Signal Editor
Create and edit input signals
Description
The Signal Editor tool lets you create and edit input signals that you can organize for multiple simulations.
Mouse, Keyboard, and Touchscreen Shortcuts
You can use these keyboard shortcuts to interact with the Signal Editor.
This table shows edit actions:
| Action | Keyboard | Mouse | Multi-Touch |
|---|---|---|---|
Insert point | Ctrl+P | Click | Tap |
Insert line | Ctrl+L | Click | Pan and pinch |
Draw | Ctrl+D | Click and draw | Pan |
Select a point | Ctrl+T | Click To select all areas, double-click | Pan and pinch To select all areas, double-tap |
Move a point | Ctrl+M | Click | Tap and move |
| Continuously delete points on a line | Click | ||
| Fit to view if zoom action is selected | Spacebar | Triple tap | |
| Fit to view when signal table is updated | Spacebar | ||
| Zoom out | Ctrl+- | Two mouse clicks, if zoom action is selected | Double tap |
| Expand along the x-axis | Ctrl+mouse pan | Touch and drag along the x-axis in opposite directions | |
| Expand along the y-axis | Shift+mouse pan | Touch and drag along the y-axis in opposite directions |
This table shows zoom actions:
| Type of Zoom or Pan | Action |
|---|---|
Zoom in along the T and Y axes. | Click |
Zoom in along the time axis. After selecting the icon, on the graph, drag the mouse to select an area to enlarge. | Click |
Zoom in along the data value axis. After selecting the icon, on the graph, drag the mouse to select an area to enlarge. | Click |
Zoom only in x while zooming in xy. | Zoom in xy while pressing Ctrl |
Zoom only in y while zooming in xy. | Zoom in xy while pressing Shift |
Zoom out from the graph. | Click |
Fit the plot to the graph. After selecting the icon, click the graph to enlarge the plot to fill the graph. | Click |
Pan the graph up, down, left, or right. Select the icon. On the graph, hold the left mouse button and move the mouse to the area of the graph that you want to view. | Click |
Snap to Grid for Alignment
You can use these alignment commands to snap to the plot grid for accuracy.
Alignment actions:
| Action | Snap to Grid |
|---|---|
Snap values to x grid lines for point and line insertion and movement and zooming. | Snap X to Grid |
Snap values to y grid lines for point and line insertion and movement and zooming. | Snap Y to Grid |
Snap values to x minor grid lines for point and line insertion and movement and zooming. | Snap X to Tick |
Snap values to y grid lines for point and line insertion and movement and zooming. | Snap Y to Tick |
Snap to incremental value in X grid. | Snap X to Increment |
Snap to incremental value in Y grid. | Snap Y to Increment |
Turn plot markers on and off. | Markers |
Open the Signal Editor
MATLAB® Command Window: Enter
signalEditor.Root Inport Mapper: To create a MAT-file for your new signal data, select Signals > New MAT-File. To link in an existing signal data file from an existing scenario and edit the signals in that file, use the Signals > Edit MAT-File.
Signal Editor block: Click
 .
.Simulink® Editor toolstrip:
In the Prepare section of the Simulation tab, click the expander.
Click Inputs & Parameter Tuning > Signal Editor.
Signals can be:
MATLAB
timeseriesobjects.timeseriesobjects cannot have emptyDataproperties.timetableobjects.timetableobjects cannot represent multiple variables.Structure of MATLAB
timeseriesortimetableobjects.Two-dimensional matrices.
Examples
In the Inputs pane, you can change signal names and hierarchy order, create duplicates of signals, and delete signals. The software ignores leading and trailing spaces in signal names.
To change a signal name, double-click the name and enter a new name.

To change the unit or interpolation of a signal, in the Inputs pane, select the signal you want to edit, then navigate to the Input Properties pane, and update the Unit or Interpolation value.

To change the order of a signal in the hierarchy, drag and release the signal. For example, you can drag and release signals into a bus.

Alternatively, in the Adjust section, use the Move Up and Move Down buttons.
To copy a signal and paste it under the original, right-click the signal and select Duplicate Signal.

