estimate
Fit vector autoregression (VAR) model to data
Syntax
Description
EstMdl = estimate(Mdl,Tbl1)Mdl to variables in
the input table or timetable Tbl1, which contains time
series data, and returns the fully specified, estimated
VAR(p) model EstMdl.
estimate selects the variables in
Mdl.SeriesNames or all variables in
Tbl1. To select different variables in
Tbl1 to fit the model to, use the
ResponseVariables name-value argument. (since R2022b)
[
returns the estimated, asymptotic standard errors of the estimated parameters EstMdl,EstSE,logL,Tbl2] = estimate(Mdl,Tbl1)EstSE, the optimized loglikelihood objective function value logL, and the table or timetable Tbl2 of all variables in Tbl1 and residuals corresponding to the response variables to which the model is fit (ResponseVariables). (since R2022b)
[___] = estimate(___,
specifies options using one or more name-value arguments in
addition to any of the input argument combinations in previous syntaxes.
Name=Value)estimate returns the output argument combination for the
corresponding input arguments. For example, estimate(Mdl,Y,Y0=PS,X=Exo) fits
the VAR(p) model Mdl to the matrix of
response data Y, and specifies the matrix of presample
response data PS and the matrix of exogenous predictor data
Exo.
Supply all input data using the same data type. Specifically:
If you specify the numeric matrix
Y, optional data sets must be numeric arrays and you must use the appropriate name-value argument. For example, to specify a presample, set theY0name-value argument to a numeric matrix of presample data.If you specify the table or timetable
Tbl1, optional data sets must be tables or timetables, respectively, and you must use the appropriate name-value argument. For example, to specify a presample, set thePresamplename-value argument to a table or timetable of presample data.
Examples
Fit a VAR(4) model to the consumer price index (CPI) and unemployment rate series. Supply the response series as a numeric matrix.
Load the Data_USEconModel data set.
load Data_USEconModelPlot the two series on separate plots.
figure; plot(DataTimeTable.Time,DataTimeTable.CPIAUCSL); title('Consumer Price Index') ylabel('Index') xlabel('Date')

figure; plot(DataTimeTable.Time,DataTimeTable.UNRATE); title('Unemployment Rate'); ylabel('Percent'); xlabel('Date');

Stabilize the CPI by converting it to a series of growth rates. Synchronize the two series by removing the first observation from the unemployment rate series.
rcpi = price2ret(DataTimeTable.CPIAUCSL); unrate = DataTimeTable.UNRATE(2:end);
Create a default VAR(4) model by using the shorthand syntax.
Mdl = varm(2,4)
Mdl =
varm with properties:
Description: "2-Dimensional VAR(4) Model"
SeriesNames: "Y1" "Y2"
NumSeries: 2
P: 4
Constant: [2×1 vector of NaNs]
AR: {2×2 matrices of NaNs} at lags [1 2 3 ... and 1 more]
Trend: [2×1 vector of zeros]
Beta: [2×0 matrix]
Covariance: [2×2 matrix of NaNs]
Mdl is a varm model object. All properties containing NaN values correspond to parameters to be estimated given data.
Estimate the model using the entire data set.
EstMdl = estimate(Mdl,[rcpi unrate])
EstMdl =
varm with properties:
Description: "AR-Stationary 2-Dimensional VAR(4) Model"
SeriesNames: "Y1" "Y2"
NumSeries: 2
P: 4
Constant: [0.00171639 0.316255]'
AR: {2×2 matrices} at lags [1 2 3 ... and 1 more]
Trend: [2×1 vector of zeros]
Beta: [2×0 matrix]
Covariance: [2×2 matrix]
EstMdl is an estimated varm model object. It is fully specified because all parameters have known values. The description indicates that the autoregressive polynomial is stationary.
