Wolbachia'};
CC=chordChart(dataMat,'rowName',rowName,'colName',colName,'Sep',1/80);
CC=CC.draw();
% 修改上方方块颜色(Modify the color of the blocks above)
CListT=[0.7765 0.8118 0.5216;0.4431 0.4706 0.3843;0.5804 0.2275 0.4549;
0.4471 0.4039 0.6745;0.0157 0 0 ];
for i=1:5
CC.setSquareT_N(i,'FaceColor',CListT(i,:))
end
% 修改下方方块颜色(Modify the color of the blocks below)
CListF=[0.5843 0.6863 0.7843;0.1098 0.1647 0.3255;0.0902 0.1608 0.5373;
0.6314 0.7961 0.2118;0.0392 0.2078 0.1059;0.0157 0 0 ;
0.8549 0.9294 0.8745;0.3882 0.3255 0.4078;0.5020 0.7216 0.3843;
0.0902 0.1843 0.1804;0.8196 0.2314 0.0706];
for i=1:11
CC.setSquareF_N(i,'FaceColor',CListF(i,:))
end
% 修改弦颜色(Modify chord color)
for i=1:5
for j=1:11
CC.setChordMN(j,i,'FaceColor',CListT(i,:),'FaceAlpha',.5)
end
end
CC.tickState('on')
CC.labelRotate('on')
CC.setFont('FontSize',17,'FontName','Cambria')
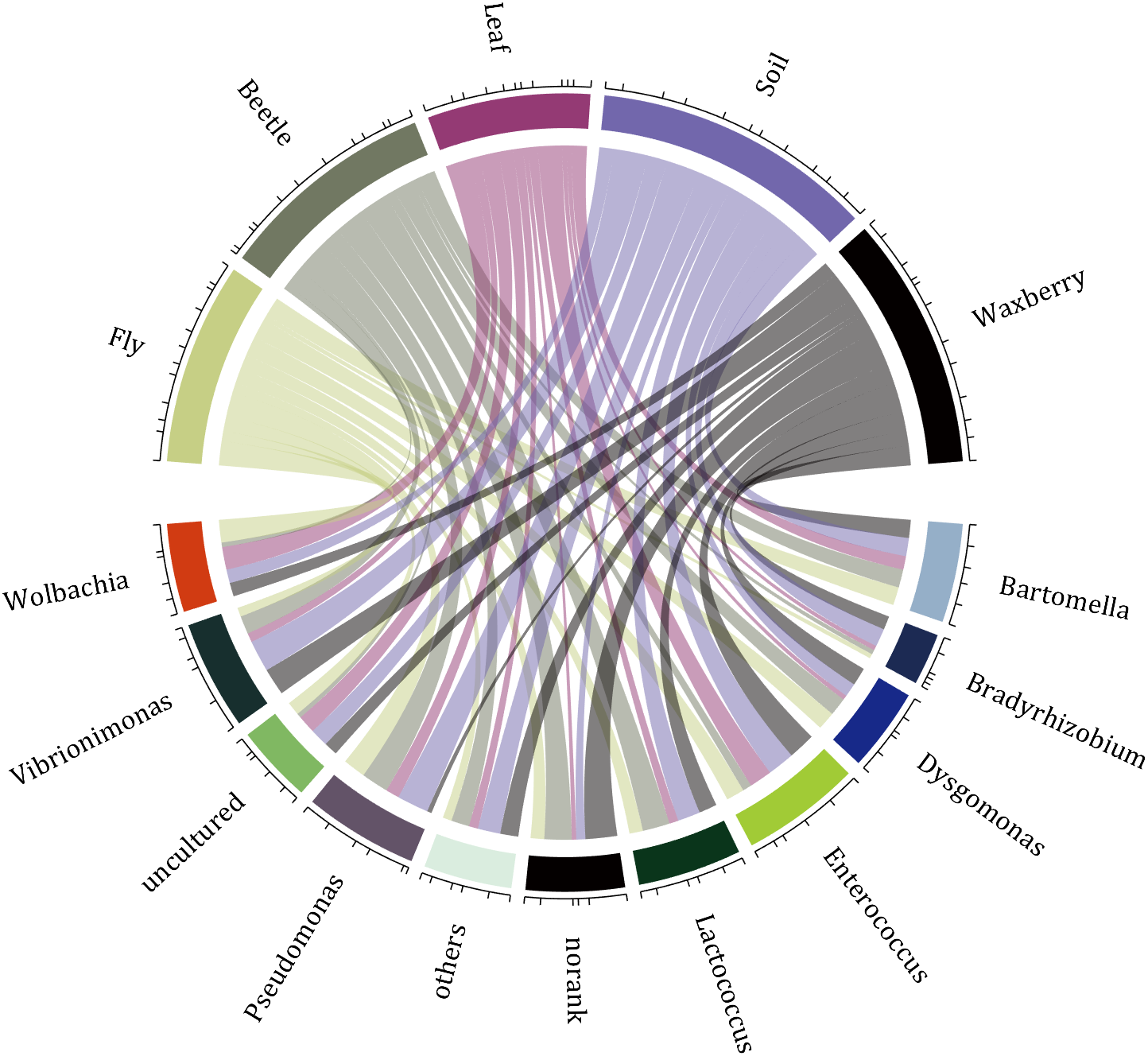
Hope to have your Reviews and Stars!!!
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑
Hello and a warm welcome to all! We're thrilled to have you visit our community. MATLAB Central is a place for learning, sharing, and connecting with others who share your passion for MATLAB and Simulink. To ensure you have the best experience, here are some tips to get you started:
- Read the Community Guidelines: Understanding our community standards is crucial. Please take a moment to familiarize yourself with them. Keep in mind that posts not adhering to these guidelines may be flagged by moderators or other community members.
- Ask Technical Questions at MATLAB Answers: If you have questions related to MathWorks products, head over to MATLAB Answers (new question form - Ask the community). It's the go-to spot for technical inquiries, with responses often provided within an hour, depending on the complexity of the question and volunteer availability. To increase your chances of a speedy reply, check out our tips on how to craft a good question (link to post on asking good questions).
- Choosing the Right Channel: We offer a variety of discussion channels tailored to different contexts. Select the one that best fits your post. If you're unsure, the General channel is always a safe bet. If you feel there's a need for a new channel, we encourage you to suggest it in the Ideas channel.
