Bus Creator
입력 신호, 입력 버스 또는 입력 메시지를 버스로 그룹화
라이브러리:
Simulink /
Commonly Used Blocks
Simulink /
Signal Routing
HDL Coder /
Signal Routing
설명
Bus Creator 블록은 입력 신호, 입력 버스 또는 입력 메시지를 하나의 버스로 결합하며, 이때 신호, 중첩된 버스 및 메시지의 개별적인 특성을 유지합니다. 기본적으로 Bus Creator 블록은 가상 버스를 생성하며, 이는 케이블 타이로 묶인 전선 다발에 비유할 수 있습니다. 또는 이 블록은 비가상 버스를 생성할 수도 있으며, 이는 C 코드의 구조체와 비슷합니다.
버스의 요소는 고유한 이름을 가져야 합니다. 기본적으로 버스의 각 요소는 Bus Creator 블록에 연결된 요소의 이름을 상속합니다. 중복된 이름이 있으면 Bus Creator 블록은 모든 입력 요소 이름에 포트 번호를 추가합니다. 이름이 없는 요소에 대해서는 Bus Creator 블록이 signaln 형식으로 이름을 생성하며, 여기서 n은 요소에 연결된 포트 번호입니다. 요소의 소스를 검색하거나 다른 블록에 연결할 요소를 선택할 때 요소를 이름으로 참조할 수 있습니다. 요소 명명 지침은 Signal Names and Labels 항목을 참조하십시오.
버스에서 요소를 이름으로 추출하려면 Bus Selector 블록을 사용하십시오.
다른 버스를 포함하는 버스를 생성하려면 해당 버스를 Bus Creator 블록의 입력 포트에 연결하십시오.
팁
서브시스템 및 모델 인터페이스에서 버스를 사용할 경우, Bus Creator 블록과 Outport 블록을 함께 사용하는 대신 Out Bus Element 블록을 사용하십시오. Out Bus Element 블록은 다음과 같은 장점이 있습니다.
블록 다이어그램에서 선이 복잡하고 지저분해지는 것을 줄여줍니다.
인터페이스를 점진적으로 변경하기가 더 쉽습니다.
예제
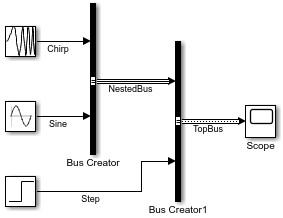
Bus Creator 블록을 사용하여 컴포넌트 내의 여러 신호를 하나의 가상 버스로 그룹화할 수 있습니다.
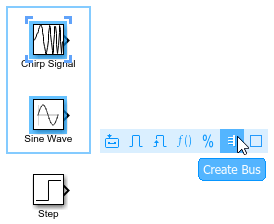
새 모델을 열고 3개의 소스 블록을 추가합니다. 예를 들어 Chirp Signal 블록, Sine Wave 블록, Step 블록을 추가합니다.

여러 블록의 출력을 포함하는 버스를 생성하려면, 해당 블록들을 클릭한 후 끌어서 선택합니다. 이 예제에서는 Chirp Signal 블록과 Sine Wave 블록을 선택합니다. 표시되는 작업 모음에서 버스 만들기를 클릭합니다.
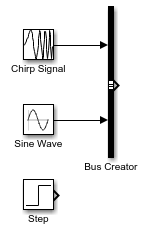
Bus Creator 블록이 추가되고 이 블록에 입력이 연결됩니다. Bus Creator 블록의 출력은 가상 버스입니다.
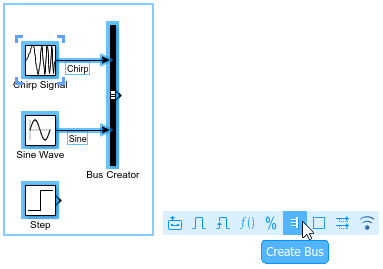
버스의 요소를 더 쉽게 식별할 수 있도록 Bus Creator 블록의 입력에 레이블을 지정합니다.
Chirp Signal 블록과 Bus Creator 블록 사이의 선을 더블 클릭합니다. 그런 다음
Chirp를 입력합니다.Sine Wave 블록과 Bus Creator 블록 사이의 선을 더블 클릭합니다. 그런 다음
Sine을 입력합니다.
