predict
Predict top LDA topics of documents
Syntax
Description
___ = predict(___,
specifies additional options using one or more name-value pair arguments.Name,Value)
Examples
To reproduce the results in this example, set rng to 'default'.
rng('default')Load the example data. The file sonnetsPreprocessed.txt contains preprocessed versions of Shakespeare's sonnets. The file contains one sonnet per line, with words separated by a space. Extract the text from sonnetsPreprocessed.txt, split the text into documents at newline characters, and then tokenize the documents.
filename = "sonnetsPreprocessed.txt";
str = extractFileText(filename);
textData = split(str,newline);
documents = tokenizedDocument(textData);Create a bag-of-words model using bagOfWords.
bag = bagOfWords(documents)
bag =
bagOfWords with properties:
Counts: [154×3092 double]
Vocabulary: ["fairest" "creatures" "desire" "increase" "thereby" "beautys" "rose" "might" "never" "die" "riper" "time" "decease" "tender" "heir" "bear" "memory" "thou" "contracted" … ]
NumWords: 3092
NumDocuments: 154
Fit an LDA model with 20 topics.
numTopics = 20; mdl = fitlda(bag,numTopics)
Initial topic assignments sampled in 0.513255 seconds. ===================================================================================== | Iteration | Time per | Relative | Training | Topic | Topic | | | iteration | change in | perplexity | concentration | concentration | | | (seconds) | log(L) | | | iterations | ===================================================================================== | 0 | 0.04 | | 1.159e+03 | 5.000 | 0 | | 1 | 0.05 | 5.4884e-02 | 8.028e+02 | 5.000 | 0 | | 2 | 0.04 | 4.7400e-03 | 7.778e+02 | 5.000 | 0 | | 3 | 0.04 | 3.4597e-03 | 7.602e+02 | 5.000 | 0 | | 4 | 0.03 | 3.4662e-03 | 7.430e+02 | 5.000 | 0 | | 5 | 0.03 | 2.9259e-03 | 7.288e+02 | 5.000 | 0 | | 6 | 0.03 | 6.4180e-05 | 7.291e+02 | 5.000 | 0 | =====================================================================================
mdl =
ldaModel with properties:
NumTopics: 20
WordConcentration: 1
TopicConcentration: 5
CorpusTopicProbabilities: [0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500]
DocumentTopicProbabilities: [154×20 double]
TopicWordProbabilities: [3092×20 double]
Vocabulary: ["fairest" "creatures" "desire" "increase" "thereby" "beautys" "rose" "might" "never" "die" "riper" "time" "decease" "tender" "heir" "bear" "memory" "thou" … ]
TopicOrder: 'initial-fit-probability'
FitInfo: [1×1 struct]
Predict the top topics for an array of new documents.
newDocuments = tokenizedDocument([
"what's in a name? a rose by any other name would smell as sweet."
"if music be the food of love, play on."]);
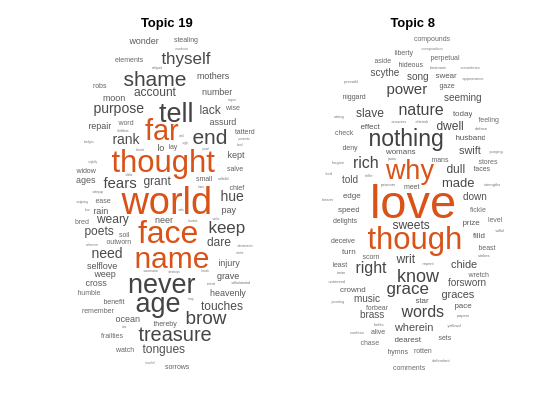
topicIdx = predict(mdl,newDocuments)topicIdx = 2×1
19
8
Visualize the predicted topics using word clouds.
figure subplot(1,2,1) wordcloud(mdl,topicIdx(1)); title("Topic " + topicIdx(1)) subplot(1,2,2) wordcloud(mdl,topicIdx(2)); title("Topic " + topicIdx(2))
Load the example data. sonnetsCounts.mat contains a matrix of word counts and a corresponding vocabulary of preprocessed versions of Shakespeare's sonnets.
load sonnetsCounts.mat
size(counts)ans = 1×2
154 3092
Fit an LDA model with 20 topics. To reproduce the results in this example, set rng to 'default'.
