robotPlatform
Description
The robotPlatform object represents a robot platform in a given
robot scenario. Use the platform to define and track the trajectory of an object in the
scenario. To simulate sensor readings for the platform, mount sensors such as the gpsSensor,
insSensor, and
robotLidarPointCloudGenerator
System object™ to the platform as robotSensor
objects. Add a body mesh to the platform for visualization using the updateMesh
object function.
Creation
Description
platform = robotPlatform(name,scenario)name and adds it to the
scenario, specified as a robotScenario
object. Specify the name argument as a string scalar. The
name argument sets the Name
property.
platform = robotPlatform(___,Name=Value)
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Example: StartTime=10 sets the initial time of the platform
trajectory to 10 seconds.
Trajectory for robot platform base motion, specified as a waypointTrajectory or polynomialTrajectory object. By default, the platform is assumed to be
stationary and at the scenario origin. To move the platform at each simulation step
of the scenario, use the move
object function.
Note
The robotPlatform object must specify the same
ReferenceFrame property as specified in the trajectory
object.
Occupied state of binary occupancy map, specified as true or
false. Set the value as true if robot
platform is incorporated in the binary occupancy map.
Data Types: logical
Initial robot platform base position, specified as a vector of the form
[x
y
z]. Only specify this name-value argument if not
specifying the BaseTrajectory property.
Data Types: single | double
Initial velocity of robot platform base, specified as a vector of the form
[vx
vy
vz]. Only specify this name-value argument if not
specifying the BaseTrajectory property.
Data Types: single | double
Initial acceleration of robot platform base, specified as a vector of the form
[ax
ay
az]. Only specify this name-value argument if not
specifying the BaseTrajectory property.
Data Types: single | double
Initial robot platform base orientation, specified as a vector of the form
[w
x
y
z], representing a quaternion. Only specify this
name-value argument if not specifying the BaseTrajectory property.
Data Types: single | double
Initial angular velocity of robot platform base, specified as a vector of the
form [wx
wy
wz]. The magnitude of the vector defines the angular
speed in radians per second. The xyz-coordinates define the axis
of clockwise rotation. Only specify this name-value argument if not specifying the
BaseTrajectory property.
Data Types: single | double
Initial joint configuration of the rigidBodyTree-based robot
platform, specified as an N-element vector. N
is the total number of joints associated with the rigidBodyTree object.
Data Types: single | double
Reference frame for computing robot platform motion, specified as
"ENU" or "NED", which matches any reference
frame in the robotScenario. All platform motion is computed relative to this inertial
frame.
Data Types: string | char
Rigid body tree robot platform, specified as a rigidBodyTree object.
Initial time of the robot platform trajectory, specified as a scalar in seconds.
Data Types: single | double
Add collision object to the platform mesh, specified as one of these values:
false— Keeps the platform mesh collision object free. Clear existing collision forrigidBodyTree-based platform."default"— Keeps existing collision mesh forrigidBodyTree-based platform. For other platforms, keeps the platform mesh collision free."mesh"— Fits collision object such ascollisionBox,collisionCylinder,collisionMesh, andcollisionSpherebased on the platform mesh type."capsule"— Fits collision capsule object with the platform mesh.One of these externally created collision objects:
The rigidBodyTree-based platform accepts externally created
collision mesh only for base body.
Transformation of collision mesh relative to the platform mesh, specified as a
4-by-4 homogeneous transformation matrix. Use the CollisionOffset input for rigidBodyTree-based
platforms only when the Collision input is specified as an externally created collision
object.
Data Types: single | double
Properties
Identifier for the robot platform, specified as a string scalar or character vector. The name must be unique within the scenario.
Data Types: char | string
Trajectory for the robot platform base motion, specified as a waypointTrajectory or polynomialTrajectory object. By default, the object assumes the base of the
platform is stationary and at the scenario origin. When specified as a
waypointTrajectory or polynomialTrajectory object,
base of the platform is moved along the trajectory during the scenario simulation. To
move the platform at each simulation step of the scenario, use the move
object function.
Note
The robotPlatform object must specify the same
ReferenceFrame property as specified in the trajectory
object.
Reference frame for computing robot platform motion, specified as
"ENU" or "NED", which matches any reference
frame in the robotScenario. The object computes all platform motion relative to this
inertial frame.