첫 번째 버스와 Step 블록의 출력을 포함하는 두 번째 버스를 만들려면, Bus Creator 블록과 Step 블록을 클릭한 후 끌어서 선택합니다. 표시되는 작업 모음에서 버스 만들기를 클릭합니다. Sine Wave 블록 및 Chirp Signal 블록은 입력 버스의 요소를 제공하므로 이러한 블록을 선택에 포함해도 결과에 영향을 미치지 않습니다.
또 다른 Bus Creator 블록이 추가되고 이 블록에 입력이 연결됩니다. Bus Creator 블록의 출력은 중첩된 버스를 포함하는 가상 버스입니다.
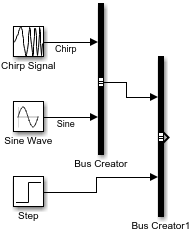
버스를 원하는 깊이까지 중첩할 수 있습니다. Bus Creator 블록의 입력 중 하나가 버스인 경우, 그 출력은 적어도 하나의 중첩된 버스를 포함하는 버스 계층 구조입니다.
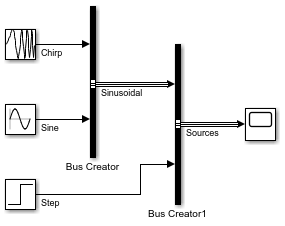
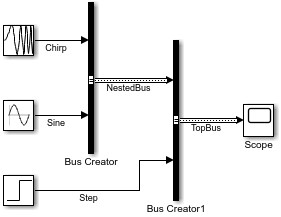
새 Bus Creator 블록의 입력에 레이블을 지정합니다.
두 Bus Creator 블록 사이의 선을 더블 클릭합니다. 그런 다음
Sinusoidal을 입력합니다.Step 블록과 Bus Creator 블록 사이의 선을 더블 클릭합니다. 그런 다음
Step을 입력합니다.
원한다면 블록들을 정렬하여 모델의 가독성을 높일 수 있습니다.
두 번째 Bus Creator 블록의 출력을 Scope 블록에 연결하고 출력의 레이블을 Sources로 지정합니다.
버스를 선 스타일로 시각적으로 식별하려면 Simulink® 툴스트립의 모델링 탭에서 모델 업데이트 또는 실행을 클릭합니다.
Bus Creator 블록을 사용하여 컴포넌트 내에서 비가상 버스를 만들 수 있습니다.
이름이 BusHierarchy인 모델을 열고 컴파일합니다. 이 모델은 Bus Creator 블록을 사용하여 가상 버스의 계층 구조를 생성합니다. 모델을 컴파일하려면 Simulink® 툴스트립의 모델링 탭에서 모델 업데이트나 실행을 클릭하십시오. 모델을 컴파일하면 선 스타일이 업데이트되며, 이를 통해 버스를 시각적으로 식별할 수 있습니다.
또는 MATLAB® 명령 창에 다음 명령을 입력합니다.
mdl = "BusHierarchy"; open_system(mdl) set_param(mdl, SimulationCommand="Update")
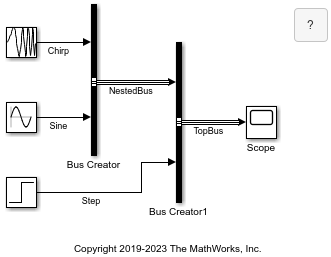
이 모델의 가상 버스는 Simulink.Bus 객체로 정의되어 있지 않습니다. 비가상 버스를 만들려면 버스 계층 구조와 일치하는 bus 객체를 지정해야 합니다.
bus 객체를 대화형 방식으로 만들려면 다음을 수행하십시오.
유형 편집기를 엽니다. Bus Creator 블록을 더블 클릭합니다. 그런 다음 출력 데이터형 상자 옆의
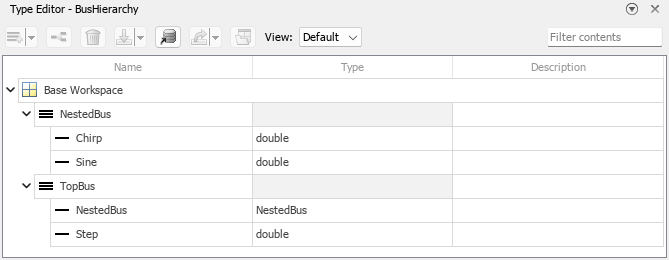 을 클릭합니다.
