compile
Class: dlhdl.Workflow
Namespace: dlhdl
Compile workflow object
Description
compile( compiles the
workflowObject)dlhdl.Workflow object and generates the parameters for deploying the
network on the target device.
compile(
compiles the workflowObject,Name,Value)dlhdl.Workflow object and generates the parameters for
deploying the network on the target device, with additional options specified by one or
more Name,Value pair arguments.
The function returns two matrices. One matrix describes the layers of the network. The
Conv Controller (Scheduling) and the FC Controller
(Scheduling) modules in the deep learning processor IP use this matrix to schedule
the convolution and fully connected layer operations. The second matrix contains the weights,
biases, and inputs of the neural network. This information is loaded onto the DDR memory and
used by the Generic Convolution Processor and the Generic FC
Processor in the deep learning processor.
When you call the compile method on the dlhdl.Workflow
object, Deep Learning HDL Toolbox™ compiles the workflow object and organizes the
Parameters for deploying the network
Network weights and biases
Deep learning processor instructions and schedules for the deep learning processor modules
Memory locations for the inputs and outputs
Input Arguments
Deep learning network deployment options, specified as a
dlhdl.Workflow object.
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose
Name in quotes.
Parameter to specify maximum input frame number limit to calculate DDR memory access allocation.
Example: 'InputFrameNumberLimit',30
Flag to enable hardware implementation of image input layer normalization function, specified as a string or character vector.
Example: HardwareNormalization = "auto"
Examples
Compile the dlhdl.Workflow object, for deployment
to the Intel®
Arria® 10 SoC development kit that has single data types.
Create a dlhdl.Workflow object and then use the
compile function to deploy the pretrained network to the target
hardware.
snet = vgg19; hT = dlhdl.Target('Intel'); hW = dlhdl.Workflow('network', snet, 'Bitstream', 'arria10soc_single','Target',hT); hW.compile
Once the code is executed the result is:
hW.compile
offset_name offset_address allocated_space
_______________________ ______________ _________________
"InputDataOffset" "0x00000000" "24.0 MB"
"OutputResultOffset" "0x01800000" "4.0 MB"
"SystemBufferOffset" "0x01c00000" "52.0 MB"
"InstructionDataOffset" "0x05000000" "20.0 MB"
"ConvWeightDataOffset" "0x06400000" "276.0 MB"
"FCWeightDataOffset" "0x17800000" "472.0 MB"
"EndOffset" "0x35000000" "Total: 848.0 MB"
ans =
struct with fields:
Operators: [1×1 struct]
LayerConfigs: [1×1 struct]
NetConfigs: [1×1 struct]
Create a
dlhdl.Workflowobject and then use thecompilefunction with optional argument ofInputFrameNumberLimitto deploy the pretrained network to the target hardware.net = resnet18; hT = dlhdl.Target('Xilinx'); hW = dlhdl.Workflow('Network', net, 'Bitstream', 'zcu102_single','Target',hT); hW.compile('InputFrameNumberLimit',30);
The result of the code execution is:
### Compiling network for Deep Learning FPGA prototyping ... ### Targeting FPGA bitstream zcu102_single. ### The network includes the following layers: 1 'data' Image Input 224×224×3 images with 'zscore' normalization (SW Layer) 2 'conv1' Convolution 64 7×7×3 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [3 3 3 3] (HW Layer) 3 'bn_conv1' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 64 channels (HW Layer) 4 'conv1_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 5 'pool1' Max Pooling 3×3 max pooling with stride [2 2] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 6 'res2a_branch2a' Convolution 64 3×3×64 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 7 'bn2a_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 64 channels (HW Layer) 8 'res2a_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 9 'res2a_branch2b' Convolution 64 3×3×64 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 10 'bn2a_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 64 channels (HW Layer) 11 'res2a' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 12 'res2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 13 'res2b_branch2a' Convolution 64 3×3×64 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 14 'bn2b_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 64 channels (HW Layer) 15 'res2b_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 16 'res2b_branch2b' Convolution 64 3×3×64 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 17 'bn2b_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 64 channels (HW Layer) 18 'res2b' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 19 'res2b_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 20 'res3a_branch2a' Convolution 128 3×3×64 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 21 'bn3a_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 128 channels (HW Layer) 22 'res3a_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 23 'res3a_branch2b' Convolution 128 3×3×128 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 24 'bn3a_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 128 channels (HW Layer) 25 'res3a' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 26 'res3a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 27 'res3a_branch1' Convolution 128 1×1×64 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [0 0 0 0] (HW Layer) 28 'bn3a_branch1' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 128 channels (HW Layer) 29 'res3b_branch2a' Convolution 128 3×3×128 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 30 'bn3b_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 128 channels (HW Layer) 31 'res3b_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 32 'res3b_branch2b' Convolution 128 3×3×128 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 33 'bn3b_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 128 channels (HW