- Reporting Issues: If you encounter posts that violate our guidelines, please use the 🚩Flag/Report feature (found in the 3-dot menu) to bring them to our attention.
- Quality Control: We strive to maintain a high standard of discussion. Accounts that post spam or too much nonsense may be subject to moderation, which can include temporary suspensions or permanent bans.
- Share Your Ideas: Your feedback is invaluable. If you have suggestions on how we can improve the community or MathWorks products, the Ideas channel is the perfect place to voice your thoughts.
Enjoy yourself and have fun! We're committed to fostering a supportive and educational environment. Dive into discussions, share your expertise, and grow your knowledge. We're excited to see what you'll contribute to the community!
Hello everyone, i hope you all are in good health. i need to ask you about the help about where i should start to get indulge in matlab. I am an electrical engineer but having experience of construction field. I am new here. Please do help me. I shall be waiting forward to hear from you. I shall be grateful to you. Need recommendations and suggestions from experienced members. Thank you.
Something that had bothered me ever since I became an FEA analyst (2012) was the apparent inability of the "camera" in Matlab's 3D plot to function like the "cameras" in CAD/CAE packages.
For instance, load the ForearmLink.stl model that ships with the PDE Toolbox in Matlab and ParaView and try rotating the model.
clear
close all
gm = importGeometry( "ForearmLink.stl" );
pdegplot(gm)
Things to observe:
- Note that I cant seem to rotate continuously around the x-axis. It appears to only support rotations from [0, 360] as opposed to [-inf, inf]. So, for example, if I'm looking in the Y+ direction and rotate around X so that I'm looking at the Z- direction, and then want to look in the Y- direction, I can't simply keep rotating around the X axis... instead have to rotate 180 degrees around the Z axis and then around the X axis. I'm not aware of any data visualization applications (e.g., ParaView, VisIt, EnSight) or CAD/CAE tools with such an interaction.