을 클릭합니다.유형 편집기에서
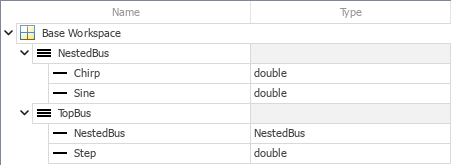
 을 클릭하여 bus 객체 2개를 만듭니다.
을 클릭하여 bus 객체 2개를 만듭니다.각 bus 객체에서
 을 클릭하여 요소 2개를 만듭니다.
을 클릭하여 요소 2개를 만듭니다.선택적으로, 객체를 더블 클릭하여 이름을 바꿉니다. 이 예제에서는 신호 이름과 버스 이름을 사용합니다.
NestedBus요소의 데이터형을NestedBus로 설정합니다.
또는 Simulink.Bus.createObject 함수를 사용합니다.
bctop = "BusHierarchy/Bus Creator1";
Simulink.Bus.createObject(mdl,bctop);이 함수는 해당 버스의 이름인 TopBus 및 NestedBus를 따서 명명된 2개의 bus 객체를 생성합니다.
이제 생성하고자 하는 비가상 버스에 해당하는 bus 객체가 준비되었으므로, 해당 Bus Creator 블록의 파라미터를 업데이트하여 상위 버스(TopBus)를 비가상 버스로 변환합니다.
속성 인스펙터를 엽니다. Simulink 툴스트립의 시뮬레이션 탭에 있는 준비 갤러리에서 속성 인스펙터를 선택합니다.
이름이
Bus Creator1인 Bus Creator 블록을 선택합니다.속성 인스펙터에서 출력 데이터형을
Bus: TopBus로 설정합니다.속성 인스펙터에서 비가상 버스로 출력을 선택합니다.
비가상 버스를 선 스타일로 식별하려면 모델을 다시 컴파일합니다.
또는 다음 명령을 입력합니다.
set_param(bctop, OutDataTypeStr="Bus: TopBus") set_param(bctop, NonVirtualBus="on") set_param(mdl, SimulationCommand="Update")
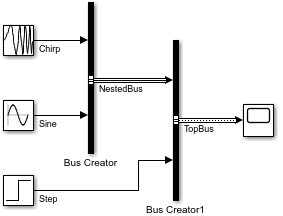
이제 TopBus는 비가상 버스이지만, NestedBus는 여전히 가상 버스입니다.
중첩된 버스를 비가상 버스로 변환하기 위해, 해당 Bus Creator 블록 파라미터를 업데이트합니다.
이름이
Bus Creator인 Bus Creator 블록을 선택합니다.속성 인스펙터에서 출력 데이터형을
Bus: NestedBus로 설정합니다.속성 인스펙터에서 비가상 버스로 출력을 선택합니다.
비가상 버스를 선 스타일로 식별하려면 모델을 다시 컴파일합니다.
또는 다음 명령을 입력합니다.
bcnested = "BusHierarchy/Bus Creator"; set_param(bcnested, OutDataTypeStr="Bus: NestedBus") set_param(bcnested, NonVirtualBus="on") set_param(mdl, SimulationCommand="Update")
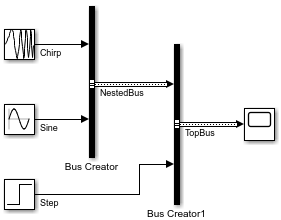
이제 NestedBus가 비가상 버스로 변환되었습니다.
bus 객체를 저장하지 않으면 모델을 다시 열 때 bus 객체를 다시 만들어야 합니다. bus 객체를 저장하는 방법에 대한 자세한 내용은 Specify Bus Properties with Bus Objects 항목을 참조하십시오.