Layer) 34 'res3b' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 35 'res3b_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 36 'res4a_branch2a' Convolution 256 3×3×128 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 37 'bn4a_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 256 channels (HW Layer) 38 'res4a_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 39 'res4a_branch2b' Convolution 256 3×3×256 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 40 'bn4a_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 256 channels (HW Layer) 41 'res4a' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 42 'res4a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 43 'res4a_branch1' Convolution 256 1×1×128 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [0 0 0 0] (HW Layer) 44 'bn4a_branch1' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 256 channels (HW Layer) 45 'res4b_branch2a' Convolution 256 3×3×256 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 46 'bn4b_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 256 channels (HW Layer) 47 'res4b_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 48 'res4b_branch2b' Convolution 256 3×3×256 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 49 'bn4b_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 256 channels (HW Layer) 50 'res4b' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 51 'res4b_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 52 'res5a_branch2a' Convolution 512 3×3×256 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 53 'bn5a_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 512 channels (HW Layer) 54 'res5a_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 55 'res5a_branch2b' Convolution 512 3×3×512 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 56 'bn5a_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 512 channels (HW Layer) 57 'res5a' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 58 'res5a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 59 'res5a_branch1' Convolution 512 1×1×256 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [0 0 0 0] (HW Layer) 60 'bn5a_branch1' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 512 channels (HW Layer) 61 'res5b_branch2a' Convolution 512 3×3×512 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 62 'bn5b_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 512 channels (HW Layer) 63 'res5b_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 64 'res5b_branch2b' Convolution 512 3×3×512 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 65 'bn5b_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 512 channels (HW Layer) 66 'res5b' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 67 'res5b_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 68 'pool5' 2-D Global Average Pooling 2-D global average pooling (HW Layer) 69 'fc1000' Fully Connected 1000 fully connected layer (HW Layer) 70 'prob' Softmax softmax (HW Layer) 71 'ClassificationLayer_predictions' Classification Output crossentropyex with 'tench' and 999 other classes (SW Layer) ### Optimizing network: Fused 'nnet.cnn.layer.BatchNormalizationLayer' into 'nnet.cnn.layer.Convolution2DLayer' ### Notice: The layer 'data' of type 'ImageInputLayer' is split into an image input layer 'data', an addition layer 'data_norm_add', and a multiplication layer 'data_norm' for hardware normalization. ### Notice: The layer 'prob' with type 'nnet.cnn.layer.SoftmaxLayer' is implemented in software. ### Notice: The layer 'ClassificationLayer_predictions' with type 'nnet.cnn.layer.ClassificationOutputLayer' is implemented in software. ### Compiling layer group: conv1>>pool1 ... ### Compiling layer group: conv1>>pool1 ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res2a_branch2a>>res2a_branch2b ... ### Compiling layer group: res2a_branch2a>>res2a_branch2b ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res2b_branch2a>>res2b_branch2b ... ### Compiling layer group: res2b_branch2a>>res2b_branch2b ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res3a_branch1 ... ### Compiling layer group: res3a_branch1 ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res3a_branch2a>>res3a_branch2b ... ### Compiling layer group: res3a_branch2a>>res3a_branch2b ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res3b_branch2a>>res3b_branch2b ... ### Compiling layer group: res3b_branch2a>>res3b_branch2b ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res4a_branch1 ... ### Compiling layer group: res4a_branch1 ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res4a_branch2a>>res4a_branch2b ... ### Compiling layer group: res4a_branch2a>>res4a_branch2b ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res4b_branch2a>>res4b_branch2b ... ### Compiling layer group: res4b_branch2a>>res4b_branch2b ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res5a_branch1 ... ### Compiling layer group: res5a_branch1 ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res5a_branch2a>>res5a_branch2b ... ### Compiling layer group: res5a_branch2a>>res5a_branch2b ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res5b_branch2a>>res5b_branch2b ... ### Compiling layer group: res5b_branch2a>>res5b_branch2b ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: pool5 ... ### Compiling layer group: pool5 ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: fc1000 ... ### Compiling layer group: fc1000 ... complete. ### Allocating external memory buffers: offset_name offset_address allocated_space _______________________ ______________ _________________ "InputDataOffset" "0x00000000" "24.0 MB" "OutputResultOffset" "0x01800000" "4.0 MB" "SchedulerDataOffset" "0x01c00000" "8.0 MB" "SystemBufferOffset" "0x02400000" "28.0 MB" "InstructionDataOffset" "0x04000000" "4.0 MB" "ConvWeightDataOffset" "0x04400000" "52.0 MB" "FCWeightDataOffset" "0x07800000" "4.0 MB" "EndOffset" "0x07c00000" "Total: 124.0 MB" ### Network compilation complete.
