ocr
Recognize text using optical character recognition
Description
[___] = ocr(___,
specifies options using one or more name-value arguments in addition to any combination of
arguments from previous syntaxes. For example, Name=Value)LayoutAnalysis="page"
treats the image as a page containing blocks of text.
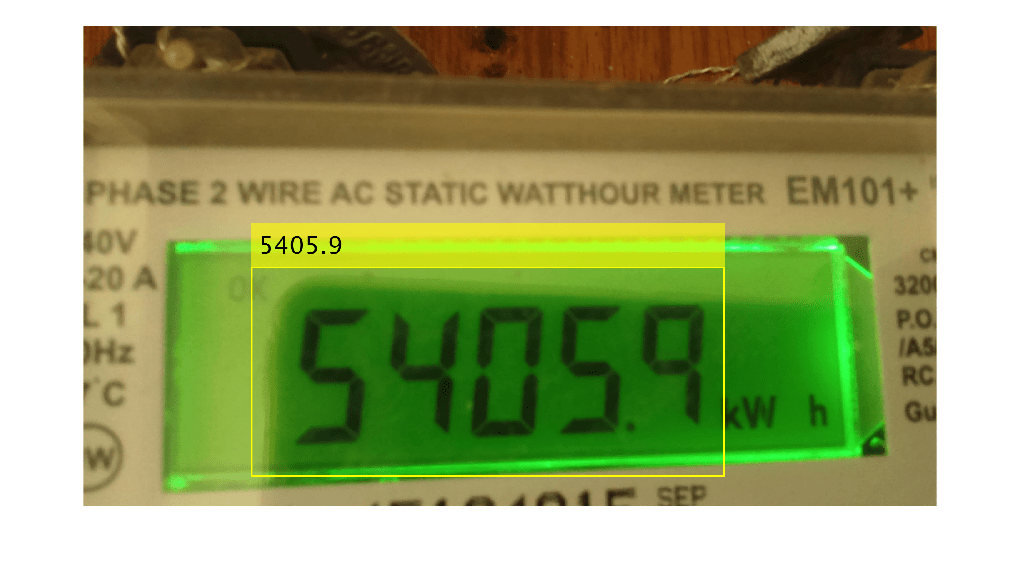
Examples
Input Arguments
Name-Value Arguments
Output Arguments
Tips
If your OCR results are not what you expect, try one or more of these options:
Increase the image size by 2– 4 times.
If the characters in the image are too close together or their edges are touching, use morphology to thin out the characters. Using morphology to thin out the characters helps create space between them.
Use binarization to check for non-uniform lighting issues. Use the
graythreshandimbinarizefunctions to binarize the image. If the characters are not visible in the results of the binarization, then the image has a potential non-uniform lighting issue. Try top-hat filtering, using theimtophatfunction, or other techniques that deal with removing non-uniform illumination.Use the
roiargument to isolate the text. You can specify theroimanually or use text detection.If your image looks like a natural scene containing words, such as a street scene, rather than a scanned document, try setting the
LayoutAnalysisargument to either"Block"or"Word".Ensure that the image contains dark text on a light background. To achieve this, you can binarize the image and invert it before passing it to the
ocrfunction.
References
[1] Smith, Ray. An Overview of the Tesseract OCR Engine. In Ninth International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR 2007), 629–33. IEEE, 2007. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDAR.2007.4376991."
[2] Smith, R., D. Antonova, and D. Lee. Adapting the Tesseract Open Source OCR Engine for Multilingual OCR. Proceedings of the International Workshop on Multilingual OCR, (2009).
[3] R. Smith. Hybrid Page Layout Analysis via Tab-Stop Detection. Proceedings of the 10th international conference on document analysis and recognition. 2009.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2014aSee Also
Apps
Functions
Objects
Topics
- Getting Started with OCR
- Segment and Read Text in Image
- Recognize Text Using Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
- Train an OCR Model to Recognize Seven-Segment Digits
- Recognize Seven-Segment Digits Using OCR
- Automate Ground Truth Labeling for OCR
- Install OCR Language Data Files
- Install Computer Vision Toolbox Add-on Support Files