컨버터(저전력)
예제를 통해 저전력 응용 분야(48V 미만)를 위한 컨버터(예: DC-DC/초퍼/벅/부스트 컨버터)를 모델링하는 방법을 알아봅니다.
추천 예제
Improve Simulation Speed of Power Electronics Systems with Reduced Order Modeling
Enhance the model simulation speed of an electro-thermal DC-DC step-down converter by converting a high-fidelity switch to a reduced order model (ROM) switch. This conversion enables faster design iterations and analysis.
- R2024b 이후
- 라이브 스크립트 열기
Design PI Controller for DC-DC Converter
Design a PI controller for a DC-DC converter using classical control theory. Alternatively, you can use Steady State Manager, Model Linearizer, Frequency Response Estimator, or PID tuner apps to streamline the design.
- R2024b 이후
- 라이브 스크립트 열기
SEPIC Voltage Control
Control the output voltage of a single-ended primary-inductor converter (SEPIC). The SEPIC is a form of DC-DC converter designed to deliver a regulated positive output voltage, regardless of whether the input voltage is higher, equal to, or lower than the intended output voltage. The Control subsystem adjusts the duty cycle of the semiconductor switch to regulate the output of the SEPIC. To adjust the duty cycle, the Control subsystem uses a PI-based control algorithm. The input voltage is constant throughout the simulation. A resistor provides the load for the system. The total simulation time is 0.1 seconds.
- R2024a 이후
- 모델 열기
Deploy SEPIC Model to FPGA
Deploy a single-ended primary-inductor converter (SEPIC) model to a Speedgoat® IO334-325K Simulink®-programmable I/O module and then run the model in real-time at a sample step size of 1 microsecond. The parts of the model that you deploy to CPU, run at 50 microseconds.
- R2024a 이후
- 모델 열기
평균값 초퍼 제어
이 예제에서는 4사분면 초퍼를 제어하는 방법을 보여줍니다. Control 서브시스템은 출력 전류를 제어하기 위해 간단한 PI 기반 제어 알고리즘을 구현합니다. 평균값 초퍼 모델은 시뮬레이션 속도를 높이는 데 사용됩니다. 시뮬레이션은 양의 기준과 음의 기준을 모두 사용합니다. 총 시뮬레이션 시간(t)은 1초입니다. t = 0.5초에서 부하 DC 전원 E의 극성이 변경됩니다.
평균값 DC-DC 컨버터 제어
이 예제에서는 벅-부스트 컨버터의 출력 전압을 제어하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 듀티 사이클을 조정하기 위해 Control 서브시스템은 PI 기반 제어 알고리즘을 사용합니다. 평균값 DC-DC 컨버터 모델은 시뮬레이션 속도를 높이는 데 사용됩니다. 입력 전압과 시스템 부하는 시뮬레이션 과정 전체에서 일정하게 유지됩니다. 총 시뮬레이션 시간(t)은 0.25초입니다. t = 0.15초에서 전압 기준이 변경되고 시스템은 벅 모드에서 부스트 모드로 전환됩니다.
부스트 컨버터 전압 제어
이 예제에서는 부스트 컨버터의 출력 전압을 제어하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 듀티 사이클을 조정하기 위해 Control 서브시스템은 PI 기반 제어 알고리즘을 사용합니다. 입력 전압은 시뮬레이션 과정 전체에서 일정한 것으로 간주합니다. 가변 저항기가 시스템에 부하를 제공합니다. 총 시뮬레이션 시간(t)은 0.25초입니다. t = 0.15초에서 부하가 변경됩니다.
벅 컨버터
이 예제에서는 30V DC 공급을 조정된 15V DC 공급으로 변환하는 스위칭 전원를 모델링하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 이 모델을 사용하여 인덕턴스 L과 평활화 커패시터 C의 크기를 조정하고 피드백 제어기를 설계합니다. 연속 제어기와 이산 제어기 중에서 선택하여 이산화의 영향을 살펴봅니다.
벅 컨버터 다항식 전압 제어
이 예제에서는 다항식 RST 제어기를 사용하여 벅 컨버터의 출력 전압을 제어하는 방법을 보여줍니다. RST 제어기는 듀티 사이클을 조정합니다. 입력 전압은 시뮬레이션 과정 전체에서 일정한 것으로 간주합니다. 가변 저항기가 시스템에 부하를 제공합니다. 총 시뮬레이션 시간(t)은 0.25초입니다. t = 0.15초에서 부하가 변경됩니다. t = 0.2초에서 전압 기준이 6V에서 4V로 변경됩니다.
