getBlock
(To be removed) Read block of bigimage object
The getBlock function of the bigimage object will be
removed in a future release. Use the getBlock function
associated with the blockedImage object
instead. For more information, see Version History.
Description
data = getBlock(bigimg,level,locationWorld)bigimg at the specified resolution level,
and returns pixel data for the entire block that contains coordinate
locationWorld.
Examples
Create a bigimage using a modified version of image "tumor_091.tif" from the CAMELYON16 data set. The original image is a training image of a lymph node containing tumor tissue. The original image has eight resolution levels, and the finest level has resolution 53760-by-61440. The modified image has only three coarse resolution levels. The spatial referencing of the modified image has been adjusted to enforce a consistent aspect ratio and to register features at each level.
bim = bigimage('tumor_091R.tif');
Display the bigimage by using the bigimageshow function. Overlay a grid that shows the block boundaries at the finest resolution level.
hb = subplot(1,2,1); bigimageshow(bim,'GridVisible','on','GridLevel',1);
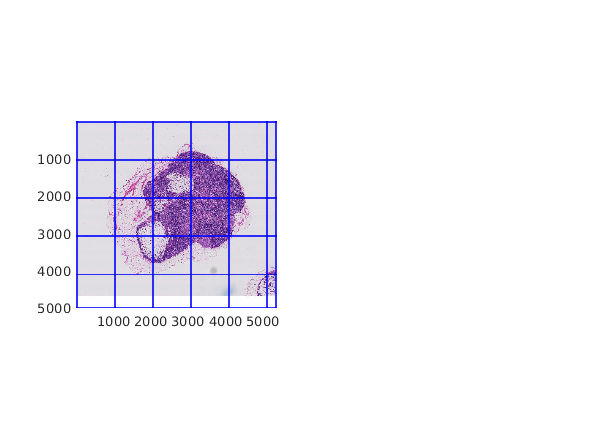
Specify the (x,y) coordinate of a block to display. Get the block containing the coordinate. Add a Point ROI over the displayed bigimage at the specified coordinate.
coord = [2500,2500];
blk = getBlock(bim,1,coord);
hp = drawpoint(hb,'Position',coord);

In the figure, display the block next to the entire bigimage. You can use imshow to display the block because the block fits in memory and has a single resolution level.
ha = subplot(1,2,2);
imshow(blk,'Parent',ha)

Add a listener to the Point ROI. When you drag the ROI with the mouse, the figure is updated to show the block containing the current ROI coordinates.
title(hb,'Drag Point to Select Block'); addlistener(hp, ... 'ROIMoved',@(~,~) imshow(getBlock(bim,1,hp.Position),'Parent',ha));

Input Arguments
Big image, specified as a bigimage object.
Resolution level, specified as a positive integer that is less than or equal to the
number of resolution levels of bigimg.
Coordinate of a point, specified as a 1-by-2 numeric vector of the form [x
y]. The location is specified in world coordinates, which are the pixel
locations relative to the highest resolution level. The position must be a valid
position within bigimg.
Output Arguments
Pixel data, returned as a numeric array of the same data type as the big image,
bigimg.ClassUnderlying
Version History
Introduced in R2019bThe getBlock function issues a warning that it will be removed
in a future release.
The bigimage object and this function will be removed in a future
release. Use the getBlock
function of the blockedImage
object instead.
To update your code, first create a blockedImage object to read your
image data. Then, follow these steps:
Convert from (x, y) world coordinates to (row, column) world coordinates by switching the order of the two elements.
Convert the world coordinates to pixel subscripts using the
world2subfunction. If you want to get the block at a resolution level other than level 1, then specify that level by using theLevelname-value argument.Convert the pixel subscripts to block subscripts using the
sub2blocksubfunction. If you want to get the block at a resolution level other than level 1, then specify that level by using theLevelname-value argument.Note that if the dimensionality of the blocked image is greater than 2, then increase the length of the vector of pixel subscripts by one for each unspecified dimension. You can specify the value
1for these additional elements. For example, a 2-D color image has a dimensionality of 3 because of the color channel. You must append one element to the vector of pixel subscripts when you call thesub2blocksubfunction.Pass the blocked image and the block subscripts to the
getBlockfunction. If you want to get the block at a resolution level other than level 1, then specify that level by using theLevelname-value argument.
| Discouraged Usage | Recommended Replacement |
|---|---|
This example uses the
filename = "tumor_091R.tif";
bim = bigimage(filename);
coordWorld = [1000 2500];
blk = getBlock(bim,1,coordWorld); | Here is equivalent code using a filename = "tumor_091R.tif";
blockedIm = blockedImage(filename);
coordWorld = [1000 2500];
coordRC = flip(coordWorld);
subPixel = world2sub(blockedIm,coordRC);
subBlock = sub2blocksub(blockedIm,[subPixel 1]);
blk = getBlock(blockedIm,subBlock); |
This example repeats the operation at resolution level 2. lvl = 2; blk = getBlock(bim,lvl,coordWorld); | This example repeats the operations at resolution level 2 by specifying
the lvl = 2; subPixel = world2sub(blockedIm,coordRC,Level=lvl); subBlock = sub2blocksub(blockedIm,[subPixel 1],Level=lvl); blk = getBlock(blockedIm,subBlock,Level=lvl); |
The getBlock function of the bigimage object is
not recommended. Use the getBlock
function of the blockedImage
object instead. The
blockedImage object offers several advantages including extension to N-D
processing, a simpler interface, and custom support for reading and writing nonstandard image
formats.
See Also
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)