확장 예제
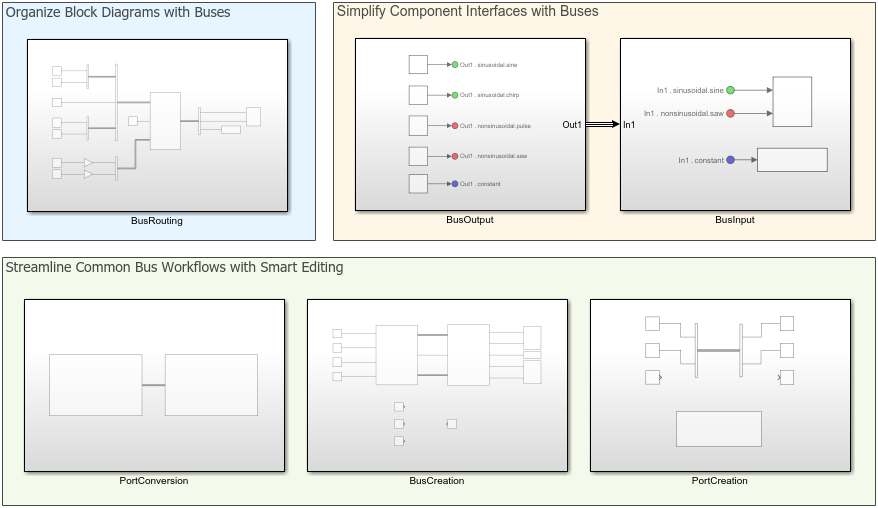
Simulink Bus Capabilities
Work with buses in components, simplify component interfaces, and streamline common bus workflows.
포트
입력
입력 포트는 버스에 포함할 요소를 받습니다. 입력 포트의 개수는 입력 개수 파라미터로 구동됩니다.
각 Bus Creator 블록은 입력 요소의 다음 조합을 지원합니다.
신호만
신호 및 신호 버스
메시지만
메시지 및 버스
버스만
가변 크기 입력 신호를 지정할 때, 이 신호의 상한을 해당 Bus Creator 블록 입력 포트가 받을 수 있는 가변 크기 신호의 상한보다 작게 지정할 수 있습니다. Bus Creator 블록 입력 포트가 받는 가변 크기 신호의 상한을 구성하려면 Simulink.BusElement 객체를 사용하십시오. 자세한 내용은 Simulink.BusElement 항목을 참조하십시오. 가변 크기 입력 신호는 해당 Bus Creator 블록 입력 포트가 받도록 구성된 가변 크기 신호와 동일한 차원을 가져야 합니다.
데이터형: single | double | half | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | string | Boolean | fixed point | enumerated | bus
복소수 지원 여부: 예
출력
출력 버스는 입력 요소들로 구성됩니다.
비가상 버스로 출력 파라미터는 출력 버스가 가상 버스인지 아니면 비가상 버스인지 지정합니다. 가상 버스이면 그 가상 버스를 구성하는 요소로 취급하고, 비가상 버스이면 스칼라로 취급합니다.
버스의 유형에 대한 자세한 내용은 Composite Interface Guidelines 항목을 참조하십시오.
데이터형: single | double | half | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | string | Boolean | fixed point | enumerated | bus
복소수 지원 여부: 예
파라미터
블록 파라미터를 대화형 방식으로 편집하려면 속성 인스펙터를 사용합니다. Simulink 툴스트립의 시뮬레이션 탭에 있는 준비 갤러리에서 속성 인스펙터를 선택하십시오.
버스를 만들려면, 블록 입력의 개수가 2보다 크거나 같은 정수여야 합니다.
입력의 개수를 늘리면, 연결되지 않은 입력 포트가 블록에 추가됩니다. 모델을 시뮬레이션하기 전에, 입력이 각 입력 포트에 연결되어 있는지 확인하십시오.
각 입력 포트가 이미 연결된 경우, Bus Creator 블록에 또 다른 선을 연결하면 입력 포트를 추가할 수 있습니다.
대화형 방식으로 포트를 추가하면 입력 개수 파라미터 값이 업데이트되고 새 입력이 입력 목록에 추가됩니다.
프로그래밍 방식의 사용법
프로그래밍 방식으로 블록 파라미터 값을 설정하려면 set_param 함수를 사용하십시오.
입력의 개수를 2보다 크거나 같은 정수로 지정합니다.
| 파라미터: | Inputs |
| 값: | '2' (디폴트 값) | integer in quotes |
| 데이터형: | char | string |
예: set_param(gcb, Inputs="3")
입력 목록은 중첩된 버스의 요소까지 포함하여, 블록으로 들어오는 요소들을 제공합니다. 요소 옆에 화살표가 있으면 그 입력이 버스임을 나타냅니다. 해당 버스의 내용을 표시하려면 화살표를 클릭하십시오.
입력 요소를 재정렬하려면 입력 목록에서 하나 이상의 최상위 요소를 선택합니다. 그런 다음 요소를 새 위치로 끌어서 놓습니다.