Alternatively, in the Adjust section, use the Duplicate button. You can also adjust the default properties of the signal you duplicate. For more information, see Create Signals with the Same Properties.
To copy a signal and paste it elsewhere in hierarchy, select Copy and then Paste.
To create signals of the same predefined type, in the
Adjust section, use the Duplicate button. To
change the predefined signal type, click the Defaults icon
![]() . The Properties for Insertion dialog box opens.
. The Properties for Insertion dialog box opens.
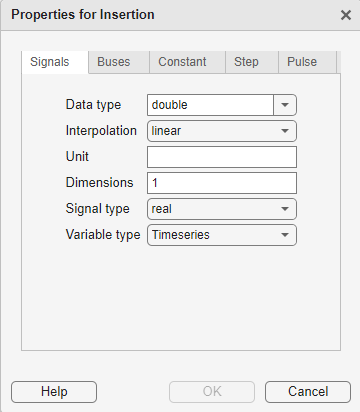
On the Signals tab:
Data type — From the list, select the signal data type.
Enumeration — When you select the
Enumdata type, this parameter displays. Enter the class name of your enumeration.If you define an enumeration class that contains the same integer value multiple times, the Signal Editor treats the first enumeration value as the canonical value and equates all subsequent instances of the same underlying integer to the enumerated name. In this example,
Red(118)) is canonical, soPinkequalsRed.classdef(Enumeration) hEnumColors_duplicateValues < Simulink.IntEnumType enumeration Red(118) Yellow(-14) Blue(90) Green(87) White(-14) Black(198) Brown(90) Pink(118) Purple(90) end methods (Static = true) function retVal = getDefaultValue() retVal = hEnumColors_duplicateValues.Blue; end end endInterpolation — From the list,select
linearorzero order hold.Unit — Enter an appropriate unit expression. For a suggested list of unit expressions, see Allowed Units.
Dimensions — Enter the number of dimensions for the signal.
Signal type — From the list, select
realorcomplex.Variable type — From the list, select
Timeseries(default),Timetable,Logged timeseries, orLogged timetable.Logged
timeseriesand loggedtimetablesobjects areSimulink.SimulationData.Signalobjects whoseValueproperty is of data typetimeseriesortimetable.
On the Buses tab:
Bus object — From the list, select the bus object for which to define the dimensions. If you leave the Bus object parameter as the default
<object name>, the Signal Editor adds empty buses.Dimensions — Enter the number of dimensions for the bus object.
On the Constant tab:
Value — Enter constant value to output.
Time — Enter sample time.
On the Step tab:
Initial value — Enter output value before step.
Final value — Enter output value after step.
Start time — Enter time when step starts.
Step time — Enter time increment when step occurs.
Step final time — Enter final step time.
On the Pulse tab:
Initial value — Enter initial default value of signal.
Value at trigger — Enter value of signal at pulse trigger.
Pulse duration — Enter length of time of pulse.
Step time — Enter time when step occurs.
Trigger time — Enter time when pulse trigger occurs.
In the Inputs section, you can select multiple scenarios or signals simultaneously and perform actions on them.
Start Signal Editor.
In the toolstrip, add two scenarios. Click Scenario twice.
To the first Scenario, add a basic signal and step. In
Insert, click Signal and
Step.
By default, basic signals are created with linear interpolation while step signals are created with zero-order hold (ZOH) interpolation.
Change the interpolation of both signals to linear. In the
Inputs pane, select both Signal and
Step. Observe that in the Input Properties
pane, the Interpolation field now shows <mixed
values>.
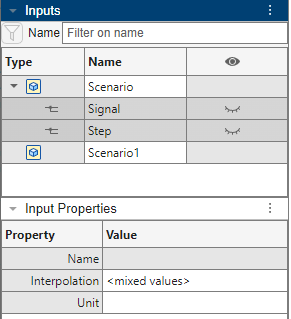
In the Interpolation field, type linear.
Individually select Signal and Step and observe
that they now both have linear interpolation.
Add the same signal types to both scenarios. In the Inputs
pane, select Scenario and Scenario1. Then in the
Insert pane, click Function Call.

Exchange rows and columns of data between Signal Editor and Excel® spreadsheets using cut, copy, and paste operations.
If you do not have an existing Excel spreadsheet, create an Excel spreadsheet and data.
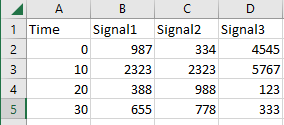
Select and copy two adjacent items, such as A5 and
B5.
In Signal Editor, create a signal and double-click the hide icon (![]() ).
).
In the signal pane, select two adjacent cells.