Display summary statistics from the estimation.
summarize(EstMdl)
AR-Stationary 2-Dimensional VAR(4) Model
Effective Sample Size: 241
Number of Estimated Parameters: 18
LogLikelihood: 811.361
AIC: -1586.72
BIC: -1524
Value StandardError TStatistic PValue
___________ _____________ __________ __________
Constant(1) 0.0017164 0.0015988 1.0735 0.28303
Constant(2) 0.31626 0.091961 3.439 0.0005838
AR{1}(1,1) 0.30899 0.063356 4.877 1.0772e-06
AR{1}(2,1) -4.4834 3.6441 -1.2303 0.21857
AR{1}(1,2) -0.0031796 0.0011306 -2.8122 0.004921
AR{1}(2,2) 1.3433 0.065032 20.656 8.546e-95
AR{2}(1,1) 0.22433 0.069631 3.2217 0.0012741
AR{2}(2,1) 7.1896 4.005 1.7951 0.072631
AR{2}(1,2) 0.0012375 0.0018631 0.6642 0.50656
AR{2}(2,2) -0.26817 0.10716 -2.5025 0.012331
AR{3}(1,1) 0.35333 0.068287 5.1742 2.2887e-07
AR{3}(2,1) 1.487 3.9277 0.37858 0.705
AR{3}(1,2) 0.0028594 0.0018621 1.5355 0.12465
AR{3}(2,2) -0.22709 0.1071 -2.1202 0.033986
AR{4}(1,1) -0.047563 0.069026 -0.68906 0.49079
AR{4}(2,1) 8.6379 3.9702 2.1757 0.029579
AR{4}(1,2) -0.00096323 0.0011142 -0.86448 0.38733
AR{4}(2,2) 0.076725 0.064088 1.1972 0.23123
Innovations Covariance Matrix:
0.0000 -0.0002
-0.0002 0.1167
Innovations Correlation Matrix:
1.0000 -0.0925
-0.0925 1.0000
Fit a VAR(4) model to the consumer price index (CPI) and unemployment rate data. The estimation sample starts at Q1 of 1980.
Load the Data_USEconModel data set.
load Data_USEconModelStabilize the CPI by converting it to a series of growth rates. Synchronize the two series by removing the first observation from the unemployment rate series.
rcpi = price2ret(DataTimeTable.CPIAUCSL); unrate = DataTimeTable.UNRATE(2:end);
Identify the index corresponding to the start of the estimation sample.
estIdx = DataTimeTable.Time(2:end) > '1979-12-31';Create a default VAR(4) model by using the shorthand syntax.
Mdl = varm(2,4);
Estimate the model using the estimation sample. Specify all observations before the estimation sample as presample data. Display a full estimation summary.
Y0 = [rcpi(~estIdx) unrate(~estIdx)]; EstMdl = estimate(Mdl,[rcpi(estIdx) unrate(estIdx)],'Y0',Y0,'Display',"full");
AR-Stationary 2-Dimensional VAR(4) Model
Effective Sample Size: 117
Number of Estimated Parameters: 18
LogLikelihood: 419.837
AIC: -803.674
BIC: -753.955
Value StandardError TStatistic PValue
__________ _____________ __________ __________
Constant(1) 0.003564 0.0024697 1.4431 0.14898
Constant(2) 0.29922 0.11882 2.5182 0.011795
AR{1}(1,1) 0.022379 0.092458 0.24204 0.80875
AR{1}(2,1) -2.6318 4.4484 -0.59163 0.5541
AR{1}(1,2) -0.0082357 0.0020373 -4.0425 5.2884e-05
AR{1}(2,2) 1.2567 0.09802 12.82 1.2601e-37
AR{2}(1,1) 0.20954 0.10182 2.0581 0.039584
AR{2}(2,1) 10.106 4.8987 2.063 0.039117
AR{2}(1,2) 0.0058667 0.003194 1.8368 0.066236
AR{2}(2,2) -0.14226 0.15367 -0.92571 0.35459
AR{3}(1,1) 0.56095 0.098691 5.6839 1.3167e-08
AR{3}(2,1) 0.44406 4.7483 0.093518 0.92549
AR{3}(1,2) 0.0049062 0.003227 1.5204 0.12841
AR{3}(2,2) -0.040037 0.15526 -0.25787 0.7965
AR{4}(1,1) 0.046125 0.11163 0.41321 0.67945
AR{4}(2,1) 6.758 5.3707 1.2583 0.20827
AR{4}(1,2) -0.0030032 0.002018 -1.4882 0.1367
AR{4}(2,2) -0.14412 0.097094 -1.4843 0.13773
Innovations Covariance Matrix:
0.0000 -0.0003
-0.0003 0.0790
Innovations Correlation Matrix:
1.0000 -0.1686
-0.1686 1.0000
Because the VAR model degree p is 4, estimate uses only the last four observations in Y0 as a presample.
