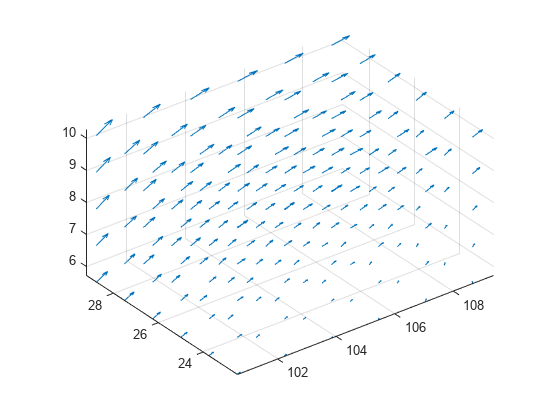
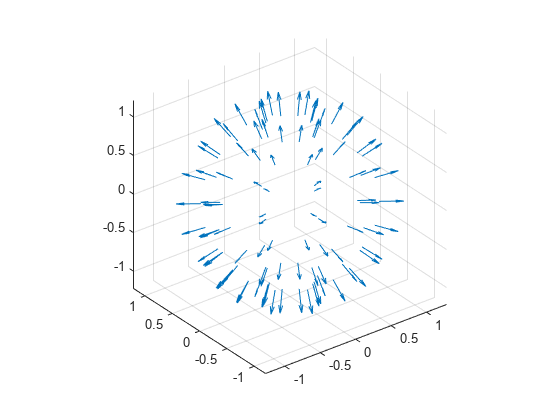
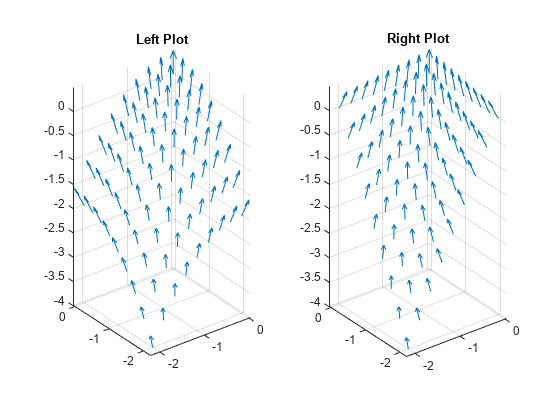
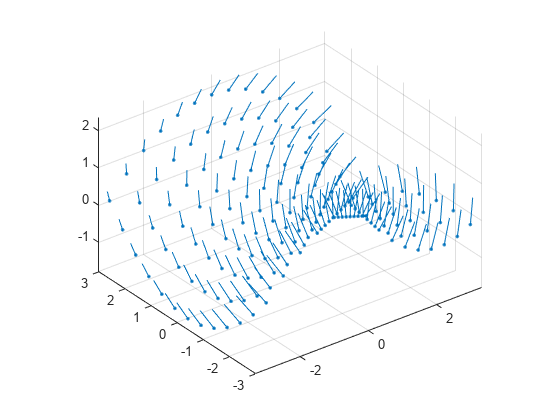
quiver3
3차원 퀴버 또는 벡터 플롯
구문
설명
quiver3(___,은 다음과 같이 화살표의 길이를 조정합니다.scale)
scale이 양수이면quiver3함수는 화살표가 중첩되지 않도록 자동으로 길이를 조정한 다음scale배만큼 늘입니다. 예를 들어,scale이 2이면 화살표의 길이가 2배로 늘어나고,scale이 0.5이면 화살표의 길이가 반으로 줄어듭니다.scale이'off'또는0이면(예:quiver3(X,Y,Z,U,V,W,'off')) 자동 스케일링이 비활성화됩니다.
quiver3(___,는 LineSpec,'filled')LineSpec으로 지정된 마커를 채웁니다.
quiver3(___,는 하나 이상의 이름-값 쌍의 인수를 사용하여 퀴버 속성을 지정합니다. 속성 목록은 Quiver 속성을 참조하십시오. 다른 모든 입력 인수 다음에 이름-값 쌍 인수를 지정합니다. 이름-값 쌍의 인수는 퀴버 플롯에 있는 모든 화살표에 적용됩니다.Name,Value)
q = quiver3(___)은 Quiver 객체를 반환합니다. 이 객체는 퀴버 플롯을 만든 후에 속성을 제어하는 경우에 유용합니다.
예제
입력 인수
이름-값 인수
확장 기능
버전 내역
R2006a 이전에 개발됨