사용자 지정 컴포넌트 및 라이브러리 생성
사용자 지정 컴포넌트 및 라이브러리 생성을 보여주는 예제를 살펴보십시오.
관련 정보
추천 예제
차량 공조 시스템(HVAC)
이 예제는 차량의 HVAC 시스템(난방, 환기, 냉방)의 습윤 공기 흐름을 모델링합니다. 차량 실내(cabin)는 외부 환경과 열을 교환하는 습윤 공기의 부피로 표현됩니다. 습윤 공기는 재순환 플랩, 송풍기, 증발기, 블렌드 도어, 히터를 통과한 후 실내로 돌려보내집니다. 재순환 플랩은 실내로부터 유입하는 흐름이나 외부 환경에서 유입하는 흐름을 선택합니다. 블렌드 도어는 히터 주위 흐름을 유도하여 온도를 제어합니다.
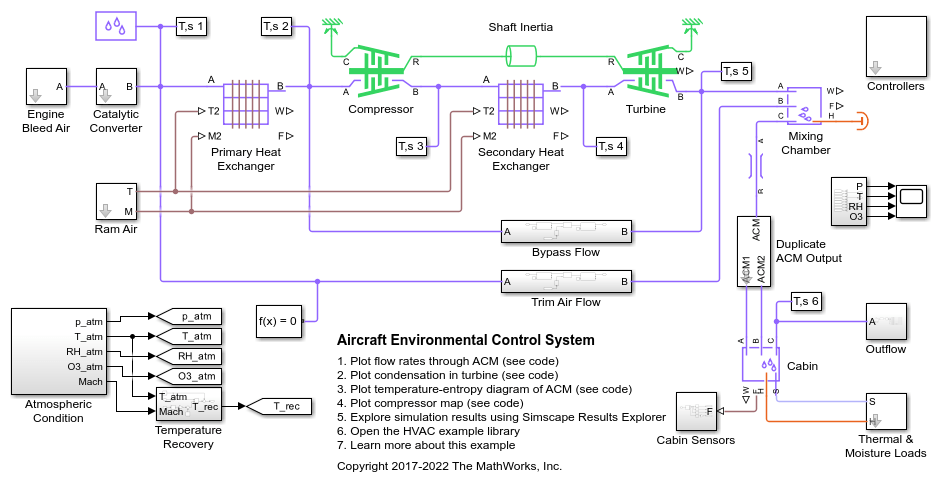
Aircraft Environmental Control System
Models an aircraft environmental control system (ECS) that regulates pressure, temperature, humidity, and ozone (O3) to maintain a comfortable and safe cabin environment. Cooling and dehumidification are provided by the air cycle machine (ACM), which operates as an inverse Brayton cycle to remove heat from pressurized hot engine bleed air. Some hot bleed air is mixed directly with the output of the ACM to adjust the temperature. Pressurization is maintained by the outflow valve in the cabin. This model simulates the ECS operating from a hot ground condition to a cold cruise condition and back to a cold ground condition.
PEM 연료전지 시스템
이 예제는 사용자 지정 Simscape™ 블록으로 PEM(양성자 교환막) 연료전지 스택을 모델링하는 방법을 보여줍니다. PEM 연료전지는 수소와 산소를 소비하고 수증기를 형성하면서 전력을 생성합니다. 이 사용자 지정 블록은 MEA(막전극접합체)를 나타내며, 산화전극 기체 유동과 환원전극 기체 유동을 나타내는 두 개의 습윤 공기 네트워크와 연결되어 있습니다.
PEM 전기분해 시스템
이 예제는 사용자 지정 Simscape™ 블록으로 PEM(양성자 교환막) 물 전해조를 모델링하는 방법을 보여줍니다. PEM 전해조는 전력을 사용하여 물을 수소와 산소로 분리합니다. 이 사용자 지정 블록은 MEA(막전극접합체)를 나타내며, 열 유체 네트워크와 두 개의 습윤 공기 네트워크에 연결됩니다. 여기서 열 유체 네트워크는 물 공급을 모델링하고, 애노드 습윤 공기 네트워크는 산소 흐름을 모델링하며, 캐소드 습윤 공기 네트워크는 수소 흐름을 모델링합니다.