Create a
dlhdl.Workflowobject withresnet18as the network for deployment to a Xilinx® Zynq® UltraScale+™ MPSoC ZCU102 board which usessingledata types.net = resnet18; hTarget = dlhdl.Target('Xilinx'); hW = dlhdl.Workflow('Network',snet,'Bitstream','zcu102_single','Target',hTarget);
Call the
compilefunction onhWhW.compile
Calling the
compilefunction, returns:### Compiling network for Deep Learning FPGA prototyping ... ### Targeting FPGA bitstream zcu102_single ... ### The network includes the following layers: 1 'data' Image Input 224×224×3 images with 'zscore' normalization (SW Layer) 2 'conv1' Convolution 64 7×7×3 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [3 3 3 3] (HW Layer) 3 'bn_conv1' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 64 channels (HW Layer) 4 'conv1_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 5 'pool1' Max Pooling 3×3 max pooling with stride [2 2] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 6 'res2a_branch2a' Convolution 64 3×3×64 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 7 'bn2a_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 64 channels (HW Layer) 8 'res2a_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 9 'res2a_branch2b' Convolution 64 3×3×64 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 10 'bn2a_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 64 channels (HW Layer) 11 'res2a' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 12 'res2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 13 'res2b_branch2a' Convolution 64 3×3×64 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 14 'bn2b_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 64 channels (HW Layer) 15 'res2b_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 16 'res2b_branch2b' Convolution 64 3×3×64 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 17 'bn2b_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 64 channels (HW Layer) 18 'res2b' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 19 'res2b_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 20 'res3a_branch2a' Convolution 128 3×3×64 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 21 'bn3a_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 128 channels (HW Layer) 22 'res3a_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 23 'res3a_branch2b' Convolution 128 3×3×128 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 24 'bn3a_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 128 channels (HW Layer) 25 'res3a' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 26 'res3a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 27 'res3a_branch1' Convolution 128 1×1×64 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [0 0 0 0] (HW Layer) 28 'bn3a_branch1' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 128 channels (HW Layer) 29 'res3b_branch2a' Convolution 128 3×3×128 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 30 'bn3b_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 128 channels (HW Layer) 31 'res3b_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 32 'res3b_branch2b' Convolution 128 3×3×128 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 33 'bn3b_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 128 channels (HW Layer) 34 'res3b' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 35 'res3b_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 36 'res4a_branch2a' Convolution 256 3×3×128 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 37 'bn4a_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 256 channels (HW Layer) 38 'res4a_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 39 'res4a_branch2b' Convolution 256 3×3×256 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 40 'bn4a_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 256 channels (HW Layer) 41 'res4a' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 42 'res4a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 43 'res4a_branch1' Convolution 256 1×1×128 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [0 0 0 0] (HW Layer) 44 'bn4a_branch1' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 256 channels (HW Layer) 45 'res4b_branch2a' Convolution 256 3×3×256 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 46 'bn4b_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 256 channels (HW Layer) 47 'res4b_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 48 'res4b_branch2b' Convolution 256 3×3×256 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 49 'bn4b_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 256 channels (HW Layer) 50 'res4b' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 51 'res4b_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 52 'res5a_branch2a' Convolution 512 3×3×256 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 53 'bn5a_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 512 channels (HW Layer) 54 'res5a_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 55 'res5a_branch2b' Convolution 512 3×3×512 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 56 'bn5a_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 512 channels (HW Layer) 57 'res5a' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 58 'res5a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 59 'res5a_branch1' Convolution 512 1×1×256 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [0 0 0 0] (HW Layer) 60 'bn5a_branch1' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 512 channels (HW Layer) 61 'res5b_branch2a' Convolution 512 3×3×512 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 62 'bn5b_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 512 channels (HW Layer) 63 'res5b_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 64 'res5b_branch2b' Convolution 512 3×3×512 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 65 'bn5b_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 512 channels (HW Layer) 66 'res5b' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 67 'res5b_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 68 'pool5' Global Average Pooling Global average pooling (HW Layer) 69 'fc1000' Fully Connected 1000 fully connected layer (HW Layer) 70 'prob' Softmax softmax (SW Layer) 71 'ClassificationLayer_predictions' Classification Output crossentropyex with 'tench' and 999 other classes (SW Layer) ### Optimizing series network: Fused 'nnet.cnn.layer.BatchNormalizationLayer' into 'nnet.cnn.layer.Convolution2DLayer' 5 Memory Regions created. Skipping: data Compiling leg: conv1>>pool1 ... Compiling leg: conv1>>pool1 ... complete. Compiling leg: res2a_branch2a>>res2a_branch2b ... Compiling leg: res2a_branch2a>>res2a_branch2b ... complete. Compiling leg: res2b_branch2a>>res2b_branch2b ... Compiling leg: res2b_branch2a>>res2b_branch2b ... complete. Compiling leg: res3a_branch2a>>res3a_branch2b ... Compiling leg: res3a_branch2a>>res3a_branch2b ... complete. Compiling leg: res3a_branch1 ... Compiling leg: res3a_branch1 ... complete. Compiling leg: res3b_branch2a>>res3b_branch2b ... Compiling leg: res3b_branch2a>>res3b_branch2b ... complete. Compiling leg: res4a_branch2a>>res4a_branch2b ... Compiling leg: res4a_branch2a>>res4a_branch2b ... complete. Compiling leg: res4a_branch1 ... Compiling leg: res4a_branch1 ... complete. Compiling leg: res4b_branch2a>>res4b_branch2b ... Compiling leg: res4b_branch2a>>res4b_branch2b ... complete. Compiling leg: res5a_branch2a>>res5a_branch2b ... Compiling leg: res5a_branch2a>>res5a_branch2b ... complete. Compiling leg: res5a_branch1 ... Compiling leg: res5a_branch1 ... complete. Compiling leg: res5b_branch2a>>res5b_branch2b ... Compiling leg: res5b_branch2a>>res5b_branch2b ... complete. Compiling leg: pool5 ... Compiling leg: pool5 ... complete. Compiling leg: fc1000 ... Compiling leg: fc1000 ... complete. Skipping: prob Skipping: ClassificationLayer_predictions Creating Schedule... ........................... Creating Schedule...complete. Creating Status Table... .......................... Creating Status Table...complete. Emitting Schedule... .......................... Emitting Schedule...complete. Emitting Status Table... ............................ Emitting Status Table...complete. ### Allocating external memory buffers: offset_name offset_address allocated_space _______________________ ______________ _________________ "InputDataOffset" "0x00000000" "24.0 MB" "OutputResultOffset" "0x01800000" "4.0 MB" "SchedulerDataOffset" "0x01c00000" "4.0 MB" "SystemBufferOffset" "0x02000000" "28.0 MB" "InstructionDataOffset" "0x03c00000" "4.0 MB" "ConvWeightDataOffset" "0x04000000" "52.0 MB" "FCWeightDataOffset" "0x07400000" "4.0 MB" "EndOffset" "0x07800000" "Total: 120.0 MB" ### Network compilation complete. ans = struct with fields: weights: [1×1 struct] instructions: [1×1 struct] registers: [1×1 struct] syncInstructions: [1×1 struct]
Create a
dlhdl.Workflowobject withresnet18as the network for deployment to a Xilinx Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC ZCU102 board which usessingledata types.net = resnet18; hTarget = dlhdl.Target('Xilinx',Interface = 'Ethernet'); hW = dlhdl.Workflow(Network = net,Bitstream ='zcu102_single',Target = hTarget);
Call the
compilefunction onhW. Enable hardware implementation of the input image layer normalization function by setting theHardwareNormalizationargument toauto.hW.compile(HardwareNormalization = 'auto')Calling the
compilefunction, returns:### Compiling network for Deep Learning FPGA prototyping ... ### Targeting FPGA bitstream zcu102_single. ### The network includes the following layers: 1 'data' Image Input 224×224×3 images with 'zscore' normalization (SW Layer) 2 'conv1' Convolution 64 7×7×3 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [3 3 3 3] (HW Layer) 3 'bn_conv1' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 64 channels (HW Layer) 4 'conv1_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 5 'pool1' Max Pooling 3×3 max pooling with stride [2 2] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 6 'res2a_branch2a' Convolution 64 3×3×64 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 7 'bn2a_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 64 channels (HW Layer) 8 'res2a_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 9 'res2a_branch2b' Convolution 64 3×3×64 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 10 'bn2a_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 64 channels (HW Layer) 11 'res2a' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 12 'res2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 13 'res2b_branch2a' Convolution 64 3×3×64 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 14 'bn2b_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 64 channels (HW Layer) 15 'res2b_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 16 'res2b_branch2b' Convolution 64 3×3×64 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 17 'bn2b_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 64 channels (HW Layer) 18 'res2b' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 19 'res2b_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 20 'res3a_branch2a' Convolution 128 3×3×64 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 21 'bn3a_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 128 channels (HW Layer) 22 'res3a_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 23 'res3a_branch2b' Convolution 128 3×3×128 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 24 'bn3a_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 128 channels (HW Layer) 25 'res3a' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 26 'res3a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 27 'res3a_branch1' Convolution 128 1×1×64 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [0 0 0 0] (HW Layer) 28 'bn3a_branch1' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 128 channels (HW Layer) 29 'res3b_branch2a' Convolution 128 3×3×128 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 30 'bn3b_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 128 channels (HW Layer) 31 'res3b_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 32 'res3b_branch2b' Convolution 128 3×3×128 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 33 'bn3b_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 128 channels (HW Layer) 34 'res3b' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 35 'res3b_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 36 'res4a_branch2a' Convolution 256 3×3×128 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 37 'bn4a_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 256 channels (HW Layer) 38 'res4a_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 39 'res4a_branch2b' Convolution 256 3×3×256 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 40 'bn4a_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 256 channels (HW Layer) 41 'res4a' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 42 'res4a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 43 'res4a_branch1' Convolution 256 1×1×128 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [0 0 0 0] (HW Layer) 44 'bn4a_branch1' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 256 channels (HW Layer) 45 'res4b_branch2a' Convolution 256 3×3×256 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 46 