Since R2022b
Fit a VAR(4) model to the consumer price index (CPI) and unemployment rate series. Supply a timetable of data and specify the series for the fit.
Load and Preprocess Data
Load the Data_USEconModel data set. Compute the CPI growth rate. Because the growth rate calculation consumes the earliest observation, include the rate variable in the timetable by prepending the series with NaN.
load Data_USEconModel
DataTimeTable.RCPI = [NaN; price2ret(DataTimeTable.CPIAUCSL)];
numobs = height(DataTimeTable)numobs = 249
Prepare Timetable for Estimation
When you plan to supply a timetable directly to estimate, you must ensure it has all the following characteristics:
All selected response variables are numeric and do not contain any missing values.
The timestamps in the
Timevariable are regular, and they are ascending or descending.
Remove all missing values from the table, relative to the CPI rate (RCPI) and unemployment rate (UNRATE) series.
varnames = ["RCPI" "UNRATE"]; DTT = rmmissing(DataTimeTable,DataVariables=varnames); numobs = height(DTT)
numobs = 245
rmmissing removes the four initial missing observations from the DataTimeTable to create a sub-table DTT. The variables RCPI and UNRATE of DTT do not have any missing observations.
Determine whether the sampling timestamps have a regular frequency and are sorted.
areTimestampsRegular = isregular(DTT,"quarters")areTimestampsRegular = logical
0
areTimestampsSorted = issorted(DTT.Time)
areTimestampsSorted = logical
1
areTimestampsRegular = 0 indicates that the timestamps of DTT are irregular. areTimestampsSorted = 1 indicates that the timestamps are sorted. Macroeconomic series in this example are timestamped at the end of the month. This quality induces an irregularly measured series.
Remedy the time irregularity by shifting all dates to the first day of the quarter.
dt = DTT.Time; dt = dateshift(dt,"start","quarter"); DTT.Time = dt; areTimestampsRegular = isregular(DTT,"quarters")
areTimestampsRegular = logical
1
DTT is regular with respect to time.
Create Model Template for Estimation
Create a default VAR(4) model by using the shorthand syntax. Specify the response variable names.
Mdl = varm(2,4); Mdl.SeriesNames = varnames
Mdl =
varm with properties:
Description: "2-Dimensional VAR(4) Model"
SeriesNames: "RCPI" "UNRATE"
NumSeries: 2
P: 4
Constant: [2×1 vector of NaNs]
AR: {2×2 matrices of NaNs} at lags [1 2 3 ... and 1 more]
Trend: [2×1 vector of zeros]
Beta: [2×0 matrix]
Covariance: [2×2 matrix of NaNs]
Fit Model to Data
Estimate the model. Pass the entire timetable DTT. By default, estimate selects the response variables in Mdl.SeriesNames to fit to the model. Alternatively, you can use the ResponseVariables name-value argument.
Return the timetable of residuals and data fit to the model. Summarize the estimated model.