rng('default')
numTopics = 20;
mdl = fitlda(counts,numTopics)Initial topic assignments sampled in 0.081603 seconds. ===================================================================================== | Iteration | Time per | Relative | Training | Topic | Topic | | | iteration | change in | perplexity | concentration | concentration | | | (seconds) | log(L) | | | iterations | ===================================================================================== | 0 | 0.04 | | 1.159e+03 | 5.000 | 0 | | 1 | 0.05 | 5.4884e-02 | 8.028e+02 | 5.000 | 0 | | 2 | 0.05 | 4.7400e-03 | 7.778e+02 | 5.000 | 0 | | 3 | 0.05 | 3.4597e-03 | 7.602e+02 | 5.000 | 0 | | 4 | 0.05 | 3.4662e-03 | 7.430e+02 | 5.000 | 0 | | 5 | 0.05 | 2.9259e-03 | 7.288e+02 | 5.000 | 0 | | 6 | 0.04 | 6.4180e-05 | 7.291e+02 | 5.000 | 0 | =====================================================================================
mdl =
ldaModel with properties:
NumTopics: 20
WordConcentration: 1
TopicConcentration: 5
CorpusTopicProbabilities: [0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500 0.0500]
DocumentTopicProbabilities: [154×20 double]
TopicWordProbabilities: [3092×20 double]
Vocabulary: ["1" "2" "3" "4" "5" "6" "7" "8" "9" "10" "11" "12" "13" "14" "15" "16" "17" "18" "19" "20" "21" "22" "23" "24" "25" "26" … ] (1×3092 string)
TopicOrder: 'initial-fit-probability'
FitInfo: [1×1 struct]
Predict the top topics for the first 5 documents in counts.
topicIdx = predict(mdl,counts(1:5,:))
topicIdx = 5×1
3
15
19
3
14
To reproduce the results in this example, set rng to 'default'.
rng('default')Load the example data. The file sonnetsPreprocessed.txt contains preprocessed versions of Shakespeare's sonnets. The file contains one sonnet per line, with words separated by a space. Extract the text from sonnetsPreprocessed.txt, split the text into documents at newline characters, and then tokenize the documents.
filename = "sonnetsPreprocessed.txt";
str = extractFileText(filename);
textData = split(str,newline);
documents = tokenizedDocument(textData);Create a bag-of-words model using bagOfWords.
bag = bagOfWords(documents)
bag =
bagOfWords with properties:
NumWords: 3092
Counts: [154×3092 double]
Vocabulary: ["fairest" "creatures" "desire" "increase" "thereby" "beautys" "rose" "might" "never" "die" "riper" "time" "decease" "tender" "heir" "bear" "memory" "thou" … ] (1×3092 string)
NumDocuments: 154
Fit an LDA model with 20 topics. To suppress verbose output, set 'Verbose' to 0.
numTopics = 20;
mdl = fitlda(bag,numTopics,'Verbose',0);Predict the top topics for a new document. Specify the iteration limit to be 200.
newDocument = tokenizedDocument("what's in a name? a rose by any other name would smell as sweet."); iterationLimit = 200; [topicIdx,scores] = predict(mdl,newDocument, ... 'IterationLimit',iterationLimit)
topicIdx = 19
scores = 1×20
0.0250 0.0250 0.0250 0.0250 0.1250 0.0250 0.0250 0.0250 0.0250 0.0730 0.0250 0.0250 0.0770 0.0250 0.0250 0.0250 0.0250 0.0250 0.2250 0.1250
View the prediction scores in a bar chart.
figure bar(scores) title("LDA Topic Prediction Scores") xlabel("Topic Index") ylabel("Score")

Input Arguments
Input LDA model, specified as an ldaModel object.
Input documents, specified as a tokenizedDocument array, a string array of words, or a cell array of
character vectors. If documents is a
tokenizedDocument, then it must be a column vector. If
documents is a string array or a cell array of character
vectors, then it must be a row of the words of a single document.
Tip
To ensure that the function does not discard useful information, you must first preprocess the input documents using the same steps used to preprocess the documents used to train the model.
Input bag-of-words or bag-of-n-grams model, specified as a bagOfWords object or a bagOfNgrams object. If bag is a
bagOfNgrams object, then the function treats each n-gram as a
single word.
Frequency counts of words, specified as a matrix of nonnegative integers. If you specify
'DocumentsIn' to be 'rows', then the value
counts(i,j) corresponds to the number of times the
jth word of the vocabulary appears in the ith
document. Otherwise, the value counts(i,j) corresponds to the number
of times the ith word of the vocabulary appears in the
jth document.
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose
Name in quotes.
Example: 'IterationLimit',200 specifies the iteration limit to
be 200.
Orientation of documents in the word count matrix, specified as the comma-separated pair
consisting of 'DocumentsIn' and one of the following:
'rows'– Input is a matrix of word counts with rows corresponding to documents.'columns'– Input is a transposed matrix of word counts with columns corresponding to documents.
This option only applies if you specify the input documents as a matrix of word counts.
Note
If you orient your word count matrix so that documents correspond to columns and specify
'DocumentsIn','columns', then you might experience a significant
reduction in optimization-execution time.
Maximum number of iterations, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of 'IterationLimit' and a positive integer.
Example: 'IterationLimit',200
Relative tolerance on log-likelihood, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting
of 'LogLikelihoodTolerance' and a positive scalar. The optimization
terminates when this tolerance is reached.
Example: 'LogLikelihoodTolerance',0.001
Output Arguments
Predicted topic indices, returned as a vector of numeric indices.
Predicted topic probabilities, returned as a
D-by-K matrix, where
D is the number of input documents and
K is the number of topics in the LDA model.
score(i,j) is the probability that topic
j appears in document i. Each row
of score sums to one.
Version History
Introduced in R2017b
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)