'bn4b_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 256 channels (HW Layer) 47 'res4b_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 48 'res4b_branch2b' Convolution 256 3×3×256 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 49 'bn4b_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 256 channels (HW Layer) 50 'res4b' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 51 'res4b_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 52 'res5a_branch2a' Convolution 512 3×3×256 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 53 'bn5a_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 512 channels (HW Layer) 54 'res5a_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 55 'res5a_branch2b' Convolution 512 3×3×512 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 56 'bn5a_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 512 channels (HW Layer) 57 'res5a' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 58 'res5a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 59 'res5a_branch1' Convolution 512 1×1×256 convolutions with stride [2 2] and padding [0 0 0 0] (HW Layer) 60 'bn5a_branch1' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 512 channels (HW Layer) 61 'res5b_branch2a' Convolution 512 3×3×512 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 62 'bn5b_branch2a' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 512 channels (HW Layer) 63 'res5b_branch2a_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 64 'res5b_branch2b' Convolution 512 3×3×512 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [1 1 1 1] (HW Layer) 65 'bn5b_branch2b' Batch Normalization Batch normalization with 512 channels (HW Layer) 66 'res5b' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer) 67 'res5b_relu' ReLU ReLU (HW Layer) 68 'pool5' 2-D Global Average Pooling 2-D global average pooling (HW Layer) 69 'fc1000' Fully Connected 1000 fully connected layer (HW Layer) 70 'prob' Softmax softmax (HW Layer) 71 'ClassificationLayer_predictions' Classification Output crossentropyex with 'tench' and 999 other classes (SW Layer) ### Optimizing network: Fused 'nnet.cnn.layer.BatchNormalizationLayer' into 'nnet.cnn.layer.Convolution2DLayer' ### Notice: The layer 'data' of type 'ImageInputLayer' is split into an image input layer 'data', an addition layer 'data_norm_add', and a multiplication layer 'data_norm' for hardware normalization. ### Notice: The layer 'prob' with type 'nnet.cnn.layer.SoftmaxLayer' is implemented in software. ### Notice: The layer 'ClassificationLayer_predictions' with type 'nnet.cnn.layer.ClassificationOutputLayer' is implemented in software. ### Compiling layer group: conv1>>pool1 ... ### Compiling layer group: conv1>>pool1 ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res2a_branch2a>>res2a_branch2b ... ### Compiling layer group: res2a_branch2a>>res2a_branch2b ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res2b_branch2a>>res2b_branch2b ... ### Compiling layer group: res2b_branch2a>>res2b_branch2b ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res3a_branch1 ... ### Compiling layer group: res3a_branch1 ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res3a_branch2a>>res3a_branch2b ... ### Compiling layer group: res3a_branch2a>>res3a_branch2b ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res3b_branch2a>>res3b_branch2b ... ### Compiling layer group: res3b_branch2a>>res3b_branch2b ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res4a_branch1 ... ### Compiling layer group: res4a_branch1 ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res4a_branch2a>>res4a_branch2b ... ### Compiling layer group: res4a_branch2a>>res4a_branch2b ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res4b_branch2a>>res4b_branch2b ... ### Compiling layer group: res4b_branch2a>>res4b_branch2b ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res5a_branch1 ... ### Compiling layer group: res5a_branch1 ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res5a_branch2a>>res5a_branch2b ... ### Compiling layer group: res5a_branch2a>>res5a_branch2b ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: res5b_branch2a>>res5b_branch2b ... ### Compiling layer group: res5b_branch2a>>res5b_branch2b ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: pool5 ... ### Compiling layer group: pool5 ... complete. ### Compiling layer group: fc1000 ... ### Compiling layer group: fc1000 ... complete. ### Allocating external memory buffers: offset_name offset_address allocated_space _______________________ ______________ _________________ "InputDataOffset" "0x00000000" "24.0 MB" "OutputResultOffset" "0x01800000" "4.0 MB" "SchedulerDataOffset" "0x01c00000" "8.0 MB" "SystemBufferOffset" "0x02400000" "28.0 MB" "InstructionDataOffset" "0x04000000" "4.0 MB" "ConvWeightDataOffset" "0x04400000" "52.0 MB" "FCWeightDataOffset" "0x07800000" "4.0 MB" "EndOffset" "0x07c00000" "Total: 124.0 MB" ### Network compilation complete. ans = struct with fields: weights: [1×1 struct] instructions: [1×1 struct] registers: [1×1 struct] syncInstructions: [1×1 struct] constantData: {{1×2 cell} [0.0171 0.0175 0.0174 0 0.0171 0.0175 0.0174 0 0.0171 0.0175 0.0174 0 0.0171 0.0175 0.0174 0 … ]}During compilation the compiler splits the image input layer into an image input layer, addition layer, and multiplication layer for hardware implementation.
Reduce the time to train a sequence forecasting network by swapping out the LSTM later for a gated recurrent unit (GRU) layer. Use the deployed network to predict future values by using open-loop and closed-loop forecasting. Use MATLAB® to retrieve the prediction results from the target device.
Modified Waveform Data Network
The network attached to this example was trained using the Time Series Forecasting Using Deep Learning. In this example the LSTM layer was swapped out for a GRU layer. This example uses the WaveformData.mat data set, which contains 2000 synthetically generated waveforms of varying lengths with three channels. This example uses a trained network with a GRU layer to forecast future values of the waveforms given the values from the previous time steps using both closed loop and open loop forecasting.
Load the Pretrained Network
To load the GRU layer network enter:
load grunetUse the analyzeNetwork function to obtain information about the network layers. the function returns a graphical representation of the network that contains detailed parameter information for every layer in the network.
analyzeNetwork(net)

Define FPGA Board Interface
Define the target FPGA board programming interface by using the dlhdl.Target object. Specify that the interface is for a Xilinx board with an Ethernet interface.