Data Types: char | string
Rigid body tree robot platform, specified as a rigidBodyTree object.
Robot platform base body mesh, specified as an extendedObjectMesh
object. The body mesh describes the 3-D model of the platform for visualization
purposes. The body mesh is used to generate 3-D point cloud. The default mesh is a
cuboid of the form [xlength
ylength
zlength] in meters.
Robot platform base body mesh color when displayed in the scenario, specified as an RGB triplet.
Data Types: single | double
Transform between robot platform base body and mesh frames, specified as a 4-by-4 homogeneous transformation matrix that maps points in the platform mesh frame to points in the body frame.
Data Types: single | double
Status of robot platform in binary occupancy map, specified as
true or false.
Data Types: logical
Collision mesh associated with the robot platform base body mesh, specified as a
collision object. The supported collision object types are: collisionBox, collisionCapsule, collisionCylinder, collisionMesh, and collisionSphere.
Transform between the robot platform base body and collision mesh, specified as a 4-by-4 homogeneous transformation matrix.
Data Types: single | double
Sensors mount on robot platform, specified as an array of robotSensor
objects.
Object Functions
attach | Attach target robot platform to source robot platform |
checkCollision | Check collision between robot platform and target bodies |
detach | Detach target robot platform from source robot platform |
move | Move robot platform in scenario |
read | Read robot platform in scenario |
updateMesh | Update robot platform body mesh |
Examples
Create a robot scenario.
scenario = robotScenario(UpdateRate=100,StopTime=1);
Add the ground plane and a box as meshes.
addMesh(scenario,"Plane",Size=[3 3],Color=[0.7 0.7 0.7]); addMesh(scenario,"Box",Size=[0.5 0.5 0.5],Position=[0 0 0.25], ... Color=[0 1 0])
Create a waypoint trajectory for the robot platform using an ENU reference frame.
waypoint = [0 -1 0; 1 0 0; -1 1 0; 0 -1 0]; toa = linspace(0,1,length(waypoint)); traj = waypointTrajectory("Waypoints",waypoint, ... "TimeOfArrival",toa, ... "ReferenceFrame","ENU");
Create a rigidBodyTree object of the TurtleBot 3 Waffle Pi robot with loadrobot.
robotRBT = loadrobot("robotisTurtleBot3WafflePi");Create a robot platform with trajectory.
platform = robotPlatform("TurtleBot",scenario, ... BaseTrajectory=traj);
Set up platform mesh with the rigidBodyTree object.
updateMesh(platform,"RigidBodyTree",Object=robotRBT)Create an INS sensor object and attach the sensor to the platform.
ins = robotSensor("INS",platform,insSensor("RollAccuracy",0), ... UpdateRate=scenario.UpdateRate);
Visualize the scenario.
[ax,plotFrames] = show3D(scenario); axis equal hold on
In a loop, step through the trajectory to output the position, orientation, velocity, acceleration, and angular velocity.
count = 1; while ~isDone(traj) [Position(count,:),Orientation(count,:),Velocity(count,:), ... Acceleration(count,:),AngularVelocity(count,:)] = traj(); count = count+1; end
Create a line plot for the trajectory. First create the plot with plot3, then manually modify the data source properties of the plot. This improves the performance of the plotting.
trajPlot = plot3(nan,nan,nan,"Color",[1 1 1],"LineWidth",2); trajPlot.XDataSource = "Position(:,1)"; trajPlot.YDataSource = "Position(:,2)"; trajPlot.ZDataSource = "Position(:,3)";
Set up the simulation. Then, iterate through the positions and show the scene each time the INS sensor updates. Advance the scene, move the robot platform, and update the sensors.
setup(scenario) for idx = 1:count-1 % Read sensor readings. [isUpdated,insTimestamp(idx,1),sensorReadings(idx)] = read(ins); if isUpdated % Use fast update to move platform visualization frames. show3D(scenario,FastUpdate=true,Parent=ax); % Refresh all plot data and visualize. refreshdata drawnow limitrate end % Advance scenario simulation time. advance(scenario); % Update all sensors in the scene. updateSensors(scenario) end hold off

Create a robotScenario object.
