mil188qamdemod
MIL-STD-188-110 B/C standard-specific quadrature amplitude demodulation
Description
Z = mil188qamdemod(Y,M)Y, that was modulated in
accordance with MIL-STD-188-110 and the modulation order M. For
a description of MIL-STD-188-110 QAM demodulation, see MIL-STD-188-110 QAM Hard Demodulation and MIL-STD-188-110 QAM Soft Demodulation.
Z = mil188qamdemod(Y,M,Name=Value)mil188qamdemod(Y,M,PlotConstellation=true) specifies
modulation order M and plots the constellation. Specify
name-value arguments after all other input arguments.
Examples
Demodulate a 16-QAM signal that was modulated as specified in MIL-STD-188-110B. Plot the received constellation and verify that the output matches the input.
Set the modulation order and generate random data.
M = 16; numSym = 20000; x = randi([0 M-1],numSym,1);
Modulate the data and pass through a noisy channel.
txSig = mil188qammod(x,M);
rxSig = awgn(txSig,25,'measured');Plot the transmitted and received signal.
plot(rxSig,'b*') hold on; grid plot(txSig,'r*') xlim([-1.5 1.5]); ylim([-1.5 1.5]) xlabel('In-Phase') ylabel('Quadrature') legend('Received constellation','Reference constellation')
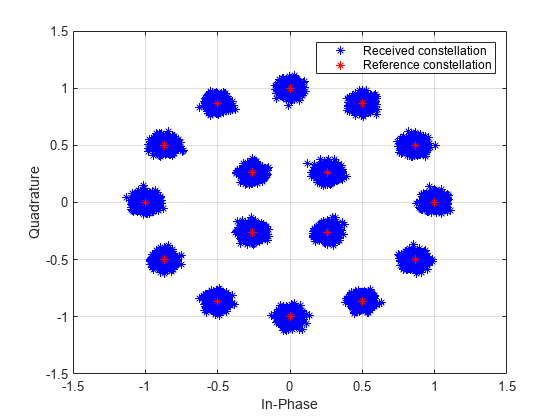
Demodulate the received signal. Compare the demodulated data to the original data.
z = mil188qamdemod(rxSig,M); isequal(x,z)
ans = logical
1
Demodulate a 64-QAM signal that was modulated as specified in MIL-STD-188-110C. Compute hard decision bit output and verify that the output matches the input.
Set the modulation order and generate random bit data.
M = 64; numBitsPerSym = log2(M); x = randi([0 1],1000*numBitsPerSym,1);
Modulate the data. Use name-value pairs to specify bit input data and to plot the constellation.
txSig = mil188qammod(x,M,InputType='bit',PlotConstellation=true);
Demodulate the received signal. Compare the demodulated data to the original data.
z = mil188qamdemod(txSig,M,OutputType='bit');
isequal(z,x)ans = logical
1
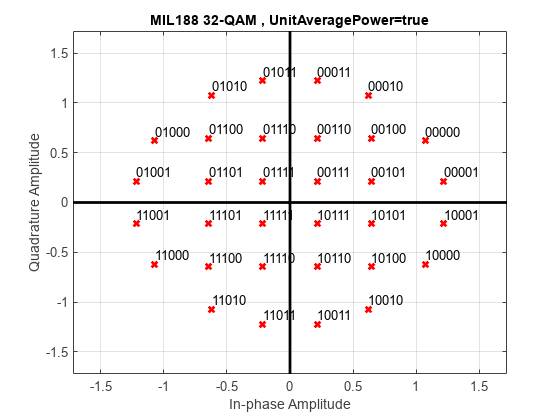
Demodulate a 32-QAM signal and calculate soft bits.
Set the modulation order and generate a random bit sequence.
M = 32; numSym = 20000; numBitsPerSym = log2(M); x = randi([0 1], numSym*numBitsPerSym,1);
Modulate the data. Use name-value pairs to specify bit input data and unit average power, and to plot the constellation.
txSig = mil188qammod(x,M,InputType='bit',UnitAveragePower=true, ... PlotConstellation=true);
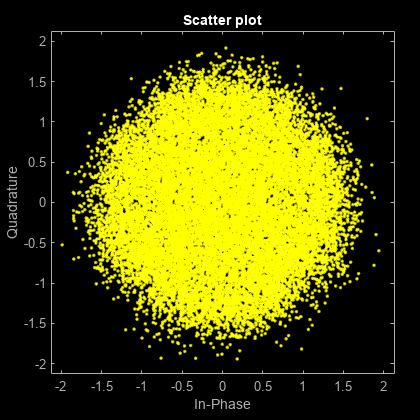
Pass the transmitted data through white Gaussian noise.
rxSig = awgn(txSig,10,'measured');View the constellation using a scatter plot.
scatterplot(rxSig)
Demodulate the signal, computing soft bits using the approximate LLR algorithm.
z = mil188qamdemod(rxSig,M,OutputType='approxllr', ... NoiseVariance=10^(-1));
Input Arguments
Modulated signal, specified as a complex scalar, vector, or matrix. When
Y is a matrix, each column is treated as an
independent channel.
