Import Data into Signal Labeler
Import members into Signal Labeler in one of three ways to create labeled signal sets:
Import Signals from the MATLAB Workspace — Import each signal as a member to label them individually, or import a labeled signal set.
Import Signals from Files — Import each file as a member to label all the signals contained in a file together.
Import and Play Audio File Data in Signal Labeler — Import audio files and folders (requires an Audio Toolbox™ license).
Supported Signal Types
The Signal Labeler app works with real- or complex-valued vectors,
matrices, MATLAB® timetables, labeledSignalSet objects, and signalDatastore objects. The app also supports MAT files and CSV files.
Note
Signal Labeler does not support:
Signals with
InforNaNvalues, multidimensional arrays, or sparse matrices.labeledSignalSetobjects containing complex-valued labels or labels with LabelDataType specified as"table"or"timetable".
Example: Numeric Arrays
specifies a two-channel signal consisting of sinusoids embedded in white noise. The signal does not contain time information unless you specify it. In Signal Labeler, you can import the signal in samples, or you can add time information when you import it.num = cos(pi./[4;2]*(0:159))'+randn(160,2);
Example: MATLAB Timetables
both specify that the noisy two-channel sinusoid is sampled at 100 Hz. For more information, see thett1 = timetable(num,'SampleRate',100); tt2 = timetable(seconds((0:159)'/100),num);timetabledocumentation.Example:
labeledSignalSetObjectsspecifies that the noisy sinusoid is in samples.lss = labeledSignalSet(num);
Example:
labeledSignalSetObjects with Time Informationboth specify that the noisy sinusoid is sampled at 100 Hz.lst1 = labeledSignalSet(num,'SampleRate',100); lst2 = labeledSignalSet(timetable(seconds((0:159)'/100),num));Example: Multisignal Members
has two members. The first member contains three 10-sample signals. The second member contains nine 17-sample signals.msn = labeledSignalSet({randn(10,3),randn(17,9)});has two members. The first member contains three signals sampled at 1 Hz for 10 seconds. The second member contains two signals sampled at 1 Hz for 7 seconds and one 30-sample signal sampled at 100 Hz.mst = labeledSignalSet({{timetable(seconds(1:10)',randn(10,3))}, ... {timetable(seconds(1:7)',randn(7,2)), ... timetable(randn(30,1),'SampleRate',100)}});Example:
signalDatastoreObject Pointing to FilesSpecify the path to a set of sample sound signals included as MAT files with MATLAB®. Each file contains a signal variable and a sample rate. List the names of the files.
folder = fullfile(matlabroot,"toolbox","matlab","audiovideo"); lst = dir(append(folder,"/*.mat")); nms = {lst(:).name}'
nms = 7×1 cell {'chirp.mat' } {'gong.mat' } {'handel.mat' } {'laughter.mat'} {'mtlb.mat' } {'splat.mat' } {'train.mat' }Create a signal datastore that points to the specified folder. Set the sample rate variable name to
Fs, which is common to all files. Generate a subset of the datastore that excludes the filemtlb.mat, which differs from the other files in that the signal variable is not calledy.sds = signalDatastore(folder,"SampleRateVariableName","Fs"); sdss = subset(sds,~strcmp(nms,"mtlb.mat"));
Use the subset datastore as the source for a
labeledSignalSetobject.lss = labeledSignalSet(sdss)
lss = labeledSignalSet with properties: Source: [1×1 signalDatastore] NumMembers: 6 TimeInformation: "inherent" Labels: [6×0 table] Description: "" Use labelDefinitionsHierarchy to see a list of labels and sublabels. Use setLabelValue to add data to the set.
Choose a Color Scheme
You can choose a color scheme for the labels and signals you import into Signal Labeler. In the import dialog, select an option from the Label and signal color scheme list:
Use Different Colors— Display labels and signals in different colors.Use Same Colors— Display labels and signals in the same color.Use Same Colors Across Members— Display all signals within a multichannel member in the same color, and labels in a different color.
Once imported, you can change the color selection by rick-clicking on a member name in
the Labeled Signal Set Members browser and choosing Change
Color, Use Different Colors, or Use Same
Colors from the context-menu. You can also click a color value on the
Value column to open the Pick a Color
menu, where you can select a standard or custom line color.