벅 컨버터 열 모델
이 예제에서는 동기식 벅 컨버터에서 MOSFET의 열 동특성을 모델링합니다. 이는 열 동특성이 있는 벅 컨버터 모델의 구조와 일치합니다. 전기 스위칭 동특성을 생략하면 훨씬 더 큰 시간 스텝으로 시뮬레이션을 진행할 수 있으므로 MOSFET의 정상 상태 온도를 계산하는 데 걸리는 시간이 크게 단축됩니다.
벅 컨버터 전압 제어
이 예제에서는 벅 컨버터의 출력 전압을 제어하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 듀티 사이클을 조정하기 위해 Control 서브시스템은 PI 기반 제어 알고리즘을 사용합니다. 입력 전압은 시뮬레이션 과정 전체에서 일정한 것으로 간주합니다. 가변 저항기가 시스템에 부하를 제공합니다. 총 시뮬레이션 시간(t)은 0.25초입니다. t = 0.15초에서 부하가 변경됩니다.
Buck Converter with Faults
Model and assess the impact of component tolerances and fault events on the operation of a switching power supply. The R, L, and C components all have tolerances, operational limits, and faults defined. The faults can be enabled within the block dialog or using MATLAB® Commands. The capacitor fault is already enabled to cut in at 1.5e-3 seconds.
열 동특성이 있는 벅 컨버터
이 예제에서는 30V DC 공급을 조정된 15V DC 공급으로 변환하는 스위칭 전원를 모델링하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 이 모델은 피드백 제어기를 설계하는 것은 물론, 인덕턴스 L과 평활화 커패시터 C의 크기를 조정하는 데에도 사용할 수 있습니다. 연속 제어기와 이산 제어기 중에서 선택하여 이산화의 영향을 살펴볼 수 있습니다. 스위칭 소자를 이상적 스위치가 아니라 MOSFET으로 모델링하면 소자의 On 저항을 정확하게 나타낼 수 있습니다. 이 모델은 스위칭 소자의 스위치온/스위치오프 타이밍도 캡처하는데, 이 타이밍은 주로 게이트 커패시턴스 값과 PWM 드라이버 출력 저항에 따라 달라집니다.
Class E DC-DC Converter
A Class E power converter with frequency control. A simple integral control is implemented in Simulink® in the Controller block, and is designed to deliver 100W into a 5ohm load. The switch is an LDMOS, high-voltage transistor with a nonlinear capacitance model, and R Trans is the equivalent series resistance of the transformer. The Output scope shows the drain-source voltage for evaluation of the voltage stress on the switch. Note that, due to the nonlinear output capacitance of the transistor, the peak voltage stress is higher than would be expected if the output capacitance were constant. In addition, the scope also shows the frequency control signal, the output voltage, and the reference value for the output voltage. This model can be used to calculate the output power information from components in the circuit.
Conducted Emission of a Buck Converter
A buck converter configured for a measurement of common- and differential-mode noise on the source. In order to simulate the common-mode noise, the capacitive coupling between the circuit and a reference plane must be included in the model. In this circuit, the capacitance between the switching node (between the high- and low-side transistors) and the reference plane is also included.
DC-DC LLC 컨버터
이 예제에서는 주파수 제어를 사용하는 DC-DC LLC 전력 컨버터를 보여줍니다. Controller 블록은 Simulink®에서 간단한 적분 제어를 구현합니다. 이 적분 제어는 변수 Vout_nominal에 지정된 공칭 출력 전압을 달성합니다. Output 스코프는 주파수 제어 신호, 출력 전압, 그리고 출력 전압에 대한 기준 값을 보여줍니다. 시작 시, 기준 값은 원하는 설정점에 이를 때까지 상승합니다. LLC 파워트레인의 설계는 1차 고조파 근사를 사용하여 자동으로 계산됩니다.
First and Fourth Quadrant Chopper Control
Control a two-quadrant chopper. The two-quadrant chopper operates in the first and fourth quadrants, allowing positive and negative output voltage. The Control subsystem implements a simple PI-based control algorithm for controlling the output current. The total simulation time (t) is 0.5 seconds. At t = 0.25 seconds, the polarity of the load DC source E is changed.
First and Second Quadrant Chopper Control
Control a two-quadrant chopper. The two-quadrant chopper operates in the first and second quadrants, allowing positive and negative output current. The Control subsystem implements a simple PI-based control algorithm for controlling the output current. The load of the system is considered constant throughout the simulation.