[EstMdl,~,~,Tbl2] = estimate(Mdl,DTT); summarize(EstMdl)
AR-Stationary 2-Dimensional VAR(4) Model
Effective Sample Size: 241
Number of Estimated Parameters: 18
LogLikelihood: 811.361
AIC: -1586.72
BIC: -1524
Value StandardError TStatistic PValue
___________ _____________ __________ __________
Constant(1) 0.0017164 0.0015988 1.0735 0.28303
Constant(2) 0.31626 0.091961 3.439 0.0005838
AR{1}(1,1) 0.30899 0.063356 4.877 1.0772e-06
AR{1}(2,1) -4.4834 3.6441 -1.2303 0.21857
AR{1}(1,2) -0.0031796 0.0011306 -2.8122 0.004921
AR{1}(2,2) 1.3433 0.065032 20.656 8.546e-95
AR{2}(1,1) 0.22433 0.069631 3.2217 0.0012741
AR{2}(2,1) 7.1896 4.005 1.7951 0.072631
AR{2}(1,2) 0.0012375 0.0018631 0.6642 0.50656
AR{2}(2,2) -0.26817 0.10716 -2.5025 0.012331
AR{3}(1,1) 0.35333 0.068287 5.1742 2.2887e-07
AR{3}(2,1) 1.487 3.9277 0.37858 0.705
AR{3}(1,2) 0.0028594 0.0018621 1.5355 0.12465
AR{3}(2,2) -0.22709 0.1071 -2.1202 0.033986
AR{4}(1,1) -0.047563 0.069026 -0.68906 0.49079
AR{4}(2,1) 8.6379 3.9702 2.1757 0.029579
AR{4}(1,2) -0.00096323 0.0011142 -0.86448 0.38733
AR{4}(2,2) 0.076725 0.064088 1.1972 0.23123
Innovations Covariance Matrix:
0.0000 -0.0002
-0.0002 0.1167
Innovations Correlation Matrix:
1.0000 -0.0925
-0.0925 1.0000
EstMdl is an estimated varm model object. It is fully specified because all parameters have known values.
Display the head of the table Tbl2.
head(Tbl2)
Time COE CPIAUCSL FEDFUNDS GCE GDP GDPDEF GPDI GS10 HOANBS M1SL M2SL PCEC TB3MS UNRATE RCPI RCPI_Residuals UNRATE_Residuals
_____ _____ ________ ________ ____ _____ ______ ____ ____ ______ ____ ____ _____ _____ ______ __________ ______________ ________________
Q1-49 144.1 23.91 NaN 45.6 270 16.531 40.9 NaN 53.961 NaN NaN 177 1.17 5 -0.0058382 -0.013422 0.64674
Q2-49 141.9 23.92 NaN 47.3 266.2 16.35 34 NaN 53.058 NaN NaN 178.6 1.17 6.2 0.00041815 0.0051673 0.6439
Q3-49 141 23.75 NaN 47.2 267.7 16.256 37.3 NaN 52.501 NaN NaN 178 1.07 6.6 -0.0071324 0.0030175 -0.099092
Q4-49 140.5 23.61 NaN 46.6 265.2 16.272 35.2 NaN 52.291 NaN NaN 180.4 1.1 6.6 -0.0059122 -0.001196 -0.0066535
Q1-50 144.6 23.64 NaN 45.6 275.2 16.222 44.4 NaN 52.696 NaN NaN 183.1 1.12 6.3 0.0012698 0.0024607 -0.013354
Q2-50 150.6 23.88 NaN 46.1 284.6 16.286 49.9 NaN 53.997 NaN NaN 187 1.15 5.4 0.010101 0.010823 -0.53098
Q3-50 159 24.34 NaN 45.9 302 16.63 56.1 NaN 55.7 NaN NaN 200.7 1.3 4.4 0.01908 0.012566 -0.38177
Q4-50 166.9 24.98 NaN 49.5 313.4 16.95 65.9 NaN 56.213 NaN NaN 198.1 1.34 4.3 0.025954 0.010998 0.50761
Because the VAR model has degree of 4, estimation requires four presample observations. Consequently, estimate uses the first four rows (all quarters of 1948) of DTT as a presample, fits the model to the remaining observations, and returns only those observations used in estimation in Tbl2.