To create the target object, enter:
hTarget_gru = dlhdl.Target('Xilinx',Interface='Ethernet');
To use the JTAG interface, install Xilinx™ Vivado™ Design Suite 2020.2. To set the Xilinx Vivado toolpath, enter:
hdlsetuptoolpath('ToolName', 'Xilinx Vivado', 'ToolPath', 'C:\Xilinx\Vivado\2020.2\bin\vivado.bat'); hTarget = dlhdl.Target('Xilinx',Interface='JTAG');
Prepare Network for Deployment
Prepare the network for deployment by creating a dlhdl.Workflow object. Specify the network and the bitstream name. Ensure that the bitstream name matches the data type and the FPGA board. In this example the target FPGA board is the Xilinx ZCU102 SOC board. The bitstream uses a single data type.
hW_gru = dlhdl.Workflow(Network=net,Bitstream='zcu102_lstm_single',Target=hTarget_gru);Tu run the example on the Xilinx ZC706 board, enter:
hW = dlhdl.Workflow(Network=net,Bitstream='zc706_lstm_single',Target=hTarget);
Compile the GRU Layer Network
Run the compile method of the dlhdl.Workflow object to compile the network and generate the instructions, weights, and biases for deployment. The total number of frames exceeds the default value of 30. Set the InputFrameNumberLimit name-value argument to 1000 to run predictions in chunks of 1000 frames to prevent timeouts.
dn = compile(hW_gru,'InputFrameNumberLimit',1000)### Compiling network for Deep Learning FPGA prototyping ...
### Targeting FPGA bitstream zcu102_lstm_single.
### The network includes the following layers:
1 'sequenceinput' Sequence Input Sequence input with 3 dimensions (SW Layer)
2 'gru' GRU GRU with 128 hidden units (HW Layer)
3 'fc' Fully Connected 3 fully connected layer (HW Layer)
4 'regressionoutput' Regression Output mean-squared-error with response 'Response' (SW Layer)
### Notice: The layer 'sequenceinput' with type 'nnet.cnn.layer.ImageInputLayer' is implemented in software.
### Notice: The layer 'regressionoutput' with type 'nnet.cnn.layer.RegressionOutputLayer' is implemented in software.
### Compiling layer group: gru.wh ...
### Compiling layer group: gru.wh ... complete.
### Compiling layer group: gru.rh ...
### Compiling layer group: gru.rh ... complete.
### Compiling layer group: gru.w1 ...
### Compiling layer group: gru.w1 ... complete.
### Compiling layer group: gru.w2 ...
### Compiling layer group: gru.w2 ... complete.
### Compiling layer group: fc ...
### Compiling layer group: fc ... complete.
### Allocating external memory buffers:
offset_name offset_address allocated_space
_______________________ ______________ _________________
"InputDataOffset" "0x00000000" "16.0 kB"
"OutputResultOffset" "0x00004000" "16.0 kB"
"SchedulerDataOffset" "0x00008000" "676.0 kB"
"SystemBufferOffset" "0x000b1000" "20.0 kB"
"InstructionDataOffset" "0x000b6000" "4.0 kB"
"FCWeightDataOffset" "0x000b7000" "204.0 kB"
"EndOffset" "0x000ea000" "Total: 936.0 kB"
### Network compilation complete.
dn = struct with fields:
weights: [1×1 struct]
instructions: [1×1 struct]
registers: [1×1 struct]
syncInstructions: [1×1 struct]
constantData: {{1×2 cell} [1×128 double]}
ddrInfo: [1×1 struct]
resourceTable: [6×2 table]
Program Bitstream onto FPGA and Download Network Weights
To deploy the network on the Xilinx ZCU102 SoC hardware, run the deploy function of the dlhdl.Workflow object. This function uses the output of the compile function to program the FPGA board by using the programming file. It also downloads the network weights and biases. The deploy function starts programming the FPGA device and displays progress messages, and the required time to deploy the network.
deploy(hW_gru)
### FPGA bitstream programming has been skipped as the same bitstream is already loaded on the target FPGA. ### Deep learning network programming has been skipped as the same network is already loaded on the target FPGA.
Test Network
Prepare the test data for prediction. Normalize the test data using the statistics calculated from the training data. Forecast the values using the GRU layer network. To forecast the values of future time steps of a sequence, specify the targets as the test sequences with values shifted by one time step. In other words, at each time step of the input sequence, the GRU layer network learns to predict the value of the next time step.
load WaveformData.mat data = cellfun(@(x)x',data,UniformOutput=false); numChannels = size(data{1},1); numObservations = numel(data); idxTrain = 1:floor(0.9*numObservations); idxTest = floor(0.9*numObservations)+1:numObservations; dataTrain = data(idxTrain); dataTest = data(idxTest); for n = 1:numel(dataTrain) X = dataTrain{n}; XTrain{n} = X(:,1:end-1); TTrain{n} = X(:,2:end); end muX = mean(cat(2,XTrain{:}),2); sigmaX = std(cat(2,XTrain{:}),0,2); muT = mean(cat(2,TTrain{:}),2); sigmaT = std(cat(2,TTrain{:}),0,2); for n = 1:size(dataTest,1) X = dataTest{n}; XTest{n} = (X(:,1:end-1) - muX) ./ sigmaX; TTest{n} = (X(:,2:end) - muT) ./ sigmaT; end
Make predictions using the test data.
YTest_gru = predict(hW_gru,XTest{1},Profile = 'on');### Resetting network state.