Paste the contents from the spreadsheet to the Signal Editor data table.
Tip
You can cut, copy, and paste directly into a spreadsheet or Signal Editor data table. However, if you cut, copy, and paste to a selected target area, the selected target area must be the same size as the source area.

In the Signal Editor tab, create signal data from the standard waveform options.
Constant — Straight line waveform with a default value of 1.

Step — Step waveform with default initial value of
0and final value of5.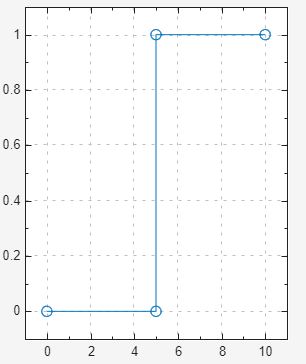
Pulse — Pulse waveform with default initial value of
0, pulse at trigger5, and pulse duration of 1.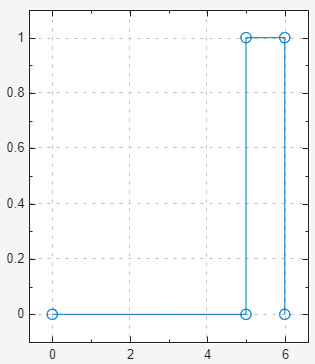
To change the data from these waveforms, you can manually modify them in the plot. If you want to create multiple waveform plots with the same set of initial data, you can change the default signal properties for the waveform.
Start Signal Editor.
In the toolstrip, click Scenario.
To add a pulse waveform to the scenario, select the scenario and from the Insert section, select Pulse.
In the signal hierarchy, double-click the hide icon (![]() ).
).
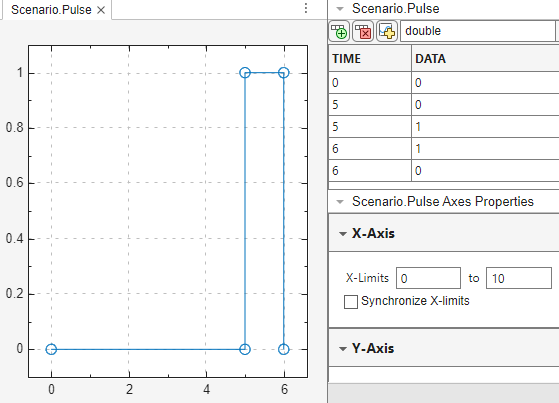
To change the default of the pulse waveform and its data, in the toolstrip, click
Defaults (![]() ).
).
In the Properties for Insertion dialog box, on the Pulse tab, change the values as desired.

To add a second pulse waveform to the scenario, select the scenario, and from the Insert section, click Pulse.

You can add and delete data to the signals in a linked scenario. To create a model to work with, see Add Signals to Scenarios.
In the MATLAB Command Window, create data by entering this command:
ts = timeseries([0;20],[0;10]);
Add a scenario. Click Scenario.
In the Signal Editor, in the File section, click Import.
In the Import window, in the Select signals to import pane,
select the ts signal and click OK.
Drag the ts signal into the scenario.
In the Signal Editor, in the Inputs pane, double-click the hide
icon (![]() ) for the signal
) for the signal ts.
The focus moves to the Edit tab.
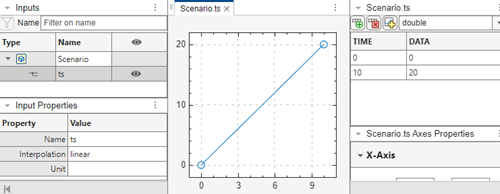
Add data to the signal ts.
In the Scenario.ts pane, click the add row icon (
 ), and add signals. To add a signal row between
other signals, click the signal above, then click the add row icon.
), and add signals. To add a signal row between
other signals, click the signal above, then click the add row icon. When done, click anywhere in the pane to update the plot. To reorient the plot, click Fit to View.