입력 요소를 추가 또는 제거하려면  또는
또는  을 각각 클릭합니다. 모델을 시뮬레이션하기 전에 각 입력 포트가 연결되어 있는지 확인하십시오.
을 각각 클릭합니다. 모델을 시뮬레이션하기 전에 각 입력 포트가 연결되어 있는지 확인하십시오.
입력 요소 목록을 새로 고치려면  을 클릭합니다. 예를 들어, 다음의 경우에 입력 목록을 새로 고치십시오.
을 클릭합니다. 예를 들어, 다음의 경우에 입력 목록을 새로 고치십시오.
대화 상자가 열려 있는 상태에서 입력 요소의 이름을 바꾼 경우.
명명되지 않은 입력 요소를 추가하거나 제거하거나 다시 정렬한 경우. Bus Creator 블록은 이러한 요소의 이름을
signalN으로 지정하며, 여기서 N은 해당 블록 포트의 번호입니다. 해당 블록 포트가 변경되면 자동 생성된 이름도 바뀝니다.
정규 표현식 사용 여부와 관계없이 이름을 기준으로 입력 요소를 필터링하려면 필터 상자에 검색어를 입력하십시오. 검색어를 따옴표로 묶지 마십시오. 선택적으로,  을 클릭하면 필터링된 결과를 계층 없이 단순 나열할 수 있습니다. 단순 나열된 목록은 점 표기법을 사용하여 버스 계층 구조를 반영합니다. 기본적으로, 필터링된 결과는 계층적 트리로 표시됩니다.
을 클릭하면 필터링된 결과를 계층 없이 단순 나열할 수 있습니다. 단순 나열된 목록은 점 표기법을 사용하여 버스 계층 구조를 반영합니다. 기본적으로, 필터링된 결과는 계층적 트리로 표시됩니다.
R2025a 이전: 정규 표현식을 사용하여 필터링하려면  을 클릭하십시오. 그런 다음 정규 표현식 사용을 선택합니다.
을 클릭하십시오. 그런 다음 정규 표현식 사용을 선택합니다.
블록으로 들어오는 요소의 소스를 선택하려면, 목록에서 해당 요소를 선택하십시오. 그런 다음  을 클릭하십시오. 선택된 소스 블록의 파라미터가 속성 인스펙터에 표시됩니다. 여러 요소의 소스 블록을 선택하면, 현재 포커스가 있는 소스 블록의 파라미터가 속성 인스펙터에 표시됩니다.
을 클릭하십시오. 선택된 소스 블록의 파라미터가 속성 인스펙터에 표시됩니다. 여러 요소의 소스 블록을 선택하면, 현재 포커스가 있는 소스 블록의 파라미터가 속성 인스펙터에 표시됩니다.
입력 목록에서 변경한 내용은 실행 취소하거나 다시 실행할 수 없습니다.
팁
출력 데이터형을
Simulink.Bus객체로 설정한 경우, 최상위 입력이 어떤Simulink.BusElement객체와 매핑되는지 표시하려면 최상위 입력 위에 커서를 올립니다. 입력이 어느Simulink.BusElement객체와 매핑되는지, 예를 들어Input1 → BusElementObject1이 괄호 안에 표시됩니다.정규 표현식을 사용하면 입력 요소가 패턴과 일치하는지 여부에 따라 필터링할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 이름이 소문자
t로 끝나는 모든 요소를 표시하려면 필터 상자에t$를 입력합니다. 자세한 내용은 정규 표현식 항목을 참조하십시오.
출력 버스의 데이터형을 지정합니다.
Bus: <object name>을 선택한 경우, <object name>을 Simulink.Bus 객체의 이름으로 바꾸십시오. 모델을 편집할 때 이 bus 객체에 액세스할 수 있어야 합니다.
팁
유형 편집기를 사용하여
Simulink.Bus객체를 만들려면 을 클릭하십시오.
을 클릭하십시오.출력 버스에서
Simulink.Bus객체를 만들려면Simulink.Bus.createObject함수를 사용하십시오.
프로그래밍 방식의 사용법
프로그래밍 방식으로 블록 파라미터 값을 설정하려면 set_param 함수를 사용하십시오.
| 파라미터: | OutDataTypeStr |
| 값: | "Inherit: auto" (디폴트 값) | "Bus: <object name>" |
예: set_param(gcb, OutDataTypeStr="Bus: control")
기본적으로 Bus Creator 블록은 블록 입력의 이름을 출력 버스 요소의 이름으로 사용합니다. 이는 Simulink.Bus 객체를 데이터형으로 지정한 경우에도 마찬가지입니다.
