About Design Evolutions
Projects help you organize your work for large modeling projects. You can manage all the files you need in one place, including all MATLAB® and Simulink® files, and any other file types you need, such as data, requirements, reports, spreadsheets, tests, or generated files.
The Design Evolution Manager app helps you to manage different versions of a project. Evolutions capture the state of a project at key stages in your design process. Design Evolution Manager displays evolutions in an evolution tree hierarchy. You can use the relationships between evolutions and the metadata you associate with the different components of the evolution tree to manage and compare different versions of a design, model your design process, and communicate the rationale of behind design decisions.
Key Terms and Concepts
An evolution is a snapshot of a version of the files in a project. In the evolution tree, each evolution is a box representing alternative versions of the project files you have stored. Evolutions are stored separately within the project by the Design Evolution Manager app.
An evolution tree is a collection of related evolutions, organized in a tree structure. A child evolution is created from a parent evolution.
Connectors are arrows between the evolutions that contain information about the changes made between parent and child evolutions.
A snapshot of project files are recorded to the active evolution
 in the active evolution tree
in the active evolution tree
 when you click the Update Tree
button. You can view and update metadata for non-active evolution
trees, but you must make an evolution tree active to update it.
when you click the Update Tree
button. You can view and update metadata for non-active evolution
trees, but you must make an evolution tree active to update it.You can lock
 an evolution to prevent changes to project files from
being recorded to the evolution when you update the evolution tree. Metadata, such as
the name of the evolution and notes, can still be edited.
an evolution to prevent changes to project files from
being recorded to the evolution when you update the evolution tree. Metadata, such as
the name of the evolution and notes, can still be edited.If you lock the active evolution, it no longer record changes. If you do not create a new active evolution, the Design Evolution Manager app automatically creates one when you update the evolution tree.
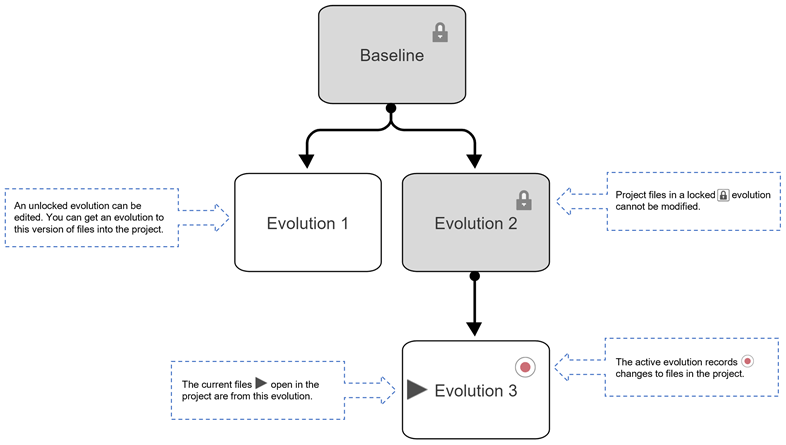
Example Evolution Tree
This image shows an example of an evolution tree. The Baseline
evolution is the reference point for the evolution tree. When you create a new evolution
tree, the Design Evolution Manager app creates a baseline evolution that captures
a snapshot of the original state of your project. Evolution 1 and
Evolution 2 capture two alternative solutions based on the
Baseline evolution. Evolution 3 is the active
evolution. Evolution 3 captures further improvements on
Evolution 2.
You can capture notes for the evolution tree, for each evolution in the tree, and for each connector between two evolutions. You can select an evolution to see the files and notes in that evolution. You can compare files from any two evolutions in the evolution tree.
The shape of the evolution tree visually maps to your design process. Your evolution tree may be linear, which indicates that each evolution is a continuation of the same design path, or your evolution tree may branch if you explore multiple design directions within one evolution tree. You can use evolutions and branches in the evolution tree to explore different design ideas, perform trade studies, or troubleshoot an existing design. Use evolutions to record successful design directions and keep a record of unsuccessful design ideas. You can trace back through your evolution tree to understand why particular changes were made to the design.
For examples showing how to integrate the Design Evolution Manager app into your workflow, see Use Design Evolution Manager with Fixed-Point Tool and Use Design Evolution Manager App to Explore Different Coder Settings.
See Also
Design Evolution Manager | Manage Evolutions and Evolution Trees | Inspect Properties, Compare, and Merge Evolutions