imimposemin
Impose minima
Description
Examples
This example shows how to modify an image so that one area is always a regional minimum.
Read an image and display it. This image is called the mask image.
mask = imread('glass.png');
imshow(mask)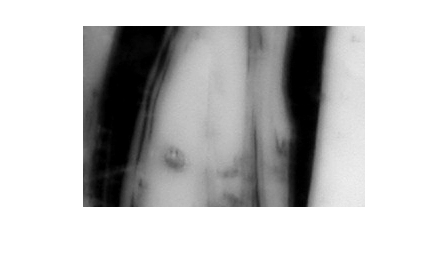
Create a binary image that is the same size as the mask image and sets a small area of the binary image to 1. These pixels define the location in the mask image where a regional minimum will be imposed. The resulting image is called the marker image.
marker = false(size(mask)); marker(65:70,65:70) = true;
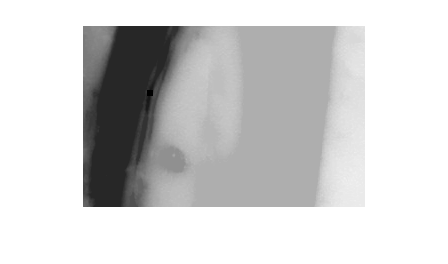
Superimpose the marker over the mask to show where these pixels of interest fall on the original image. The small white square marks the spot. This code is not essential to the impose minima operation.
J = mask;
J(marker) = 255;
figure
imshow(J)
title('Marker Image Superimposed on Mask')
Impose the regional minimum on the input image using the imimposemin function. Note how all the dark areas of the original image, except the marked area, are lighter.
K = imimposemin(mask,marker); figure imshow(K)
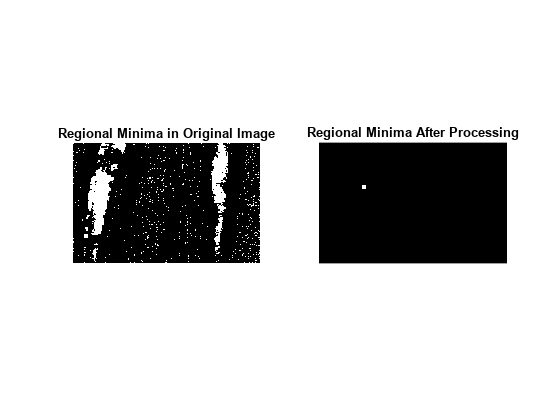
To illustrate how this operation removes all minima in the original image except the imposed minimum, compare the regional minima in the original image with the regional minimum in the processed image. These calls to imregionalmin return binary images that specify the locations of all the regional minima in both images.
BW = imregionalmin(mask); figure subplot(1,2,1) imshow(BW) title('Regional Minima in Original Image') BW2 = imregionalmin(K); subplot(1,2,2) imshow(BW2) title('Regional Minima After Processing')
Input Arguments
Grayscale mask image, specified as a numeric array of any dimension.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
Binary marker image, specified as a numeric or logical array of the same size as the
grayscale mask image I. For numeric input,
any nonzero pixels are considered to be 1 (true).
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical
Pixel connectivity, specified as one of the values in this table. The default
connectivity is 8 for 2-D images, and 26 for 3-D
images.
Value | Meaning | |
|---|---|---|
Two-Dimensional Connectivities | ||
| Pixels are connected if their edges touch. The neighborhood of a pixel are the adjacent pixels in the horizontal or vertical direction. |
Current pixel is shown in gray. |
| Pixels are connected if their edges or corners touch. The neighborhood of a pixel are the adjacent pixels in the horizontal, vertical, or diagonal direction. |
Current pixel is shown in gray. |
Three-Dimensional Connectivities | ||
| Pixels are connected if their faces touch. The neighborhood of a pixel are the adjacent pixels in:
|
Current pixel is shown in gray. |
| Pixels are connected if their faces or edges touch. The neighborhood of a pixel are the adjacent pixels in:
|
Current pixel is center of cube. |
| Pixels are connected if their faces, edges, or corners touch. The neighborhood of a pixel are the adjacent pixels in:
|
Current pixel is center of cube. |
For higher dimensions, imimposemin uses the default value
conndef(ndims(I),"maximal")
Connectivity can also be
defined in a more general way for any dimension by specifying a 3-by-3-by- ... -by-3 matrix of
0s and 1s. The 1-valued elements
define neighborhood locations relative to the center element of conn. Note
that conn must be symmetric about its center element. See Specifying Custom Connectivities for more information.
Data Types: double | logical
Output Arguments
Reconstructed image, returned as a numeric or logical array of the same size and
data type as I.
Extended Capabilities
Usage notes and limitations:
imimposeminsupports the generation of C and C++ code (requires MATLAB® Coder™). For more information, see Code Generation for Image Processing.imimposeminonly supports 2-D mask and marker images.The
connargument must be a compile-time constant and the only connectivities supported are4or8. You can also specify connectivity as a 3-by-3 matrix, but it can only be[0 1 0;1 1 1;0 1 0]orones(3).
Version History
Introduced before R2006aimimposemin now supports the generation of
C code (requires MATLAB
Coder).
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)