### Finished writing input activations.
### Running a sequence of length 115.
Deep Learning Processor Profiler Performance Results
LastFrameLatency(cycles) LastFrameLatency(seconds) FramesNum Total Latency Frames/s
------------- ------------- --------- --------- ---------
Network 26856 0.00012 115 3134945 8070.3
gru.wh 448 0.00000
gru.rh 7539 0.00003
memSeparator_0 95 0.00000
memSeparator_2 184 0.00000
gru.w1 7460 0.00003
gru.w2 7608 0.00003
gru.sigmoid_1 222 0.00000
gru.sigmoid_2 224 0.00000
gru.multiplication_2 308 0.00000
gru.multiplication_4 344 0.00000
gru.multiplication_1 294 0.00000
gru.addition_2 324 0.00000
gru.addition_1 294 0.00000
gru.tanh_1 238 0.00000
gru.multiplication_3 388 0.00000
gru.addition_3 298 0.00000
fc 420 0.00000
memSeparator_1 168 0.00000
* The clock frequency of the DL processor is: 220MHz
To evaluate the accuracy, calculate the root mean squared error (RMSE) between the predictions and the target for each test sequence.
for i = 1:size(YTest_gru,1) rmse(i) = sqrt(mean((YTest_gru(i) - TTest{1}(i)).^2,"all")); end
Visualize the errors in a histogram. Lower values indicate greater accuracy.
figure histogram(rmse) xlabel("RMSE") ylabel("Frequency")
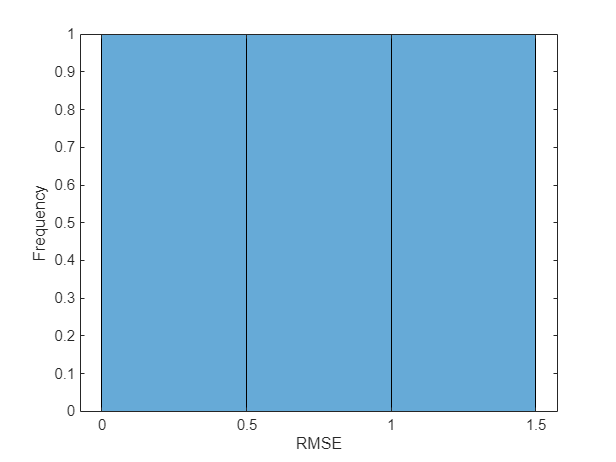
Calculate the mean RMSE over all test observations.
mean(rmse)
ans = single
0.7688
Forecast Future Time Steps
To forecast the values of multiple future time steps, when given an input time series or sequence, use the predictAndUpdateState function. This function predicts time steps one at a time and updates the network state at each prediction. For each prediction, use the previous prediction as the input to the function.
Visualize one of the test sequences in a plot.
idx = 2;
X_gru = XTest{idx};
T_gru = TTest{idx};
figure
stackedplot(X_gru',DisplayLabels="Channel " + (1:numChannels))
xlabel("Time Step")
title("Test Observation " + idx)
Open-Loop Forecasting
Open-loop forecasting predicts the next time step in a sequence using only the input data. When making predictions for subsequent time steps, you collect the true values form your data source and use those as input. For example, suppose that you want to predict the value for time step of a sequence by using data collected in time steps 1 through . To make predictions for time step , wait until you record the true value for time step and use that value as input to make the next prediction. Use open-loop forecasting when you have true values to provide to the network before making the next prediction.
Initialize the network state by resetting the state using the resetState function, then make an initial prediction using the first few time steps of the input data. Update the network state by using the first 75 time steps of the input data.
resetState(hW_gru)
offset = 75;
[~,~] = predict(hW_gru,X_gru(:,1:offset),KeepState=true,Profile='on'); ### Resetting network state.
### Finished writing input activations.
### Running a sequence of length 75.
Deep Learning Processor Profiler Performance Results
LastFrameLatency(cycles) LastFrameLatency(seconds) FramesNum Total Latency Frames/s
------------- ------------- --------- --------- ---------
Network 26867 0.00012 75 2044941 8068.7
gru.wh 438 0.00000
gru.rh 7528 0.00003
memSeparator_0 86 0.00000
memSeparator_2 184 0.00000
gru.w1 7540 0.00003
gru.w2 7629 0.00003
gru.sigmoid_1 222 0.00000
gru.sigmoid_2 224 0.00000
gru.multiplication_2 338 0.00000
gru.multiplication_4 294 0.00000
gru.multiplication_1 334 0.00000
gru.addition_2 294 0.00000
gru.addition_1 294 0.00000
gru.tanh_1 238 0.00000
gru.multiplication_3 288 0.00000
gru.addition_3 348 0.00000
fc 420 0.00000
memSeparator_1 168 0.00000
* The clock frequency of the DL processor is: 220MHz
To forecast further predictions, loop over time steps and update the network state by using the predict function and setting the KeepState name-value argument to true. Forecast values for the remaining time steps of the test observation by looping over the time steps of the input data and using them as input to the network. The first prediction is the value that corresponds to the time step offset + 1.
numTimeSteps = size(X_gru,2);
numPredictionTimeSteps = numTimeSteps - offset;
Y_gru = predict(hW_gru,X_gru(:,offset+1:offset+numPredictionTimeSteps),KeepState=true,Profile='on');### Finished writing input activations.