Ultracapacitor Energy Storage with Custom Component
Use the Simscape™ example library Capacitors_lib. The model is constructed using components from the example library. The circuit charges an ultracapacitor from a constant 0.05 amp current source, and then delivers a pulse of current to a load. The ultracapacitor enables a much higher current to be delivered than is possible directly from the current source. The library contains capacitor models with different levels of fidelity to allow exploration of the effect of losses and nonlinearity.
송전선로
이 예제에서는 집중(lumped) 파라미터 송전선로 모델을 보여줍니다. 이 모델은 단일 T-섹션 세그먼트를 정의하는 사용자 지정 Simscape™ 컴포넌트로 설계되었습니다. 이 모델은 각 길이가 0.1m인 50개의 세그먼트를 결합하여 5m 길이의 동축 케이블을 모델링합니다. 시뮬레이션 결과에서 송신 지연을 관찰할 수 있습니다.
엔진 냉각 시스템
이 예제에서는 사용자 지정 열 유체 블록을 사용하여 기본 엔진 냉각 시스템을 모델링하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 정용량형 펌프는 냉각 회로를 통해 물을 순환시킵니다. 엔진의 열은 냉각수에 흡수되어 라디에이터를 통해 방출됩니다. 시스템 온도는 임계값을 초과하는 경우에만 라디에이터로 흐름을 전환하는 온도 조절 장치에 의해 조절됩니다.
사용자 지정 컴포넌트가 있는 브레이턴 사이클(가스 터빈)
이 예제에서는 브레이턴 사이클을 기반으로 하는 가스 터빈 보조 동력 장치(APU)를 모델링합니다. Compressor 블록과 Turbine 블록은 Simscape™ Foundation Gas 라이브러리를 기반으로 하는 사용자 지정 컴포넌트입니다. 시스템에 입력되는 파워는 연소기로 주입되는 열로 표현되며 실제 연소 화학 반응은 모델링되지 않습니다. 압축기와 터빈이 단일 샤프트로 연결되어 터빈의 파워가 압축기를 구동합니다. APU는 배기 스트림을 더욱 확장하여 출력 파워를 생성하는 자유 터빈입니다.
랭킨 사이클(증기 터빈)
이 예제에서는 랭킨 사이클을 기반으로 하는 증기 터빈 시스템을 모델링합니다. 이 사이클에는 고압 터빈과 저압 터빈의 응축을 방지하기 위한 과열 기능과 재가열 기능이 각각 포함되어 있습니다. 또한 사이클은 추출된 증기를 밀폐된 급수 히터에 통과시켜 물을 예열하고 사이클 효율성을 향상하는 재생성도 포함합니다.
Battery Cell with Custom Electrochemical Domain
Use the Simscape™ example library ElectroChem_lib. In the model Fe3+ ions are reduced to Fe2+, and Pb is oxidized to Pb2+, thereby releasing chemical energy. The molar flow rate of lead ions is half that of the iron ions as two electrons are exchanged when Pb is oxidized to Pb2+. The chemical potential of the Pb source is by convention zero as it is a solid.
Lead-Acid Battery
Model a lead-acid battery cell using the Simscape™ language to implement the nonlinear equations of the equivalent circuit components. In this way, as opposed to modeling entirely in Simulink®, the connection between model components and the defining physical equations is more easily understood. For the defining equations and their validation, see Jackey, R. "A Simple, Effective Lead-Acid Battery Modeling Process for Electrical System Component Selection", SAE World Congress & Exhibition, April 2007, ref. 2007-01-0778.