- Note that at the 50 second mark, I set a view in ParaView: looking in the [X-, Y-, Z-] direction with Y+ up. Try as I might in Matlab, I'm unable to achieve that same view perspective.
Today I discovered that if one turns on the Camera Toolbar from the View menubar, then clicks the Orbit Camera icon, then the No Principal Axis icon:
That then it acts in the manner I've long desired. Oh, and also, for the interested, it is programmatically available: https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/cameratoolbar.html
I might humbly propose this mode either be made more discoverable, similar to the little interaction widgets that pop up in figures:
Or maybe use the middle-mouse button to temporarily use this mode (a mouse setting in, e.g., Abaqus/CAE).
Which Matlab related forums and newsgroups do you use beside MATLAB Answers? Which languages do they use? Which advantages and unique features do they have?
Do you think that these forums complement or compete against MathWorks and its communication platform?
Actually all answers are accepted.
We are modeling the introduction of a novel pathogen into a completely susceptible population. In the cells below, I have provided you with the Matlab code for a simple stochastic SIR model, implemented using the "GillespieSSA" function
Simulating the stochastic model 100 times for 

Since γ is 0.4 per day, 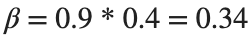 per day
per day
% Define the parameters
beta = 0.36;
gamma = 0.4;
n_sims = 100;
tf = 100; % Time frame changed to 100
% Calculate R0
R0 = beta / gamma
% Initial state values
initial_state_values = [1000000; 1; 0; 0]; % S, I, R, cum_inc
% Define the propensities and state change matrix
a = @(state) [beta * state(1) * state(2) / 1000000, gamma * state(2)];
nu = [-1, 0; 1, -1; 0, 1; 0, 0];
% Define the Gillespie algorithm function
function [t_values, state_values] = gillespie_ssa(initial_state, a, nu, tf)
t = 0;
state = initial_state(:); % Ensure state is a column vector
t_values = t;
state_values = state';
while t < tf
rates = a(state);
rate_sum = sum(rates);
if rate_sum == 0
break;
end
tau = -log(rand) / rate_sum;
t = t + tau;
r = rand * rate_sum;
cum_sum_rates = cumsum(rates);
reaction_index = find(cum_sum_rates >= r, 1);
state = state + nu(:, reaction_index);
% Update cumulative incidence if infection occurred
if reaction_index == 1
state(4) = state(4) + 1; % Increment cumulative incidence
end