### Running a sequence of length 116.
Deep Learning Processor Profiler Performance Results
LastFrameLatency(cycles) LastFrameLatency(seconds) FramesNum Total Latency Frames/s
------------- ------------- --------- --------- ---------
Network 26738 0.00012 116 3161519 8072.1
gru.wh 448 0.00000
gru.rh 7569 0.00003
memSeparator_0 86 0.00000
memSeparator_2 184 0.00000
gru.w1 7570 0.00003
gru.w2 7499 0.00003
gru.sigmoid_1 222 0.00000
gru.sigmoid_2 224 0.00000
gru.multiplication_2 308 0.00000
gru.multiplication_4 294 0.00000
gru.multiplication_1 294 0.00000
gru.addition_2 294 0.00000
gru.addition_1 294 0.00000
gru.tanh_1 288 0.00000
gru.multiplication_3 288 0.00000
gru.addition_3 298 0.00000
fc 410 0.00000
memSeparator_1 168 0.00000
* The clock frequency of the DL processor is: 220MHz
Compare the predictions with the target values.
figure t = tiledlayout(numChannels,1); title(t,"Open Loop Forecasting with GRU layer") for i = 1:numChannels nexttile plot(T_gru(i,:)) hold on plot(offset:numTimeSteps,[T_gru(i,offset) Y_gru(i,:)],'--') ylabel("Channel " + i) end xlabel("Time Step") nexttile(1) legend(["Input" "Forecasted"])

Closed-Loop Forecasting
Closed-loop forecasting predicts subsequent time steps in a sequence by using the previous predictions as input. In this case, the model does not require the true values to make the prediction. For example, suppose that you want to predict the value for time steps through of the sequence by using data collected in time steps 1 through . To make predictions for time step , use the predicted value for time step as input. Use closed-loop forecasting to forecast multiple subsequent time steps or when you do not have true values to provide to the network before making the next prediction.
Initialize the network state by resetting the state using the resetState function, then make an initial prediction, Z, using the first few time steps of the input data. Update the network state by using the first 75 time steps of the input data.
resetState(hW_gru)
[Z, ~] = predict(hW_gru,X_gru,KeepState=true,Profile='on');### Resetting network state.
### Finished writing input activations.
### Running a sequence of length 191.
Deep Learning Processor Profiler Performance Results
LastFrameLatency(cycles) LastFrameLatency(seconds) FramesNum Total Latency Frames/s
------------- ------------- --------- --------- ---------
Network 26956 0.00012 191 5206622 8070.5
gru.wh 448 0.00000
gru.rh 7549 0.00003
memSeparator_0 96 0.00000
memSeparator_2 185 0.00000
gru.w1 7539 0.00003
gru.w2 7608 0.00003
gru.sigmoid_1 221 0.00000
gru.sigmoid_2 224 0.00000
gru.multiplication_2 308 0.00000
gru.multiplication_4 324 0.00000
gru.multiplication_1 324 0.00000
gru.addition_2 324 0.00000
gru.addition_1 344 0.00000
gru.tanh_1 228 0.00000
gru.multiplication_3 308 0.00000
gru.addition_3 298 0.00000
fc 460 0.00000
memSeparator_1 168 0.00000
* The clock frequency of the DL processor is: 220MHz
To forecast further predictions, loop over time steps and update the network state by using the predict function and setting the KeepState name-value argument to true. Forecast the next 200 time steps by iteratively passing the previously predicted value to the network. Because the network does not require the input data to make any further predictions, you can specify any number of time steps to forecast.
numPredictionTimeSteps = 200;
Xt_gru = Z(:,end);
Y_gru = zeros(numChannels,numPredictionTimeSteps);
fprintf("Run %d predictions:\n", numPredictionTimeSteps);Run 200 predictions:
for t = 1:numPredictionTimeSteps [Y_gru(:,t),~] = predict(hW_gru,Xt_gru,KeepState=true); Xt_gru = Y_gru(:,t); end
Visualize the forecasted values in a plot.
offset = size(X_gru,2); numTimeSteps = offset + numPredictionTimeSteps; figure t = tiledlayout(numChannels,1); title(t,"Closed Loop Forecasting with GRU layer") for i = 1:numChannels nexttile plot(T_gru(i,1:offset)) hold on plot(offset:numTimeSteps,[T_gru(i,offset) Y_gru(i,:)],'--') ylabel("Channel " + i) end xlabel("Time Step") nexttile(1) legend(["Input" "Forecasted"])

Closed-loop forecasting allows you to forecast an arbitrary number of time steps, but can be less accurate when compared to open-loop forecasting because the network does not have access to the true values during the forecasting process.
Compare Network Predictions
Compare the predictions of the LSTM layer network to the GRU layer network. This image shows the comparison between the GRU layer network and LSTM layer network for open loop forecasting. The GRU layer network has a performance of 8070.5 frames per second and the LSTM layer network has a performance of 6463.1 frames per second. To learn how to deploy the LSTM layer network to an FPGA, see Run Sequence Forecasting on FPGA by Using Deep Learning HDL Toolbox.

This image shows the comparison between the GRU layer network and LSTM layer network for closed loop forecasting.

Version History
Introduced in R2020b
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)