Specify Time Information
The signals you import into Signal Labeler can be labeled in samples or in time. This specification stays fixed to ensure consistent labeling. You cannot mix signals in samples and signals with time information in the same session.
When specifying the time information for a set of signals that do not have it, select a time specification option in the import dialog box.
| Time Specification Option | Description |
|---|---|
Samples | This option enables you to explore and label signals without the need to specify a sample rate or a sample time. It is equivalent to plotting the signal in MATLAB without x-axis information. |
Sample Rate | Use this option when you know the rate at which the signal has been sampled. The sample rate can be expressed in Hz, kHz, MHz, or GHz. To specify the sample rate, you can use a numeric value, the name of a scalar variable in the MATLAB Workspace, or any valid MATLAB expression. Set the sample rate so that the members are plotted in units of time. |
Sample Rate Variable From File | Use this option when the sample rate is saved as a variable in the file being imported. |
Sample Time | Use this option when you know the time interval between samples. The sample time can be expressed in seconds, years, days, hours, minutes, milliseconds, microseconds, or nanoseconds. To specify the sample time, you can use a numeric value, the name of a scalar variable in the MATLAB Workspace, or any valid MATLAB expression. Set the sample time so that the members are plotted in units of time. |
Sample Time Variable From File | Use this option when the sample time is saved as a variable in the file being imported. |
Time Values | Use this option when you know the time value corresponding
to each sample. Specify the time values using a valid
MATLAB expression or the name of a variable in the
MATLAB Workspace. The time values can be stored in a
numeric or In all cases, the app derives a sample rate from the time values and displays it in the Time column of the Labeled Signal Set Members browser. An asterisk preceding the sample rate indicates that the members are nonuniformly sampled. |
Time Values Variable From File | Use this option when the time values are saved as a variable in the file being imported. |
Once a signal or set of signals has been imported into Signal Labeler, the chosen time specification stays fixed throughout the labeling session.
Import Signals from the MATLAB Workspace
To import signals to Signal Labeler from the MATLAB Workspace, on the Labeler tab, click
Import and select From Workspace
in the Members list. In the dialog box, select the signals you want
to import.
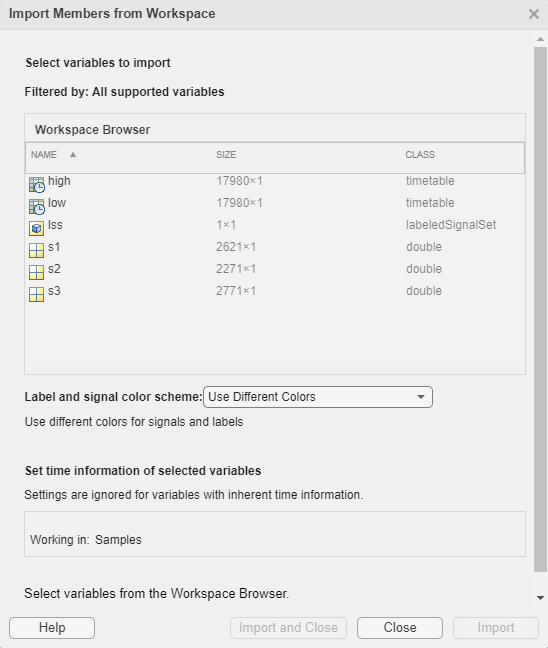
Each signal variable is treated as a member of the labeled signal set and can be labeled individually. You can also follow this procedure when you want to label multiple signal variables in different labeled signal sets.
If you initially imported a numeric array and specified it in samples, or if you initially imported a
labeledSignalSetobject in samples, you can subsequently choose only signals in samples. If you choose a numeric array, Signal Labeler imports it and treats it in samples.If you initially imported a numeric array and specified its time information, or if you initially imported a MATLAB timetable or a
labeledSignalSetobject with time information, you can subsequently choose only signals with time information. If you choose a numeric array, you must set its time information when importing it.
Note
You cannot modify the time information of a labeledSignalSet
object from within Signal Labeler. If the labeled signal set has no
time information, the app treats its members as being in samples. If the labeled
signal set has time information, the app incorporates this information when it
imports the signals. For more information, see the labeledSignalSet documentation.