플라이백 컨버터
이 모델은 플라이백 컨버터가 어떻게 5V DC 전원을 조정된 15V DC 공급으로 증가시킬 수 있는지 보여줍니다. 전압은 변압기의 1차 측 양단 간에 시변 전압을 생성함으로써 증가됩니다. 변압기는 전압을 증가시키며, 그런 다음 전압은 다이오드에 의해 DC로 다시 정류됩니다. 출력 전압에 대한 폐루프 제어는 1차 측의 스위칭 주파수를 제어하여 이뤄집니다.
4사분면 초퍼 제어
이 예제에서는 4사분면 초퍼를 제어하는 방법을 보여줍니다. Control 서브시스템은 출력 전류를 제어하기 위해 간단한 PI 기반 제어 알고리즘을 구현합니다. 시뮬레이션은 양의 기준과 음의 기준을 모두 사용합니다. 총 시뮬레이션 시간(t)은 1초입니다. t = 0.5초에서 부하 DC 전원 E의 극성이 변경됩니다.
4-스위치 벅-부스트 컨버터 제어
이 예제에서는 4-스위치 벅-부스트 컨버터의 출력 전압을 제어하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 듀티 사이클을 조정하기 위해 Control 서브시스템은 PI 기반 제어 알고리즘을 사용합니다. 부스트 모드와 벅 모드 모두에서 한 스위치는 듀티 사이클을 제어하고, 한 스위치는 역으로 동작하고, 다른 두 스위치는 고정 위치에 유지됩니다. 입력 전압과 시스템 부하는 시뮬레이션 과정 전체에서 일정하다고 간주합니다. 총 시뮬레이션 시간(t)은 0.25초입니다. t = 0.15초에서 전압 기준이 변경되고 시스템은 벅 모드에서 부스트 모드로 전환됩니다.
선형 LED 드라이버
이 예제에서는 선형 전류 레귤레이터에 기반한 LED 드라이버를 보여줍니다. 스코프는 조명 및 전류 출력과 공급 전압을 표시합니다. 약 12V를 초과하는 공급 전압에 대해서는 출력이 조절됩니다.
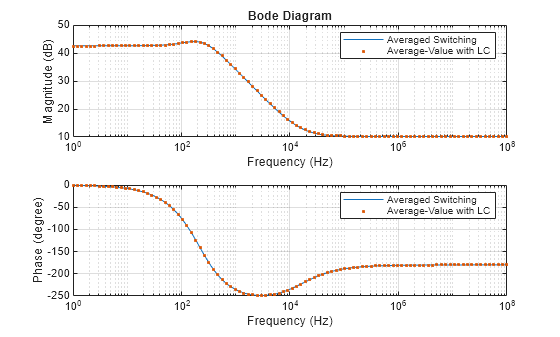
Linearize DC-DC Converter Model
Linearize a model of a DC-DC converter using averaged switching or an average-value converter.
- R2023b 이후
- 라이브 스크립트 열기
피드백이 있는 선형 전압 레귤레이터
이 예제에서는 개별 컴포넌트로 구성된 단순한 전압 레귤레이터 회로를 보여줍니다. 변동하는 공급은 20V DC와 1V 정현파 변형으로 모델링됩니다. 제너 다이오드 D1은 op-amp의 비반전 입력을 3.2V로 설정합니다. 이에 따라 op-amp가 큰 이득을 가지므로 op-amp 반전 입력 및 출력 또한 3.2V입니다. 따라서 레귤레이터 전압 출력은 3.2*(1000+470)/470=10V가 되도록 조정됩니다. 일반적인 op-amp에서 가능한 것보다 높은 전류를 제공하려면 NPN 양극성 트랜지스터가 필요합니다. 모델은 회로 동작을 확인하고 원하는 전압 조정을 달성할 수 있도록 컴포넌트 선택을 지원합니다.
Linear Voltage Regulator with Thermal Effects
A low-cost voltage regulator circuit whose performance depends on both load current and temperature. Bias resistor R1 ensures that the voltage at the transistor base is close to the rated zener voltage. The regulator output voltage is also approximately at this voltage, the base-emitter voltage being a few tenths of a volt. The precise base-emitter voltage depends on the transistor working point (which in turn depends on the load) and also the temperature. Resistor R2 only serves to provide some protection in the event of a transient output short circuit.
벅 컨버터의 MOSFET 결함
이 모델은 전력 컨버터의 MOSFET에서 발생할 수 있는 결함과 그에 따른 보호 회로의 동작을 보여줍니다. MOSFET에 결함이 발생하면, 부하 양단 간의 출력 전압이 클램핑되어 퓨즈가 끊어지도록 크로우바(crowbar) 회로가 활성화됩니다.