입력에서— 출력 버스 요소의 이름을 블록 입력에서 상속합니다.R2025a 이전: Bus 객체 대신 입력에서 이름 사용을 선택하십시오.
출력 데이터형에서— 출력 버스 요소의 이름을 지정된 bus 객체에서 상속합니다.R2025a 이전: Bus 객체 대신 입력에서 이름 사용을 선택 해제하십시오.
요소 이름을 출력 데이터형에서로 설정하면:
강한 데이터형 지정이 적용됩니다.
bus 객체 및 모델에서 요소 이름을 여러 번 입력할 필요가 없습니다. 이름을 여러 번 입력하면 의도치 않게 요소 이름 불일치가 발생할 수 있습니다.
버스로 구성된 배열의 경우 배열 요소들의 이름이 일관되어야 한다는 요구 사항이 지원됩니다.
요소 이름을 입력에서로 설정하는 경우 요소 이름 불일치 구성 파라미터를 오류로 설정하는 것이 좋습니다. 이 구성 파라미터는 입력 요소 이름이 bus 객체 내의 해당 이름과 일치하는지 확인합니다.
종속성
이 파라미터를 활성화하려면 출력 데이터형을 Simulink.Bus 객체로 설정하십시오.
프로그래밍 방식의 사용법
프로그래밍 방식으로 블록 파라미터 값을 설정하려면 set_param 함수를 사용하십시오.
| 파라미터: | InheritFromInputs |
| 값: | "on" (디폴트 값) | "off" |
예: set_param(gcb, InheritFromInputs="off")
이 테이블은 이 파라미터의 대화형 방식 값을 프로그래밍 방식의 해당 값에 매핑합니다.
요소 이름 값 | InheritFromInputs 값 |
|---|---|
입력에서(디폴트 값) | "on"(디폴트 값) |
출력 데이터형에서 | "off" |
비가상 버스를 출력하려면 이 파라미터를 선택하십시오.
비가상 버스는 C 코드의 구조체와 비슷합니다. 이 파라미터는 다음을 수행하려는 경우에 선택하십시오.
버스로 구성된 배열을 생성하는 경우.
MATLAB Function 블록 또는 Stateflow® 차트 경계를 가로지르는 버스 데이터가 있는 경우.
C 생성 코드에서 버스 데이터를 구조체로 패키징하는 경우.
외부 코드와 S-Function을 통해 상호 작용하는 경우.
생성된 코드에서 하위 컴포넌트에 전달되는 함수 인수의 개수를 줄이려는 경우.
비가상 버스의 모든 요소는 동일한 샘플 시간을 가져야 하며, 이는 연결된 Simulink.Bus 객체의 일부 요소가 상속된 샘플 시간을 지정한 경우에도 마찬가지입니다. 서로 다른 샘플 레이트를 가진 요소들이 포함된 비가상 버스를 생성하는 작업은 모두 오류가 발생합니다. 다른 비가상 버스 입력 요소들과 샘플 시간이 다른 요소나 버스의 샘플 시간을 변경하려면 Rate Transition 블록을 사용하십시오. 자세한 내용은 비가상 버스의 샘플 시간 수정하기 항목을 참조하십시오.
종속성
이 파라미터를 활성화하려면 출력 데이터형을 Simulink.Bus 객체로 설정하십시오.
프로그래밍 방식의 사용법
프로그래밍 방식으로 블록 파라미터 값을 설정하려면 set_param 함수를 사용하십시오.
| 파라미터: | NonVirtualBus |
| 값: | "off" (디폴트 값) | "on" |
예: set_param(gcb, NonVirtualBus="on")
블록 특성
데이터형 |
|
직접 피드스루 |
|
다차원 신호 |
|
가변 크기 신호 |
|
영점교차 검출 |
|
확장 기능
실제 데이터형 또는 기능 지원은 블록 구현에 따라 달라집니다.
HDL Coder™는 HDL 구현과 합성된 논리에 영향을 주는 추가 구성 옵션을 제공합니다.