scenario = robotScenario(UpdateRate=1,StopTime=10);
Create a rigidBodyTree object of the Franka Emika Panda manipulator using loadrobot.
robotRBT = loadrobot("frankaEmikaPanda");Create a rigidBodyTree-based robotPlatform object using the manipulator model.
robot = robotPlatform("Manipulator",scenario, ... RigidBodyTree=robotRBT);
Create a non-rigidBodyTree-based robotPlatform object of a box to manipulate. Specify the mesh type and size.
box = robotPlatform("Box",scenario,Collision="mesh", ... InitialBasePosition=[0.5 0.15 0.278]); updateMesh(box,"Cuboid",Collision="mesh",Size=[0.06 0.06 0.1])
Visualize the scenario.
ax = show3D(scenario,Collisions="on");
view(79,36)
lightSpecify the initial and the pick-up joint configuration of the manipulator, to move the manipulator from its initial pose to close to the box.
initialConfig = homeConfiguration(robot.RigidBodyTree);
pickUpConfig = [0.2371 -0.0200 0.0542 -2.2272 0.0013 ...
2.2072 -0.9670 0.0400 0.0400];Create an RRT path planner using the manipulatorRRT object, and specify the manipulator model.
planner = manipulatorRRT(robot.RigidBodyTree,scenario.CollisionMeshes); planner.IgnoreSelfCollision = true;
Plan the path between the initial and the pick-up joint configurations. Then, to visualize the entire path, interpolate the path into small steps.
rng("default")
path = plan(planner,initialConfig,pickUpConfig);
path = interpolate(planner,path,25);Set up the simulation.
setup(scenario)
Check the collision before manipulator picks up the box.
checkCollision(robot,"Box", ... IgnoreSelfCollision="on")
ans = logical
0
Move the joints of the manipulator along the path and visualize the scenario.
helperRobotMove(path,robot,scenario,ax)
Check the collision after manipulator picks up the box.
checkCollision(robot,"Box", ... IgnoreSelfCollision="on")
ans = logical
1
Use the attach function to attach the box to the gripper of the manipulator.
attach(robot,"Box","panda_hand", ... ChildToParentTransform=trvec2tform([0 0 0.1]))
Specify the drop-off joint configuration of the manipulator to move the manipulator from its pick-up pose to the box drop-off pose.
dropOffConfig = [-0.6564 0.2885 -0.3187 -1.5941 0.1103 ...
1.8678 -0.2344 0.04 0.04];Plan the path between the pick-up and drop-off joint configurations.
path = plan(planner,pickUpConfig,dropOffConfig); path = interpolate(planner,path,25);
Move the joints of the manipulator along the path and visualize the scenario.
helperRobotMove(path,robot,scenario,ax)
Use the detach function to detach the box from the manipulator gripper.
detach(robot)
Plan the path between the drop-off and initial joint configurations to move the manipulator from its box drop-off pose to its initial pose.
path = plan(planner,dropOffConfig,initialConfig); path = interpolate(planner,path,25);
Move the joints of the manipulator along the path and visualize the scenario.
helperRobotMove(path,robot,scenario,ax)
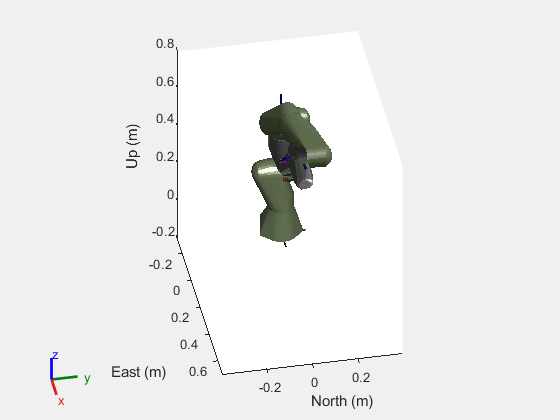
Helper function to move the joints of the manipulator.
function helperRobotMove(path,robot,scenario,ax) for idx = 1:size(path,1) jointConfig = path(idx,:); move(robot,"joint",jointConfig) show3D(scenario,fastUpdate=true,Parent=ax,Collisions="on"); drawnow advance(scenario); end end
Version History
Introduced in R2022a
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)