1사분면 초퍼 제어
이 예제에서는 1사분면 초퍼를 제어하는 방법을 보여줍니다. Control 서브시스템은 출력 전류를 제어하기 위해 간단한 PI 기반 제어 알고리즘을 구현합니다.
Push-Pull Buck Converter in Continuous Conduction Mode
Control the output voltage of a push-pull buck converter. The current flowing through the inductor is never zero. The DC-DC converter therefore operates in continuous conduction mode (CCM). To convert and maintain the nominal output voltage, the PI Controller subsystem uses a simple integral control. During startup, the reference voltage ramps up to the desired output voltage.
Push-Pull Buck Converter in Discontinuous Conduction Mode
Control the output voltage of a push-pull buck converter. The current flowing through the inductor reaches zero during the switch off cycle of the MOSFETs and therefore the DC-DC converter operates in Discontinuous Conduction Mode (DCM). This mode of conduction is mostly used for low-power applications. To convert and maintain the input DC voltage as a nominal output voltage, the PI Controller subsystem uses a simple integral control. During startup, the reference voltage is ramped up to the desired output voltage.
TVS Diode Parameterization
How to parameterize the Simscape™ Electrical™ diode to represent a Transient Voltage Suppression (TVS) diode. This example is for a TVS diode suited to protecting automotive electronics from voltage transients associated with turning off inductive loads. To view the data extracted from the datasheet, on the Modeling tab, in the Setup section, click Model Settings > Model Properties. On the Callbacks tab, click PreLoadFcn.
DC-DC Converter Model Fidelity Comparison
Use different levels of fidelity in DC-DC converters. The system contains three buck-boost converters. The top converter uses an ideal switch at a sample time of 10 us. To yield accurate results even though the model is under sampled at a sample time of 50 us, the middle converter uses an averaged switch with averaged pulse. To further increase the sample rate and to operate as an ideal averaged converter, the bottom converter uses an averaged switch and duty cycle instead of gate pulse. The Control subsystem contains a PWM generator. The Scopes subsystem contains Scope blocks that allow you to see the simulation results.
Chopper Model Fidelity Comparison
Use different levels of fidelity in chopper converters. You change the level of fidelity by changing the values for the Fidelity level, Switching device, and Integral protection diode parameters of the Four-Quadrant Chopper block. You also change the inputs to the G port. Using a higher level of fidelity improves the accuracy of the results but it also slows down simulation.
Tolerance Study Using Monte Carlo Simulations in Resonant LLC DC-DC Converter
Use Simscape™ Electrical™ to perform a Monte Carlo analysis to optimize the design of an LLC resonant DC-DC converter when some of its components have tolerances.
단상 인버터 전류 제어
이 예제에서는 단상 인버터 시스템의 전류를 제어하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 단상 인버터는 변조 파형이 입력되는 평균 스위치를 사용합니다. 이 예제는 실시간 전용 에뮬레이터에서의 실시간 평가에 적합합니다.
양방향 DC-DC 컨버터 전류 제어
이 예제에서는 양방향 DC-DC 컨버터의 인덕터 전류를 제어하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 듀티 사이클을 조정하기 위해 Control 서브시스템은 PI 기반 제어 알고리즘을 사용합니다. 양방향 DC-DC 컨버터는 평균 스위치를 사용합니다. 여러 다른 수준의 충실도를 달성하기 위해 변조 파형, 평균화된 게이트 펄스 또는 게이트 펄스를 사용할 수 있습니다.
2상 DC-DC 컨버터 전류 제어
이 예제에서는 2상 인터리빙 양방향 DC-DC 컨버터의 전류를 제어하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 2상 컨버터는 이상적 IGBT가 있는 2개의 양방향 DC-DC 컨버터로 구성됩니다. 듀티 사이클을 조정하기 위해 Control 서브시스템은 PI 기반 제어 알고리즘을 사용합니다. 컨버터의 출력 포트에서 리플을 줄이기 위해 두 위상은 동일한 듀티비로 전환되지만 상대적 위상 변위는 180도입니다. Scopes 서브시스템은 시뮬레이션 결과를 확인할 수 있는 스코프를 포함합니다.
Analysis of Synchronous Buck Converter with Self Turn-On
How the MOSFET parameters affect the self turn-on mechanism and how you can prevent it.
Power Converter Voltage Stabilizer
A voltage stabilizer circuit. It uses a full-wave rectifier, a single-wave inverter, and a buck-boost transformer to achieve voltage regulation.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)