이 블록에는 하나의 디폴트 HDL 아키텍처가 있습니다.
| ConstrainedOutputPipeline | 기존 지연을 설계 내부로 이동하여 출력에 배치하는 레지스터 개수입니다. 분산된 파이프라이닝은 이러한 레지스터를 다시 분산하지 않습니다. 디폴트 값은 |
| InputPipeline | 생성된 코드에 삽입할 입력 파이프라인 단계의 개수입니다. 분산 파이프라이닝과 제약이 있는 출력 파이프라이닝은 이러한 레지스터를 이동할 수 있습니다. 디폴트 값은 |
| OutputPipeline | 생성된 코드에 삽입할 출력 파이프라인 단계의 개수입니다. 분산 파이프라이닝과 제약이 있는 출력 파이프라이닝은 이러한 레지스터를 이동할 수 있습니다. 디폴트 값은 |
이 블록은 HDL 코드 생성 시 다음과 같은 데이터형을 지원합니다.
| 입력 포트 | 차원 | 고정소수점 | 부동소수점 | 내장 정수 | 버스 | 부울 | 복소 신호 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Port_1 | 스칼라 벡터 행렬(최대 2차원) | 예 | half형 single형 double형 | 예 | 예 | 예 | 예 |
이러한 HDL Coder 최적화를 사용하여 속도, 면적, I/O를 최적화할 수 있습니다.
면적 최적화
| 최적화 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| Resource Sharing (HDL Coder) | 리소스 공유는 HDL Coder가 기능적으로 동등한 여러 리소스를 식별하여 단일 리소스로 대체하는 면적 최적화입니다. |
| Streaming (HDL Coder) | 스트리밍은 HDL Coder가 벡터 데이터 경로를 스칼라 데이터 경로(또는 더 작은 크기의 여러 개 벡터 데이터 경로)로 변환하는 면적 최적화입니다. |
속도 최적화
| 최적화 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| Distributed Pipelining (HDL Coder) | 분산 파이프라이닝(Distributed pipelining), 즉 레지스터 타이밍 재지정은 설계 내 기존 지연을 이동시켜서 기능적 동작을 유지하면서 임계 경로를 줄이는 속도 최적화입니다. Sqrt 블록의 경우, HDL Coder는 블록 내부가 아닌 블록 주변에 파이프라인 레지스터를 분산합니다. |
| Clock-Rate Pipelining (HDL Coder) | 클록 속도 파이프라이닝(Clock-rate pipelining)은 HDL Coder에서 다른 속도 최적화와 면적 최적화가 클록 속도에서 대기 시간을 유발할 수 있도록 하는 최적화 프레임워크입니다. |
| Adaptive Pipelining (HDL Coder) | 적응형 파이프라이닝(Adaptive pipelining) 최적화는 설계 내 블록에 파이프라인 레지스터를 삽입하여 달성 가능한 클록 주파수를 개선하고 FPGA 보드의 면적 사용량을 줄일 수 있는 레지스터가 포함된 블록의 패턴이나 조합을 생성합니다. |
| 임계 경로 추정(Critical Path Estimation) (HDL Coder) | 설계에서 가장 가능성이 높은 임계 경로를 빠르게 식별하려면 임계 경로 추정을 사용합니다. 임계 경로 추정은 임계 경로를 찾는 반복적인 프로세스 속도를 높여줍니다. 임계 경로 추정에 특성화된 블록을 알아보려면 Characterized Blocks (HDL Coder) 항목을 참조하십시오. |
모범 사례는 다음 항목을 참조하십시오.
HDL 코드 생성을 위하여 버스를 사용하는 방법에 대해 자세히 알아보려면 Buses (HDL Coder) 항목을 참조하십시오.
PLC 코드 생성
Simulink® PLC Coder™를 사용하여 Structured Text 코드를 생성할 수 있습니다.
실제 데이터형 또는 기능 지원은 블록 구현에 따라 달라집니다.
버전 내역
R2006a 이전에 개발됨Bus Creator 블록은 이제 블록 파라미터 값에 대해 더 직관적이고 간소화된 편집 기능을 제공합니다.
이제 속성 인스펙터에서 Bus Creator 블록 파라미터 값을 지정할 수 있습니다. Block 파라미터 대화 상자는 계속 사용할 수 있습니다.