To be imported successfully, labeled signal sets must obey these additional rules:
If the selection includes two or more labeled signal sets, the labeled signal sets must have unique signal label definitions. If two or more sets share a label definition, the definition must have the same type and data type for all sets. For more information, see Create or Import Signal Label Definitions.
If the selection includes two or more labeled signal sets, the labeled signal sets must have unique member names. You cannot change member names from within Signal Labeler. To change the name of a member of a labeled signal set, use
setMemberNamesat the command line.If you select two or more
labeledSignalSetobjects for labeling, Signal Labeler merges them and creates a single labeled signal set containing all the members and label values of the input sets. This action is equivalent to usingmergeat the command line.Label values in
labeledSignalSetobjects must be scalars. Signal Labeler ignores those labels which do not have scalar values.
Import Signals from Files
To import signals to Signal Labeler from files, on the Labeler
tab, click Import and select From
Files in the Members list. In the dialog box,
browse to select the files that contain the signals you want to import.

Note
Signal Labeler supports MAT files and CSV files. All values in a CSV file other than headers must be numeric.
With an Audio Toolbox license you can import signals from files with compatible audio file extensions into Signal Labeler using
From Audio FilesorFrom Audio Folder.Importing
labeledSignalSetobjects from files is not supported. To import alabeledSignalSetobject, load it into the MATLAB Workspace and import it from there.
To import signals from multiple files in a folder, on the Labeler
tab, click Import and select From
Folders in the Members list. In the dialog box,
browse to select the folder that contains the files you want to import signals from. You
can also choose to include subfolders.
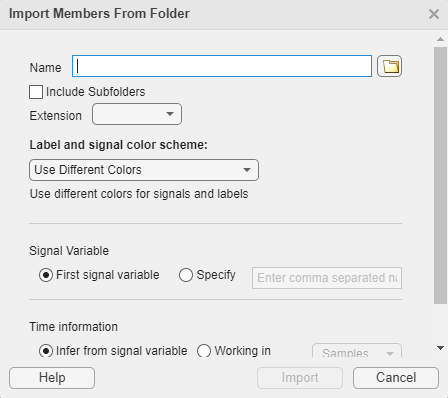
Each file is treated as a member of the labeled signal set. All the signals contained in a file belong to a single member and are labeled together. You can also import other files with the same signal variables as members of the same labeled signal set.
All members to import must have the same extension and the same variables.
Signal Labeler does not support working simultaneously with in-memory data and data from files.
If you initially imported in-memory members from the MATLAB Workspace, the
From FilesandFrom Foldersoptions are disabled from the Import menu of the Labeler tab.If you initially imported data from files, the only workspace variables you can then import from the MATLAB Workspace are
labeledSignalSetobjects whose input data sources aresignalDatastoreobjects pointing to files. For an example, see Supported Signal Types.
By default, Signal Labeler reads the first signal variable of
each file. To determine the name of the first variable in a file,
signalDatastore follows these steps:
For MAT files:
s = load(fileName); varNames = fieldnames(s); firstVar = s.(varNames{1});For CSV files:
opts = detectImportOptions(fileName,'PreserveVariableNames',true); varNames = opts.VariableNames; firstVar = string(varNames{1});
To specify the signal variables that you want to read, click Specify and enter a comma-separated list of signal variable names.
Tip
If a CSV file does not have variable names specified in a header line, then
the variables are called Var1 for the first column,
Var2 for the second column, and so on.
See Also
Apps
Functions
Topics
- Label Signal Attributes, Regions of Interest, and Points
- Label ECG Signals and Track Progress
- Examine Labeled Signal Set
- Automate Signal Labeling with Custom Functions
- Label Spoken Words in Audio Signals
- Use Signal Labeler App
- Import and Play Audio File Data in Signal Labeler
- Create or Import Signal Label Definitions
- Label Signals Interactively or Automatically
- Custom Labeling Functions
- Customize Labeling View
- Spectrogram Computation in Signal Labeler
- Dashboard
- Export Data and Create Data Sets
- Signal Labeler Usage Tips