t_values = [t_values; t];
state_values = [state_values; state'];
end
end
% Function to simulate the stochastic model multiple times and plot results
function simulate_stoch_model(beta, gamma, n_sims, tf, initial_state_values, R0, plot_type)
% Define the propensities and state change matrix
a = @(state) [beta * state(1) * state(2) / 1000000, gamma * state(2)];
nu = [-1, 0; 1, -1; 0, 1; 0, 0];
% Set random seed for reproducibility
rng(11);
% Initialize plot
figure;
hold on;
for i = 1:n_sims
[t, output] = gillespie_ssa(initial_state_values, a, nu, tf);
% Check if the simulation had only one step and re-run if necessary
while length(t) == 1
[t, output] = gillespie_ssa(initial_state_values, a, nu, tf);
end
if strcmp(plot_type, 'cumulative_incidence')
plot(t, output(:, 4), 'LineWidth', 2, 'Color', rand(1, 3));
elseif strcmp(plot_type, 'prevalence')
plot(t, output(:, 2), 'LineWidth', 2, 'Color', rand(1, 3));
end
end
xlabel('Time (days)');
if strcmp(plot_type, 'cumulative_incidence')
ylabel('Cumulative Incidence');
ylim([0 inf]);
elseif strcmp(plot_type, 'prevalence')
ylabel('Prevalence of Infection');
ylim([0 50]);
end
title(['Stochastic model output for R0 = ', num2str(R0)]);
subtitle([num2str(n_sims), ' simulations']);
xlim([0 tf]);
grid on;
hold off;
end
% Simulate the model 100 times and plot cumulative incidence
simulate_stoch_model(beta, gamma, n_sims, tf, initial_state_values, R0, 'cumulative_incidence');
% Simulate the model 100 times and plot prevalence
simulate_stoch_model(beta, gamma, n_sims, tf, initial_state_values, R0, 'prevalence');
Northern lights captured from this weekend at MathWorks campus ✨
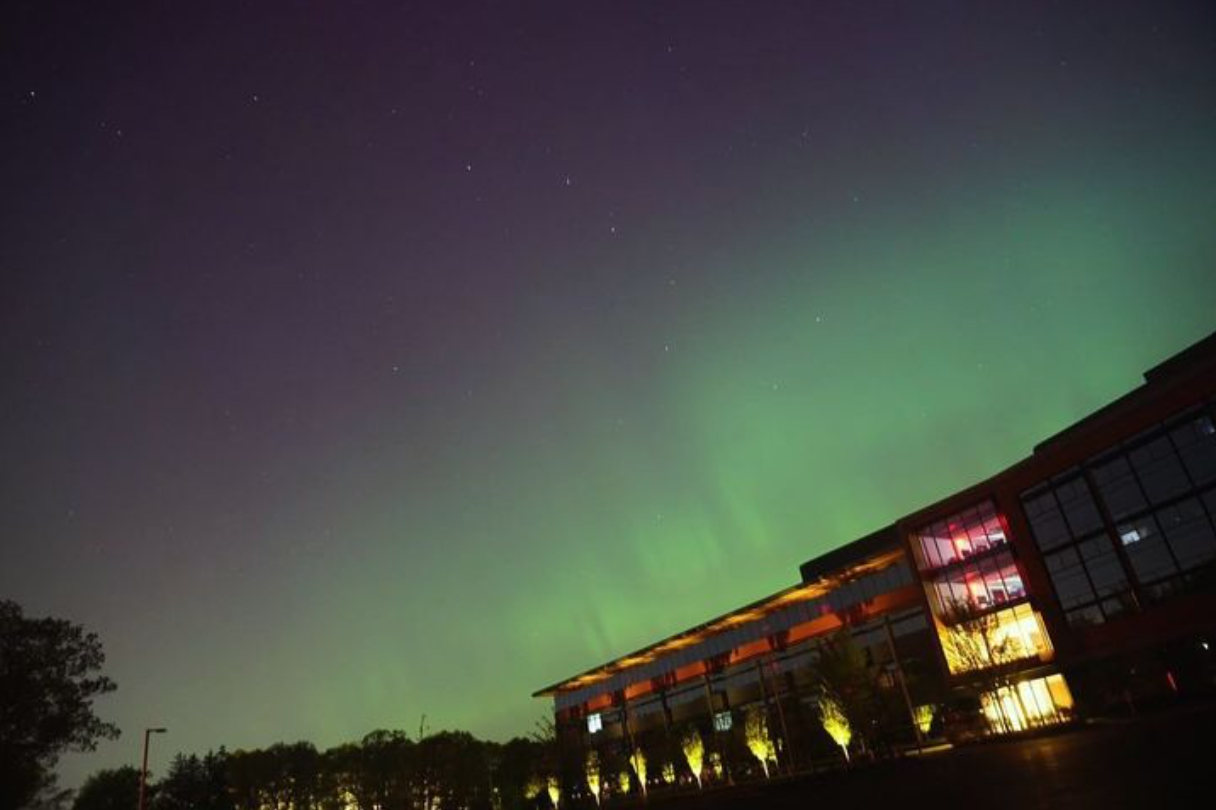

Did you get a chance to see lights and take some photos?
I recently wrote up a document which addresses the solution of ordinary and partial differential equations in Matlab (with some Python examples thrown in for those who are interested). For ODEs, both initial and boundary value problems are addressed. For PDEs, it addresses parabolic and elliptic equations. The emphasis is on finite difference approaches and built-in functions are discussed when available. Theory is kept to a minimum. I also provide a discussion of strategies for checking the results, because I think many students are too quick to trust their solutions. For anyone interested, the document can be found at https://blanchard.neep.wisc.edu/SolvingDifferentialEquationsWithMatlab.pdf









