딥러닝을 사용하여 사운드 분류하기
이 예제에서는 딥러닝 프로세스를 사용하여 사운드를 분류하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
데이터 세트 만들기
1000개의 백색 잡음 신호, 1000개의 브라운 잡음 신호, 1000개의 핑크 잡음 신호를 생성합니다. 각 신호는 44.1kHz 샘플 레이트를 가정하여 0.5초의 지속 시간을 나타냅니다.
fs = 44.1e3; duration = 0.5; N = duration*fs; wNoise = 2*rand([N,1000]) - 1; wLabels = repelem(categorical("white"),1000,1); bNoise = filter(1,[1,-0.999],wNoise); bNoise = bNoise./max(abs(bNoise),[],'all'); bLabels = repelem(categorical("brown"),1000,1); pNoise = pinknoise([N,1000]); pLabels = repelem(categorical("pink"),1000,1); classNames = ["white", "brown", "pink"];
데이터 세트 탐색하기
백색 잡음 신호를 듣고 melSpectrogram function을 사용하여 이 신호를 시각화합니다.
sound(wNoise(:,1),fs)
melSpectrogram(wNoise(:,1),fs)
title('White Noise')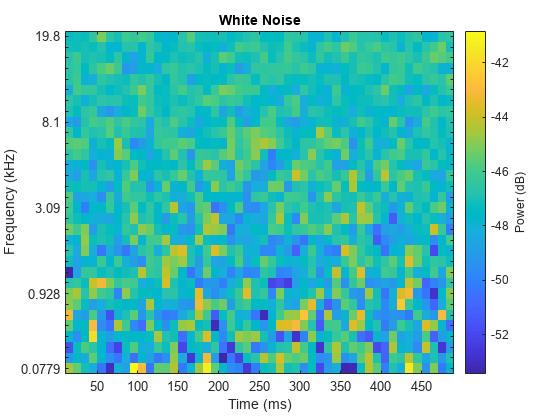
브라운 잡음 신호를 확인합니다.
sound(bNoise(:,1),fs)
melSpectrogram(bNoise(:,1),fs)
title('Brown Noise')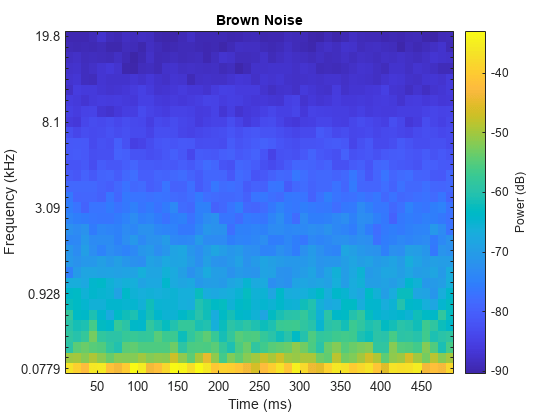
핑크 잡음 신호를 검사합니다.
sound(pNoise(:,1),fs)
melSpectrogram(pNoise(:,1),fs)
title('Pink Noise')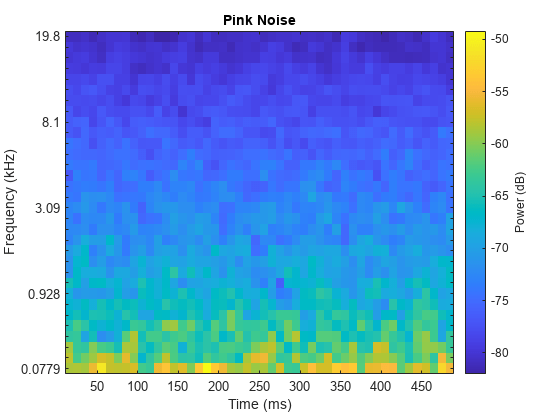
훈련 세트와 검증 세트로 데이터 세트 구분하기
백색 잡음 신호 중 800개, 브라운 잡음 신호 중 800개, 핑크 잡음 신호 중 800개의 신호로 구성된 훈련 세트를 만듭니다.
audioTrain = [wNoise(:,1:800),bNoise(:,1:800),pNoise(:,1:800)]; labelsTrain = [wLabels(1:800);bLabels(1:800);pLabels(1:800)];
나머지 200개의 백색 잡음 신호, 200개의 브라운 잡음 신호, 200개의 핑크 잡음 신호를 사용하여 검증 세트를 만듭니다.
audioValidation = [wNoise(:,801:end),bNoise(:,801:end),pNoise(:,801:end)]; labelsValidation = [wLabels(801:end);bLabels(801:end);pLabels(801:end)];
특징 추출
오디오 데이터는 고차원이며 일반적으로 중복된 정보를 포함합니다. 먼저 특징을 추출한 다음 추출된 특징을 사용하여 모델을 훈련시켜서 차원을 축소할 수 있습니다. 시간에 따라 멜 스펙트럼의 중심과 기울기를 추출하기 위해 audioFeatureExtractor 객체를 만듭니다.
aFE = audioFeatureExtractor(SampleRate=fs, ... SpectralDescriptorInput="melSpectrum", ... spectralCentroid=true, ... spectralSlope=true);
extract를 호출하여 오디오 훈련 데이터에서 특징을 추출합니다.
featuresTrain = extract(aFE,audioTrain); [numHopsPerSequence,numFeatures,numSignals] = size(featuresTrain)
numHopsPerSequence = 42
numFeatures = 2
numSignals = 2400
검증 특징을 추출합니다.
featuresValidation = extract(aFE,audioValidation); featuresValidation = squeeze(num2cell(featuresValidation,[1,2]));
신경망을 정의하고 훈련시키기
신경망 아키텍처를 정의합니다. 자세한 내용은 딥러닝 계층 목록 (Deep Learning Toolbox) 항목을 참조하십시오.
layers = [ ... sequenceInputLayer(numFeatures) lstmLayer(50,OutputMode="last") fullyConnectedLayer(numel(unique(labelsTrain))) softmaxLayer];
훈련 옵션을 정의하려면 trainingOptions (Deep Learning Toolbox)를 사용합니다.
options = trainingOptions("adam", ... Shuffle="every-epoch", ... ValidationData={featuresValidation,labelsValidation}, ... Plots="training-progress", ... Metrics="accuracy", ... Verbose=false);
신경망을 훈련시키려면 trainnet을 사용하십시오.
net = trainnet(featuresTrain,labelsTrain,layers,"crossentropy",options);
신경망 테스트하기
훈련된 신경망을 사용하여 새 백색 잡음, 브라운 잡음, 핑크 잡음 신호를 분류합니다.
wNoiseTest = 2*rand([N,1]) - 1; scores = predict(net,extract(aFE,wNoiseTest)); scores2label(scores,classNames)
ans = categorical
white
bNoiseTest = filter(1,[1,-0.999],wNoiseTest);
bNoiseTest= bNoiseTest./max(abs(bNoiseTest),[],'all');
scores = predict(net,extract(aFE,bNoiseTest));
scores2label(scores,classNames)ans = categorical
brown
pNoiseTest = pinknoise(N); scores = predict(net,extract(aFE,pNoiseTest)); scores2label(scores,classNames)
ans = categorical
pink
참고 항목
classifySound | audioFeatureExtractor | audioDataAugmenter | audioDatastore | 신호 레이블 지정기