다음 표에서는 파라미터 및 상호 작용 변경 사항을 설명합니다.
| 목표 | R2025a 이전 버전의 동작 | R2025a 이후 버전의 동작 |
|---|---|---|
| 변경 내용 적용. | 변경 작업을 수행합니다. 그런 다음 적용 또는 확인을 클릭합니다. | 변경 작업을 수행합니다. 속성 인스펙터 또는 블록 파라미터 대화 상자에서 블록 파라미터 값을 지정하면 그 즉시 변경 사항이 적용됩니다. |
| 정규 표현식을 사용한 필터링. |  을 클릭하고 정규 표현식 사용을 선택합니다. 그런 다음 이름별 필터링 상자에 검색어를 입력합니다. 을 클릭하고 정규 표현식 사용을 선택합니다. 그런 다음 이름별 필터링 상자에 검색어를 입력합니다. | 필터 상자에 검색어를 입력합니다. |
| 필터링된 결과를 단순 목록으로 표시. | 필터링된 결과를 단순 목록으로 표시를 클릭합니다. |  을 클릭합니다. 을 클릭합니다. |
| 소스 블록 찾기. | 입력을 하나 이상 선택합니다. 그런 다음 찾기를 클릭합니다. 소프트웨어가 소스 블록을 강조 표시합니다. | 입력을 하나 이상 선택합니다. 그런 다음 소프트웨어가 소스 블록을 선택하고, 현재 포커스가 있는 블록의 파라미터가 속성 인스펙터에 표시됩니다. |
| 블록 입력 추가. | 추가를 클릭합니다. |  을 클릭합니다. 을 클릭합니다. |
| 입력 목록 새로 고침. | 새로 고침을 클릭합니다. |  을 클릭합니다. 을 클릭합니다. |
| 블록 입력 제거. | 제거를 클릭합니다. |  을 클릭합니다. 을 클릭합니다. |
| 입력 재정렬. | 인접한 입력을 하나 이상 선택합니다. 그런 다음 위로 또는 아래로를 클릭하여 입력이 원하는 위치에 오도록 합니다. | 입력을 하나 이상 선택합니다. 그런 다음 입력을 원하는 위치로 끌어서 놓습니다. |
유형 편집기를 열어 Simulink.Bus 객체 정의. |  을 클릭하고 모드를 을 클릭하고 모드를 Bus 객체로 설정합니다. 그런 다음 편집 버튼을 클릭합니다. |  을 클릭합니다. 을 클릭합니다. |
| 출력 버스 요소 이름의 소스 지정. | Bus 객체 대신 입력에서 이름 사용 체크박스를 선택하거나 선택 해제합니다. | 요소 이름을 입력에서 또는 출력 데이터형에서로 설정합니다. |
| 입력의 이름 바꾸기. | 입력 요소의 신호 레이블을 편집합니다. 또는 입력의 이름은 위에 표시된 이름과 일치해야 합니다를 선택하고, 요소를 선택하고, 새 이름을 선택한 신호 이름 바꾸기 상자에 지정합니다. | 입력 요소의 신호 레이블을 편집합니다. |
입력의 이름은 위에 표시된 이름과 일치해야 합니다 파라미터와 선택한 신호 이름 바꾸기 파라미터가 제거되었습니다. 필요한 이름을 지정하려면 Simulink.Bus 객체를 대신 사용하십시오.
출력 데이터형을
Simulink.Bus객체로 설정합니다.다음 옵션 중 하나를 선택합니다.
출력 버스 요소 이름을 지정된
Simulink.Bus객체에서 상속하려면 요소 이름을출력 데이터형에서로 설정합니다.지정된
Simulink.Bus객체의 이름과 입력 이름이 일치하도록 요구하려면 요소 이름을입력에서로 설정하고 요소 이름 불일치 구성 파라미터를오류로 설정합니다. 이 구성 파라미터는 입력 이름이Simulink.Bus객체 내의 해당 이름과 일치하는지 확인합니다.
Inputs을 쉼표로 구분된 요소 이름 목록으로 설정하는 것은 권장되지 않습니다.
R2023a부터, Bus Creator 블록은 해당 Bus Creator 블록 입력 포트가 받을 수 있는 가변 크기 신호의 상한보다 작은 상한을 가진 가변 크기 입력 신호를 지원합니다.
이 개선 사항을 통해 입력 신호의 상한이 해당 Bus Creator 블록 입력 포트가 받을 수 있는 가변 크기 신호의 상한과 같지 않은 경우에도 가변 크기 입력 신호를 사용할 수 있습니다.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)