Plot the residuals.
figure tiledlayout(2,1) nexttile plot(Tbl2.Time,Tbl2.RCPI_Residuals) hold on yline(0,"r--"); hold off title("CPI Rate Residuals") nexttile plot(Tbl2.Time,Tbl2.UNRATE_Residuals) hold on yline(0,"r--"); hold off title("Unemployment Rate Residuals")
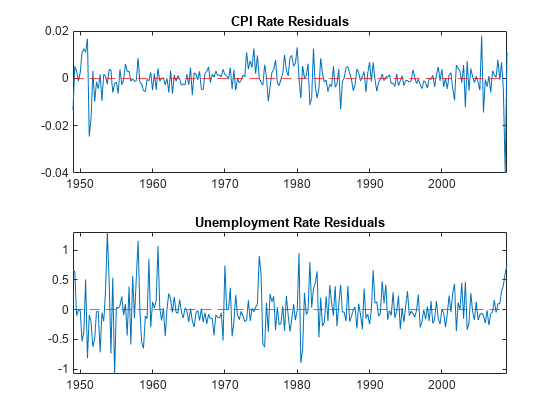
Estimate a VAR(4) model of the consumer price index (CPI), unemployment rate, and real gross domestic product (GDP). Include a linear regression component containing the current quarter and the last four quarters of government consumption expenditures and investment (GCE).
Load the Data_USEconModel data set. Compute the real GDP.
load Data_USEconModel
DataTimeTable.RGDP = DataTimeTable.GDP./DataTimeTable.GDPDEF*100;Plot all variables on separate plots.
figure tiledlayout(2,2) nexttile plot(DataTimeTable.Time,DataTimeTable.CPIAUCSL); ylabel('Index') title('Consumer Price Index') nexttile plot(DataTimeTable.Time,DataTimeTable.UNRATE); ylabel('Percent') title('Unemployment Rate') nexttile plot(DataTimeTable.Time,DataTimeTable.RGDP); ylabel('Output') title('Real Gross Domestic Product') nexttile plot(DataTimeTable.Time,DataTimeTable.GCE); ylabel('Billions of $') title('Government Expenditures')
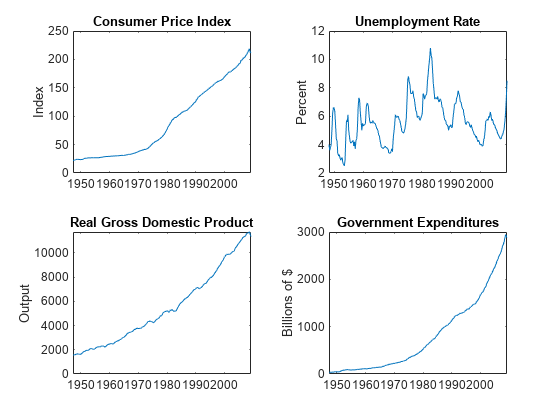
Stabilize the CPI, GDP, and GCE series by converting each to a series of growth rates. Synchronize the unemployment rate series with the others by removing its first observation.
inputVariables = {'CPIAUCSL' 'RGDP' 'GCE'};
Data = varfun(@price2ret,DataTimeTable,'InputVariables',inputVariables);
Data.Properties.VariableNames = inputVariables;
Data.UNRATE = DataTimeTable.UNRATE(2:end);Expand the GCE rate series to a matrix that includes its current value and up through four lagged values. Remove the GCE variable from Data.
rgcelag4 = lagmatrix(Data.GCE,0:4); Data.GCE = [];
Create a default VAR(4) model by using the shorthand syntax. You do not have to specify the regression component when creating the model.
Mdl = varm(3,4);
Estimate the model using the entire sample. Specify the GCE rate matrix as data for the regression component. Extract standard errors and the loglikelihood value.
[EstMdl,EstSE,logL] = estimate(Mdl,Data.Variables,'X',rgcelag4);Display the regression coefficient matrix.
EstMdl.Beta
ans = 3×5
0.0777 -0.0892 -0.0685 -0.0181 0.0330
0.1450 -0.0304 0.0579 -0.0559 0.0185
-2.8138 -0.1636 0.3905 1.1799 -2.3328
EstMdl.Beta is a 3-by-5 matrix. Rows correspond to response series, and columns correspond to predictors.