Remove the time 20 line from the signal. Select 20 and click ![]() .
.
Alternatively, if you want to replace all the signal data for ts
with a signal defined with signal notations, click the replace button
![]() and use the Author and Replace Signal Data dialog box
to define new data.
and use the Author and Replace Signal Data dialog box
to define new data.
You can move one signal point, two signal points, or an entire plot in Signal Editor. Create a plot to work with, for example, see Create Freehand Signal Data Using Mouse or Multi-Touch Gestures.
Click the Select
![]() button. This action persists until you select another
action.
button. This action persists until you select another
action.
Click a point. The move icon ![]() appears on top of the point.
appears on top of the point.
Drag the point to another area of the plot.
Tip
You cannot drag the point horizontally past adjacent points.
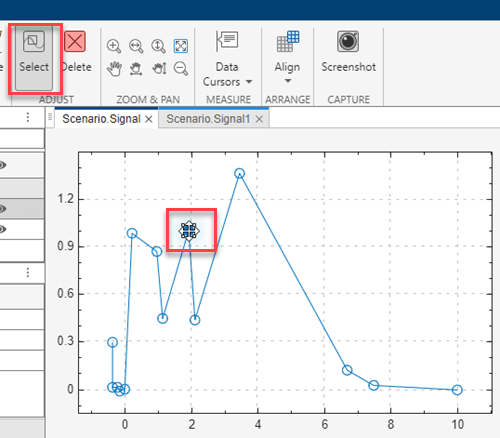
To move two contiguous signal points, click one point.
Click a point.
Click anywhere on the line between the two contiguous points.
Drag to the other point on the same line.
The move icon ![]() appears on top of the points.
appears on top of the points.
Drag the points to another area of the plot.
Tip
You cannot drag the point horizontally past adjacent points.

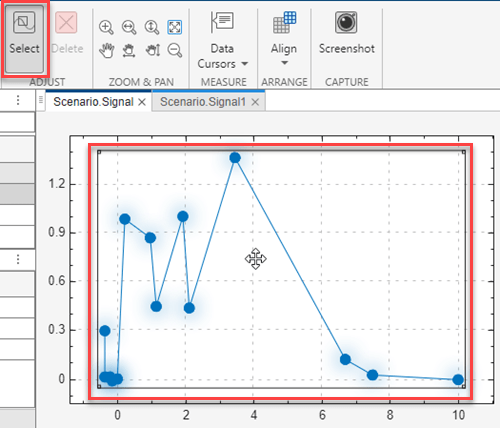
To move an entire plot, select the entire plot. Alternatively, double-click anywhere on the plot.
The move icon ![]() appears on top of the plot.
appears on top of the plot.
Drag the plot to another area of the canvas.
Related Examples
Parameters
File
Open a new Signal Editor session.
Open MAT-file containing signals to be displayed and edited in Signal Editor.
Save the contents of Signal Editor. Clicking this button also makes the signal data visible to the Signal Editor block.
Import signals from registered file types that Signal Editor supports. For more information, see Import Custom File Type.
Save signals to registered file types that Signal Editor supports. For more information, see Export Signals to Custom Registered File Types.
Scenario
Create scenario to contain signals.
Insert
Change the predefined signal type and properties by clicking
![]() .
.
Insert basic signal by clicking ![]() . For more information, see Work with Basic Signal Data.
. For more information, see Work with Basic Signal Data.
Insert function-call signal by clicking ![]() .
.
If you need a function-call signal for a root inport with explicit periodic sample time, insert a ground signal instead. Simulink then executes the function-call automatically.
Insert constant signal with value of 1 by clicking ![]() .
.
Insert bus by clicking ![]() . To the bus you can add signals using any of the other
signal insertions techniques.
. To the bus you can add signals using any of the other
signal insertions techniques.
Author signal using MATLAB expressions or workspace variables by clicking ![]() . The dialog box displays:
. The dialog box displays:

