show
Description
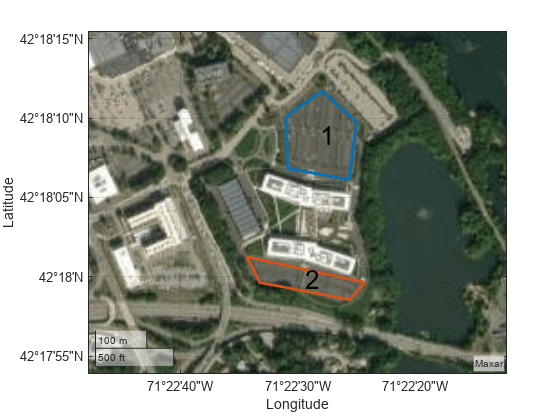
ax = show(space)space with numbering
corresponding to the order that the polygons were specified at the time of creation of
space. You can also use the show function for
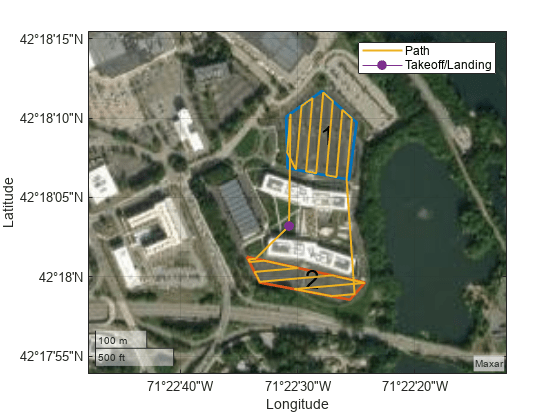
showing coverage space polygons that were decomposed with the coverageDecomposition function.
ax = show(space,Name=Value)
Examples
Input Arguments
Name-Value Arguments
Output Arguments
Version History
Introduced in R2023a