Display the matrix of standard errors corresponding to the coefficient estimates.
EstSE.Beta
ans = 3×5
0.0250 0.0272 0.0275 0.0274 0.0243
0.0368 0.0401 0.0405 0.0403 0.0358
1.4552 1.5841 1.6028 1.5918 1.4145
EstSE.Beta is commensurate with EstMdl.Beta.
Display the loglikelihood value.
logL
logL = 1.7056e+03
Input Arguments
VAR model containing unknown parameter values, specified as a varm model object returned by varm.
NaN-valued elements in properties indicate unknown, estimable parameters. Specified elements indicate equality constraints on parameters in model estimation. The innovations covariance matrix Mdl.Covariance cannot contain a mix of NaN values and real numbers; you must fully specify the covariance or it must be completely unknown (NaN(Mdl.NumSeries)).
Observed multivariate response series to which estimate fits the
model, specified as a numobs-by-numseries numeric
matrix.
numobs is the sample size. numseries is the
number of response variables (Mdl.NumSeries).
Rows correspond to observations, and the last row contains the latest observation.
Columns correspond to individual response variables.
Y represents the continuation of the presample response series in
Y0.
Data Types: double
Since R2022b
Time series data, to which estimate fits the model, specified
as a table or timetable with numvars variables and
numobs rows.
Each variable is a numeric vector representing a single path of
numobs observations. You can optionally specify
numseries response variables to fit to the model by using the
ResponseVariables name-value argument, and you can specify
numpreds predictor variables for the exogenous regression
component by using the PredictorVariables name-value argument.
Each row is an observation, and measurements in each row occur simultaneously.
If Tbl1 is a timetable, it must represent a sample with a regular
datetime time step (see isregular), and the datetime vector
Tbl1.Time must be ascending or descending.
If Tbl1 is a table, the last row contains the latest
observation.
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose
Name in quotes.
Example: estimate(Mdl,Y,Y0=Presample,X=Exo) fits the
VAR(p) model Mdl to the matrix of response
data Y, and specifies the matrix of presample response data
Presample and the matrix of exogenous predictor data
Exo.
Since R2022b
Variables to select from Tbl1 to treat as response variables
yt, specified as one of the following
data types:
String vector or cell vector of character vectors containing
numseriesvariable names inTbl1.Properties.VariableNamesA length
numseriesvector of unique indices (integers) of variables to select fromTbl1.Properties.VariableNamesA length
numvarslogical vector, whereResponseVariables(selects variablej) = truejTbl1.Properties.VariableNames, andsum(ResponseVariables)isnumseries
The selected variables must be numeric vectors and cannot contain missing values
(NaN).
If the number of variables in Tbl1 matches
Mdl.NumSeries, the default specifies all variables in
Tbl1. If the number of variables in Tbl1
exceeds Mdl.NumSeries, the default matches variables in
Tbl1 to names in Mdl.SeriesNames.
Example: ResponseVariables=["GDP" "CPI"]
Example: ResponseVariables=[true false true false] or
ResponseVariable=[1 3] selects the first and third table
variables as the response variables.
Data Types: double | logical | char | cell | string
Presample response observations to initialize the model for estimation, specified as a
numpreobs-by-numseries numeric matrix.
numpreobs is the number of presample observations. Use
Y0 only when you supply a matrix of response data
Y.
Rows correspond to presample observations, and the last row contains the latest
observation. Y0 must have at least Mdl.P rows. If
you supply more rows than necessary, estimate uses the latest
Mdl.P observations only.
Columns must correspond to the numseries response variables in
Y.
By default, estimate uses Y(1:Mdl.P,:) as
presample observations, and then fits the model to Y((Mdl.P +
1):end,:). This action reduces the effective sample size.
Data Types: double
Since R2022b
Presample data to initialize the model for estimation, specified as a table or
timetable, the same type as Tbl1, with
numprevars variables and numpreobs rows. Use
Presample only when you supply a table or timetable of data
Tbl1.
