fevd
Generate forecast error variance decomposition (FEVD) of state-space model
Since R2021a
Syntax
Description
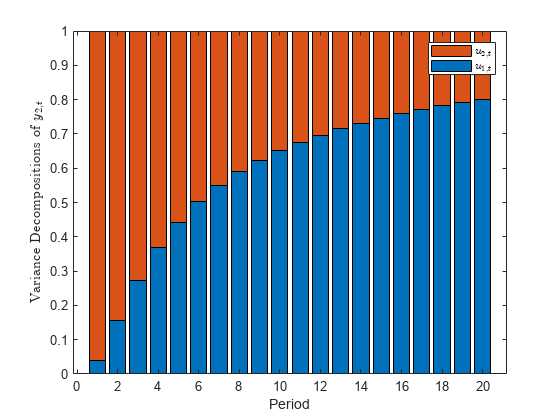
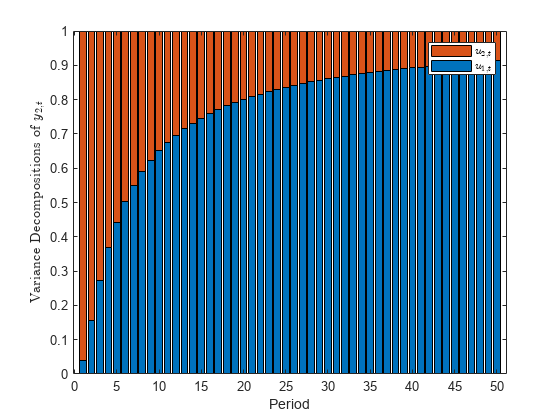
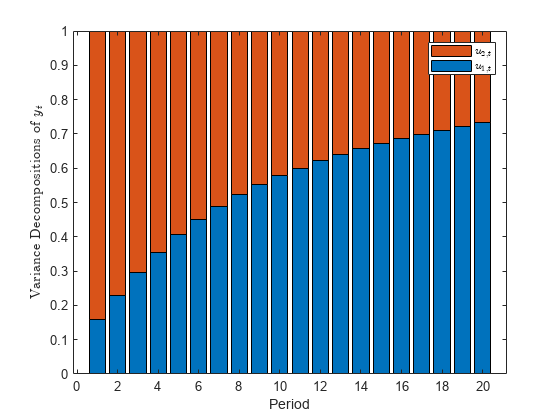
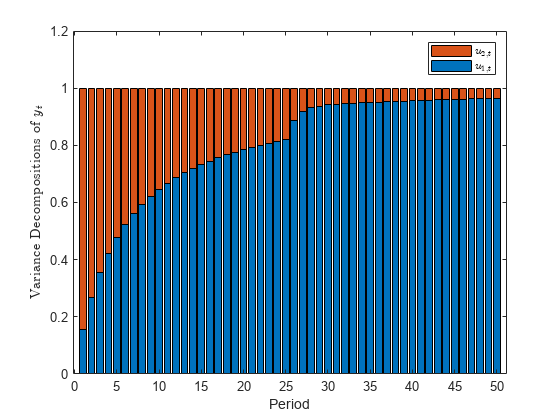
The fevd function returns the forecast error variance decomposition (FEVD) of the measurement variables in a state-space model attributable to component-wise shocks to each state disturbance. The FEVD provides information about the relative importance of each state disturbance in affecting the forecast error variance of all measurement variables in the system. Other state-space model tools to characterize the dynamics of a specified system include the following:
The impulse response function (IRF), computed by
irfand plotted byirfplot, traces the effects of a shock to a state disturbance on the state and measurement variables in the system.Model-implied temporal correlations, computed by
corrfor a standard state-space model, measure the association between current and lagged state or measurement variables, as prescribed by the form of the model.
Fully Specified State-Space Model
Decomposition = fevd(Mdl)Decomposition of the fully specified state-space model Mdl.
Decomposition = fevd(Mdl,Name,Value)'NumPeriods',10 specifies estimating the FEVD for periods 1 through 10.
Partially Specified State-Space Model and Confidence Interval Estimation
Decomposition = fevd(___,'Params',estParams)Mdl. estParams specifies estimates of all unknown parameters in the model, using any of the input argument combinations in the previous syntaxes.
[ also returns the lower and upper 95% Monte Carlo confidence bounds Decomposition,Lower,Upper] = fevd(___,'Params',estParams,'EstParamCov',EstParamCov)Lower and Upper of each measurement variable FEVD. EstParamCov specifies the estimated covariance matrix of the parameter estimates, as returned by the estimate function, and is required for confidence interval estimation.
Examples
Input Arguments
Name-Value Arguments
Output Arguments
More About
Algorithms
If you do not supply the
EstParamCovname-value argument, confidence bounds of each period overlap.fevduses Monte Carlo simulation to compute confidence intervals.fevdrandomly drawsNumPathsvariates from the asymptotic sampling distribution of the unknown parameters inMdl, which is Np(Params,EstParamCov), where p is the number of unknown parameters.For each randomly drawn parameter set j,
fevddoes the following:Create a state-space model that is equal to
Mdl, but substitute in parameter set j.Compute the random FEVD of the resulting model γj(t), where t = 1 through
NumPaths.
For each time t, the lower bound of the confidence interval is the
(1 –quantile of the simulated FEVD at period t γ(t), wherec)/2cConfidence. Similarly, the upper bound of the confidence interval at time t is the(1 –upper quantile of γ(t).c)/2
Version History
Introduced in R2021a