리튬 배터리 셀 - 1개의 RC-분기 등가 회로
이 예제는 RC 분기가 하나 있는 등가 회로 모델의 요소를 구현하기 위해 Simscape™ 언어를 사용하여 리튬 셀을 모델링하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 정의 방정식 및 그에 대한 검증은 다음 자료를 참조하십시오. T. Huria, M. Ceraolo, J. Gazzarri, R. Jackey, "High Fidelity Electrical Model with Thermal Dependence for Characterization and Simulation of High Power Lithium Battery Cells," IEEE International Electric Vehicle Conference, March 2012.
리튬 배터리 셀 - 2개의 RC-분기 등가 회로
이 예제는 RC 분기가 두 개 있는 등가 회로 모델의 요소를 구현하기 위해 Simscape™ 언어를 사용하여 리튬 셀을 모델링하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 정의 방정식 및 그에 대한 검증은 다음 자료를 참조하십시오. T. Huria, M. Ceraolo, J. Gazzarri, R. Jackey, "High Fidelity Electrical Model with Thermal Dependence for Characterization and Simulation of High Power Lithium Battery Cells," IEEE International Electric Vehicle Conference, March 2012.
Lithium-Ion Battery Pack with Fault Using Arrays
Simulate a battery pack that consists of multiple series-connected cells. It also shows how you can introduce a fault into one of the cells to see the impact on battery performance and cell temperatures. The battery pack is modeled in Simscape™ language by connecting cell models in series using arrays. You can represent the fault by defining different parameters for the faulty cell.
Variable Transport Delay
Use Simscape™ to model a variable transport delay. The Transport Delay block models signal propagation through media moving between the Input and the Output terminals. The media velocity may vary, thus it is specified through the block port. The distance between the terminals as well as the initial output are constant and they are specified as block parameters.
Asynchronous PWM Voltage Source
How the Simscape™ Foundation Library PS Asynchronous Sample & Hold block can be used to build components with more complex behaviors. The model implements a controllable PWM voltage source where the PWM on-time (the duty cycle) is proportional to the physical signal input u.
Discrete-Time PWM Voltage Source
How the discrete-time Simscape™ Foundation Library PS Counter block can be used to build components with more complex behaviors. The model implements a controllable PWM voltage source where the PWM on-time (the duty cycle) is proportional to the physical signal input u.
Actuation Circuit with Custom Pneumatic Components
Model a controlled actuator using simplified custom pneumatic components. There are two across variables, defined as pressure and temperature, and two through variables, defined as mass flow rate and heat flow rate. The simplified approach means that every node in the circuit must have a volume of gas associated with it. This physical volume of gas in the circuit is represented by the Constant Volume Pneumatic Chamber blocks, the Pneumatic Piston Chamber blocks, and the Pneumatic Atmospheric Reference block. Conversely, the Foundation Library gas components require no such connection rules at every node. See the 공압 액추에이션 회로 example for a more capable way of modeling pneumatic systems using Foundation Library gas components.
Simscape Functions
Write Simscape™ functions to compute numerical values with Simscape expressions and how to use Simscape functions to improve code reuse across components. The top two Simscape component blocks ( inside the "Use no Simscape functions" box ) are respectively created using two Simscape component files. Comparing these two component files, similar Simscape expressions can be observed on the right hand side of the equation to compute numerical values, which is essentially a modification of exp(i) to provide protection for large magnitude of i. Such expressions are common in standard diode modeling. Using Simscape functions, such expressions are abstracted out into a Simscape function file, and their usages inside the component files are replaced by calls to such Simscape functions. The bottom two Simscape component blocks ( inside the "Use Simscape functions" box ) are created using component files using Simscape functions.
Mass on Cart Using an Ideal Hard Stop
A cart bouncing between the two ends of an ideal hard stop, while a mass slides freely on top of it. The friction between the mass and cart is modeled using an ideal, modechart-based friction block, while the hard stop is modeled using instantaneous modes and entry actions. When the cart hits the bounds of the hard stop, the impulsive force is propagated to the mass above, causing it to be displaced as it transitions from static to dynamic friction modes.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)