Each variable is a single path of numpreobs observations
representing the presample of the corresponding variable in
Tbl1.
Each row is a presample observation, and measurements in each row occur
simultaneously. numpreobs must be at least Mdl.P.
If you supply more rows than necessary, estimate uses the latest
Mdl.P observations only.
If Presample is a timetable, all the following conditions must be true:
Presamplemust represent a sample with a regular datetime time step (seeisregular).The inputs
Tbl1andPresamplemust be consistent in time such thatPresampleimmediately precedesTbl1with respect to the sampling frequency and order.The datetime vector of sample timestamps
Presample.Timemust be ascending or descending.
If Presample is a table, the last row contains the latest
presample observation.
By default, estimate uses the first or earliest
Mdl.P observations in Tbl1 as a presample,
and then it fits the model to the remaining numobs – Mdl.P
observations. This action reduces the effective sample size.
Since R2022b
Variables to select from Presample to use for presample data,
specified as one of the following data types:
String vector or cell vector of character vectors containing
numseriesvariable names inPresample.Properties.VariableNamesA length
numseriesvector of unique indices (integers) of variables to select fromPresample.Properties.VariableNamesA length
numprevarslogical vector, wherePresampleResponseVariables(selects variablej) = truejPresample.Properties.VariableNames, andsum(PresampleResponseVariables)isnumseries
The selected variables must be numeric vectors and cannot contain missing values
(NaN).
PresampleResponseNames does not need to contain the same names as
in Tbl1; estimate uses the data in selected
variable PresampleResponseVariables( as
a presample for
j)ResponseVariables(.j)
The default specifies the same response variables as those selected from
Tbl1, see ResponseVariables.
Example: PresampleResponseVariables=["GDP" "CPI"]
Example: PresampleResponseVariables=[true false true false] or
PresampleResponseVariable=[1 3] selects the first and third table
variables for presample data.
Data Types: double | logical | char | cell | string
Predictor data for the regression component in the model, specified as a numeric
matrix containing numpreds columns. Use X only
when you supply a matrix of response data Y.
numpreds is the number of predictor variables.
Rows correspond to observations, and the last row contains the latest observation.
estimate does not use the regression component in the
presample period. X must have at least as many observations as are
used after the presample period:
If you specify
Y0,Xmust have at leastnumobsrows (seeY).Otherwise,
Xmust have at leastnumobs–Mdl.Pobservations to account for the presample removal.
In either case, if you supply more rows than necessary,
estimate uses the latest observations only.
Columns correspond to individual predictor variables. All predictor variables are present in the regression component of each response equation.
By default, estimate excludes the regression component,
regardless of its presence in Mdl.
Data Types: double
Since R2022b
Variables to select from Tbl1 to treat as exogenous predictor variables
xt, specified as one of the following data types:
String vector or cell vector of character vectors containing
numpredsvariable names inTbl1.Properties.VariableNamesA length
numpredsvector of unique indices (integers) of variables to select fromTbl1.Properties.VariableNamesA length
numvarslogical vector, wherePredictorVariables(selects variablej) = truejTbl1.Properties.VariableNames, andsum(PredictorVariables)isnumpreds
The selected variables must be numeric vectors and cannot contain missing values
(NaN).
By default, estimate excludes the regression component, regardless
of its presence in Mdl.
Example: PredictorVariables=["M1SL" "TB3MS" "UNRATE"]
Example: PredictorVariables=[true false true false] or
PredictorVariable=[1 3] selects the first and third table variables to
supply the predictor data.
Data Types: double | logical | char | cell | string
Estimation information display type, specified as a value in this table.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
"off" | estimate does not display estimation
information at the command line. |
"table" | estimate displays a table of estimation
information. Rows correspond to parameters, and columns correspond to
estimates, standard errors, t statistics, and
p values. |
"full" | In addition to a table of summary statistics,
estimate displays the estimated innovations
covariance and correlation matrices, loglikelihood value, Akaike
Information Criterion (AIC), Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC), and
other estimation information. |
Example: Display="full"
Data Types: string | char
Maximum number of solver iterations allowed, specified as a positive numeric scalar.
estimate dispatches
MaxIterations to mvregress.