Y must be modulated in accordance with
MIL-STD-188-110 [1].
Data Types: single | double
Complex Number Support: Yes
Modulation order, specified as a positive integer power of two. The modulation order specifies the total number of points in the signal constellation.
Example: 16
Data Types: double
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Example: Z =
mil188qamdemod(Y,M,OutputType='bit',OutputDataType='single');
Output type, specified as 'integer',
'bit', 'llr', or
'approxllr'. For a description of returned
output, see Z.
Data type of the output, specified as one of the data types listed in
this table. Acceptable values for OutputDataType
depend on the OutputType value.
OutputType
Value | Acceptable
OutputDataType Values |
|---|---|
'integer' | 'double',
'single',
'int8',
'int16',
'int32',
'uint8',
'uint16', or
'uint32' |
'bit' | 'double',
'single',
'int8',
'int16',
'int32',
'uint8',
'uint16',
'uint32', or
'logical' |
The default value is the data type of input Y.
Dependencies
To enable this argument, set OutputType to
either 'integer' or 'bit'.
Otherwise, the output data type matches the data type of input
Y.
Unit average power flag, specified as logical 0
(false) or 1
(true).
When
UnitAveragePoweristrue, the function scales the constellation to an average power of 1 watt referenced to 1 ohm.When
UnitAveragePowerisfalse, the function scales the constellation based on specifications in the relevant standard, as described in [1].
Data Types: logical
Noise variance, specified as one of these options:
Positive scalar — The function uses the same noise variance value on all input elements.
Vector of positive values — For all the elements of the input along the corresponding last dimension, the function uses the noise variance specified by each element of the vector. The vector length must be equal to the number of columns in the input signal.
When the noise variance or signal power result in computations involving extreme positive or negative magnitudes, see MIL-STD-188-110 QAM Soft Demodulation for algorithm selection considerations.
Dependencies
This name-value pair argument applies only when OutputType is set to 'llr' or
'approxllr'.
Data Types: double
Option to plot constellation, specified as logical
0 (false) or
1 (true). To plot the
constellation, set PlotConstellation to
true.
Data Types: logical
Output Arguments
Demodulated signal, returned as a scalar, vector, or matrix. The value and
dimension of this output vary depending on the specified OutputType value, as shown in this table.
OutputType
Value | Return Value of
mil188qamdemod | Dimensions of Z |
|---|---|---|
'integer' | Demodulated integer values from 0 to
(M – 1) | Z has the same dimensions as input
Y. |
'bit' | Demodulated bits | The number of rows in Z
is log2(sum(M)) times the number of rows in
Y. Each demodulated symbol is mapped
to a group of log2(sum(M)) elements in a column, where the first
element represents the MSB and the last element represents
the LSB. |
'llr' | Log-likelihood ratio value for each bit | |
'approxllr' | Approximate log-likelihood ratio value for each bit |
Algorithms
The hard demodulation algorithm uses optimum decision region-based demodulation. Since all the constellation points are equally probable, maximum a posteriori probability (MAP) detection reduces to a maximum likelihood (ML) detection. The ML detection rule is equivalent to choosing the closest constellation point to the received symbol. The decision region for each constellation point is designed by drawing perpendicular bisectors between adjacent points. A received symbol is mapped to the proper constellation point based on which decision region it lies in.
Since all MIL-STD constellations are quadrant-based symmetric, for each symbol the optimum decision region-based demodulation:
Maps the received symbol into the first quadrant
Chooses the decision region for the symbol
Maps the constellation point back to its original quadrant using the sign of real and imaginary parts of the received symbol
For soft demodulation, two soft-decision log-likelihood ratio (LLR) algorithms are available: exact LLR and approximate LLR. The exact LLR algorithm is more accurate but has slower execution speed than the approximate LLR algorithm. For further description of these algorithms, see the Hard- vs. Soft-Decision Demodulation topic.
Note
The exact LLR algorithm computes exponentials using finite precision arithmetic. For computations involving very large positive or negative magnitudes, the exact LLR algorithm yields:
Infor-Infif the noise variance is a very large valueNaNif the noise variance and signal power are both very small values
The approximate LLR algorithm does not compute exponentials. You can avoid
Inf, -Inf, and NaN results by using
the approximate LLR algorithm.
References
[1] MIL-STD-188-110B & C: "Interoperability and Performance Standards for Data Modems." Department of Defense Interface Standard, USA.
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
Version History
Introduced in R2018a
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)