Time — Enter the range of time for the data.
Data — Enter the MATLAB expression for the signal.
Data type — Select or enter the signal data type.
doublesingleint8uint8int16uin16int32uint32booleanfixdt(1,16)fixdt(1,16,0)fixdt(1,16,2^0,0)stringEnum: <class name>
If you enter your time and data and then select a fixed-point data type, the Signal Editor displays a fixed-point proposed data type for your data.
To help you select a fixed-point data type, click the Show Histogram button (
 ). Clicking this button displays a plot of the
signal data using the selected fixed-point data type. The graph displays:
). Clicking this button displays a plot of the
signal data using the selected fixed-point data type. The graph displays:Column Information Values The negative, positive, and zero signal values. Potential Overflows Bins the signal values that may overflow. In-Range Bins the signal values that are within acceptable range. Potential Underflows Bins the signal values that may underflow. To see the difference that a data type may have on the histogram, select:
User Specified
Binary Scaling
Slope & Bias Scaling
For more information, see Histogram Plot of Signal (Fixed-Point Designer).
To apply the proposed fixed-point data type to your data, click the Use proposed data type button (
 ).
).
For more information, see Create Signals with MATLAB Expressions and Variables.
Insert step waveform signal with an initial value of 0 and a
final value of 1 by clicking ![]() .
.
Insert ground signal by clicking ![]() .
.
Insert pulse signal waveform signal with an initial value of 0,
trigger value of 1, and initial pulse duration of
1 by clicking ![]() .
.
Adjust
Copy signal and paste it under original signal.
Move signal up the signal hierarchy in a bus or scenario by clicking the signal and then clicking Move Up.
Move signal down the signal hierarchy in a bus or scenario by clicking the signal and then clicking Move Down.
Delete signal by selecting one or more signals and clicking ![]() .
.
Programmatic Use
signalEditor opens the Signal Editor from the MATLAB Command Window.
Tip
Load the model first with load
signalEditor(Model= opens the
Signal Editor for the model, 'modelName');'modelName'. You can specify one model per
call to the signalEditor function.
Note
Load the model before starting the Signal Editor for the model.
signalEditor(___,DataSource=
opens the Signal Editor for the data source, 'dataSourceName');'dataSourceName'. You can
specify one data set file per call to the signalEditor function.
Note
You can start multiple sessions of Signal Editor for the same model. However, you can associate a data set file with only one Signal Editor at a time. A data set file cannot have multiple Signal Editor sessions associated with it.
signalEditor(___,InitialScenario=
opens the Signal Editor with the signals from 'scenario_name');'scenario_name' already
plotted.
Version History
Introduced in R2017bThe Signal Editor tool has these updates:
Replace a signal with a waveform — In the Inputs hierarchy pane, right-click on the signal you want to replace, select
Replace the signal withfrom the context menu, and select one of these waveforms.ConstantStepPulseMATLAB expression, which starts the Author and Replace Signal Data dialog box.
Copy and paste signal names, properties, and data
To copy all signal information, including name, properties and data, in the Inputs hierarchy pane, right-click on the signal you want to replace and select
Copy. Then paste in another area of the Inputs hierarchy pane. In the hierarchy pane, you can paste to the same scenario, a different scenario, or outside a scenario.To copy signal data and time only, in the signal pane, copy the signal and data from the table and paste it into another row and/or column of the signal pane. The size of the pasted data and signal must match the size of the copied signal and data.
To replace all signal data with the contents of the clipboard, copy signal data from another source, such as a Microsoft® Excel spreadsheet or another Signal Editor signal data table, and then in the signal pane, right-click and select Replace signal data with > Clipboard data. Note:
Signal data table and clipboard data table must have the same number of columns.
The first column of the clipboard data table must be monotonically increasing.
The data type of the existing signal data must be able to cast to the clipboard data.
Update a signal in the signal pane. If the signal value is outside the plot area, apply Fit to view to the plot associated with the signal in the signal pane without leaving the signal pane. To apply Fit to view to the associated plot from the signal pane, in the signal pane press Spacebar.
The signal data table now accepts hexadecimal (0x) and binary (0b) data formats. To see the data in hexadecimal or binary, the Display Format parameter now lets you set the display format for floating-point and fixed-point data to binary or hexadecimal.
The Signal Editor tool has these updates:
Set up and preserve the display format for the scenario data table that contains the TIME and DATA columns using the Display Format parameter. The Signal Editor tool remembers up to five signal data settings. The Display Format parameter sets the display format for time and for floating-point and fixed-point data. For more information, see Change Signal Data Output Format Settings.
To programmatically open the Signal Editor tool with the active scenario signals already plotted, use the new
signalEditorfunctionInitialScenarioargument with an existing scenario.When you click Browse in the Export dialog box, the Save as type parameter now provides a list of supported file extensions to which to export the file.
When you start the Signal Editor interface separately from the block, you can now provide the model parameter to access variables from the MAT-file attached to the model. Prior to R2024b, you could provide the model parameter to access variables from only the model workspace or data dictionary.
The Signal Editor tool has these updates:
Move signals in Signal Editor — See Move Signal Points in Signal Editor.
Change x- and y-axes limits — See Change x- and y-axes Limits.
Synchronize signals by time — See Add and Edit Multidimensional Signals.
Signal and associated table data selection now linked — See Add and Edit Multidimensional Signals.
See Also
Blocks
Live Editor Tasks
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)