rfckt.coaxial
Coaxial transmission line
Description
Use the rfckt.coaxial object to create a coaxial
transmission line that is characterized by line dimensions, stub type, and
termination.
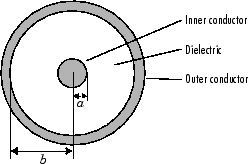
A coaxial transmission line is shown in cross-section in the following figure. Its physical characteristics include the radius of the inner conductor of the coaxial transmission line a, and the radius of the outer conductor b.
Note
txlineCoaxial is recommended over rfckt.coaxial
because it enables you to:
Create a coaxial transmission line.
Build a
circuitobject with a coaxial transmission line.Model a coaxial transmission line element in an RF chain created using an
rfbudgetobject or the RF Budget Analyzer app, and then export this element to RF Blockset™ or torfsystemSystem object™ for circuit envelope analysis.
(since R2023b)
Creation
Description
h = rfckt.coaxial returns a coaxial transmission line
object whose properties are set to their default values.
h = rfckt.coaxial(Name,Value) sets properties using
one or more name-value pairs. For example,
rfckt.coaxial('OuterRadius',0.0043) creates a coaxial
transmission line object with outer radius of 0.0043 meters. You can specify
multiple name-value pairs. Enclose each property name in quotes. Properties
not specified retain their default values.
Properties
Object Functions
analyze | Analyze RFCKT object in frequency domain |
calculate | Calculate specified parameters for rfckt objects or rfdata objects |
circle | Draw circles on Smith Chart |
extract | Extract specified network parameters from rfckt object or data object |
listformat | List valid formats for specified circuit object parameter |
listparam | List valid parameters for specified circuit object |
loglog | Plot specified circuit object parameters using log-log scale |
plot | Plot circuit object parameters on X-Y plane |
plotyy | Plot parameters of RF circuit or RF data on xy-plane with two Y-axes |
getop | Display operating conditions |
polar | Plot specified object parameters on polar coordinates |
semilogx | Plot RF circuit object parameters using log scale for x-axis |
semilogy | Plot RF circuit object parameters using log scale for y-axis |
smith | Plot circuit object parameters on Smith Chart |
write | Write RF data from circuit or data object to file |
getz0 | Calculate characteristic impedance of RFCKT transmission line object |
read | Read RF data from file to new or existing circuit or data object |
restore | Restore data to original frequencies |
getop | Display operating conditions |
Examples
Algorithms
The analyze method treats the transmission line as a 2-port linear
network. It computes the AnalyzedResult property of a stub or as a
stubless line using the data stored in the rfckt.coaxial object
properties as follows:
If you model the transmission line as a stubless line, the
analyzemethod first calculates the ABCD-parameters at each frequency contained in the modeling frequencies vector. It then uses theabcd2sfunction to convert the ABCD-parameters to S-parameters.The
analyzemethod calculates the ABCD-parameters using the physical length of the transmission line, d, and the complex propagation constant, k, using the following equations:Z0 and k are vectors whose elements correspond to the elements of f, the vector of frequencies specified in the
analyzeinput argumentfreq. Both can be expressed in terms of the resistance (R), inductance (L), conductance (G), and capacitance (C) per unit length (meters) as follows:where
In these equations:
a is the radius of the inner conductor.
b is the radius of the outer conductor.
σcond is the conductivity in the conductor.
μ is the permeability of the dielectric.
ε is the permittivity of the dielectric.
ε″ is the imaginary part of ε, ε″ = ε0εrtan δ, where:
ε0 is the permittivity of free space.
εr is the
EpsilonRproperty value.tan δ is the
LossTangentproperty value.
δcond is the skin depth of the conductor, which the method calculates as .
f is a vector of modeling frequencies determined by the Outport (RF Blockset) block.
If you model the transmission line as a shunt or series stub, the
analyzemethod first calculates the ABCD-parameters at the specified frequencies. It then uses theabcd2sfunction to convert the ABCD-parameters to S-parameters.When you set the
StubModeproperty to'Shunt', the 2-port network consists of a stub transmission line that you can terminate with either a short circuit or an open circuit as shown in the following figure.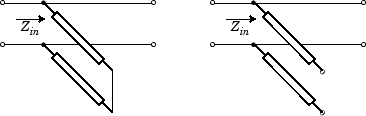
Zin is the input impedance of the shunt circuit. The ABCD-parameters for the shunt stub are calculated as:
When you set the
StubModeproperty to'Series', the 2-port network consists of a series transmission line that you can terminate with either a short circuit or an open circuit as shown in the following figure.
Zin is the input impedance of the series circuit. The ABCD-parameters for the series stub are calculated as
References
[1] Pozar, David M. Microwave Engineering, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2005.
Version History
Introduced before R2006a