Example: MaxIterations=2000
Data Types: double
Note
NaNvalues inY,Y0, andXindicate missing values.estimateremoves missing values from the data by list-wise deletion.For the presample,
estimateremoves any row containing at least oneNaN.For the estimation sample,
estimateremoves any row of the concatenated data matrix[Y X]containing at least oneNaN.
This type of data reduction reduces the effective sample size.
estimateissues an error when any table or timetable input contains missing values.
Output Arguments
Estimated VAR(p) model, returned as a varm model object. EstMdl is a fully specified varm model.
estimate uses mvregress to implement multivariate normal, maximum likelihood estimation. For more details, see Estimation of Multivariate Regression Models.
Estimated, asymptotic standard errors of the estimated parameters, returned as a structure array containing the fields in this table.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Constant | Standard errors of model constants corresponding to the estimates in EstMdl.Constant, a numseries-by-1 numeric vector |
AR | Standard errors of the autoregressive coefficients corresponding to estimates in EstMdl.AR, a cell vector with elements corresponding to EstMdl.AR |
Beta | Standard errors of regression coefficients corresponding to the estimates in EstMdl.Beta, a numseries-by-numpreds numeric matrix |
Trend | Standard errors of linear time trends corresponding to the estimates in EstMdl.Trend, a numseries-by-1 numeric vector |
If estimate applies equality constraints during estimation by fixing any parameters to a value, then corresponding standard errors of those parameters are 0.
estimate extracts all standard errors from the inverse of the expected Fisher information matrix returned by mvregress (see Standard Errors).
Optimized loglikelihood objective function value, returned as a numeric scalar.
Multivariate residuals from the fitted model EstMdl, returned as
a numeric matrix containing numseries columns.
estimate returns E only when you supply a
matrix of response data Y.
If you specify
Y0, thenEhasnumobsrows (seeY).Otherwise,
Ehasnumobs–Mdl.Prows to account for the presample removal.
Since R2022b
Multivariate residuals and estimation data, returned as a table or timetable, the same
data type as Tbl1. estimate returns
Tbl2 only when you supply the input
Tbl1.
Tbl2 contains the residuals E from the model
fit to the selected variables in Tbl1, and it contains all
variables in Tbl1. estimate names the
residuals corresponding to variable
ResponseJTbl1
ResponseJ_ResidualsTbl1 is
GDP, Tbl2 contains a variable for the
residuals in the response equation of GDP with the name
GDP_Residuals.
If you specify presample response data, Tbl2 and
Tbl1 have the same number of rows, and their rows correspond.
Otherwise, because estimate removes initial observations from
Tbl1 for the required presample by default,
Tbl2 has numobs – Mdl.P rows to account for
that removal.
If Tbl1 is a timetable, Tbl1 and
Tbl2 have the same row order, either ascending or
descending.
References
[1] Hamilton, James D. Time Series Analysis. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 1994.
[2] Johansen, S. Likelihood-Based Inference in Cointegrated Vector Autoregressive Models. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1995.
[3] Juselius, K. The Cointegrated VAR Model. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2006.
[4] Lütkepohl, H. New Introduction to Multiple Time Series Analysis. Berlin: Springer, 2005.
Version History
Introduced in R2017aIn addition to accepting input data in numeric arrays,
estimate accepts input data in tables and timetables. estimate chooses default series on which to operate, but you can use the following name-value arguments to select variables.
ResponseVariablesspecifies the response series names in the input data to which the model is fit.PredictorVariablesspecifies the predictor series names in the input data for a model regression component.Presamplespecifies the input table or timetable of presample response data.PresampleResponseVariablesspecifies the response series names fromPresample.
If you specify a positive definite innovations covariance matrix for the
Covariance property, estimate treats your
specification as an equality constraint in model estimation.
See Also
Apps
Objects
Functions
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)