partition
데이터저장소 파티셔닝
구문
설명
예제
대규모 파일 모음을 저장할 데이터저장소를 만듭니다. 이 예제에서는 샘플 파일 airlinesmall.csv의 복사본 10개를 사용합니다. 테이블 형식 데이터의 누락된 필드를 처리하기 위해 이름-값 쌍 TreatAsMissing과 MissingValue를 지정합니다.
files = repmat({'airlinesmall.csv'},1,10);
ds = tabularTextDatastore(files,...
'TreatAsMissing','NA','MissingValue',0);데이터저장소를 3개의 파티션으로 분할하고 첫 번째 파티션을 반환합니다. partition 함수는 데이터저장소 ds에 들어 있는 데이터 중에서 약 삼분의 일 분량에 해당하는 첫 번째 부분을 반환합니다.
subds = partition(ds,3,1);
데이터저장소의 Files 속성은 데이터저장소에 들어 있는 파일의 목록을 포함합니다. 데이터저장소 ds와 분할된 데이터저장소 subds의 Files 속성에서 파일 개수를 확인합니다. 데이터저장소 ds에는 10개의 파일이 들어 있고, 파티션 subds에는 처음 4개의 파일이 들어 있습니다.
length(ds.Files)
ans = 10
length(subds.Files)
ans = 4
샘플 파일 mapredout.mat에서 데이터저장소를 만듭니다. 이 파일은 mapreduce 함수의 출력 파일입니다.
ds = datastore('mapredout.mat');ds의 디폴트 파티션 개수를 가져옵니다.
n = numpartitions(ds);
데이터저장소를 디폴트 파티션 개수로 파티셔닝하고 첫 번째 파티션에 대응하는 데이터저장소를 반환합니다.
subds = partition(ds,n,1);
subds에서 데이터를 읽습니다.
while hasdata(subds) data = read(subds); end
3개의 이미지 파일이 포함된 데이터저장소를 만듭니다.
ds = imageDatastore({'street1.jpg','peppers.png','corn.tif'})
ds =
ImageDatastore with properties:
Files: {
' ...\matlab\toolbox\matlab\demos\street1.jpg';
' ...\matlab\toolbox\matlab\imagesci\peppers.png';
' ...\matlab\toolbox\matlab\imagesci\corn.tif'
}
ReadSize: 1
Labels: {}
ReadFcn: @readDatastoreImage
파일을 기준으로 데이터저장소를 파티셔닝하고 두 번째 파일에 대응하는 파트를 반환합니다.
subds = partition(ds,'Files',2)
subds =
ImageDatastore with properties:
Files: {
' ...\matlab\toolbox\matlab\imagesci\peppers.png'
}
ReadSize: 1
Labels: {}
ReadFcn: @readDatastoreImage
subds에는 하나의 파일이 포함됩니다.
샘플 파일 mapredout.mat에서 데이터저장소를 만듭니다. 이 파일은 mapreduce 함수의 출력 파일입니다.
ds = datastore('mapredout.mat');병렬 풀의 3개의 워커에 대한 데이터저장소를 3개의 파트로 파티셔닝합니다.
numWorkers = 3; p = parpool('local',numWorkers); n = numpartitions(ds,p); parfor ii=1:n subds = partition(ds,n,ii); while hasdata(subds) data = read(subds); end end
성기게 세분한 파티션을 정교하게 세분한 서브셋과 비교합니다.
비디오 파일 xylophone.mp4에서 모든 프레임을 읽어 들이고 반복을 수행할 ArrayDatastore 객체를 만듭니다. 결과로 생성되는 객체에는 141개의 프레임이 있습니다.
v = VideoReader("xylophone.mp4"); allFrames = read(v); arrds = arrayDatastore(allFrames,IterationDimension=4,OutputType="cell",ReadSize=4);
인접한 프레임들의 특정 집합을 추출하기 위해 arrds로부터 4개의 성기게 세분한 파티션을 만듭니다. 두 번째 파티션을 추출합니다. 이 파티션에는 35개의 프레임이 있습니다.
partds = partition(arrds,4,2); imshow(imtile(partds.readall()))
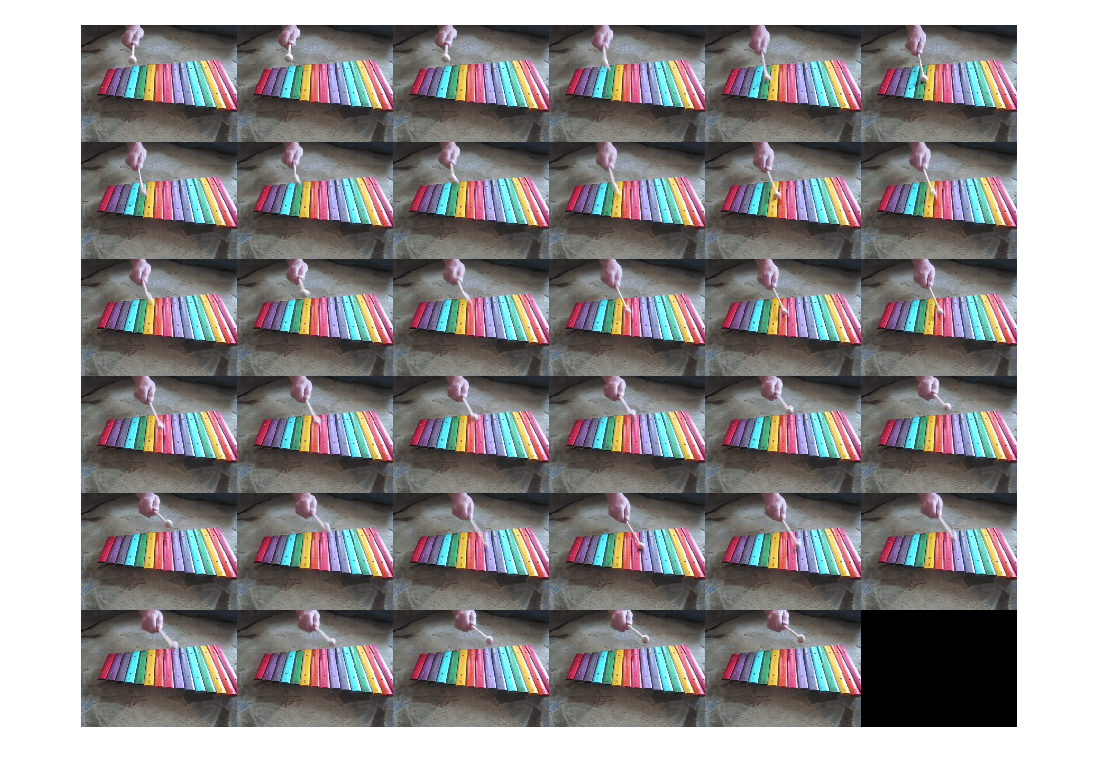
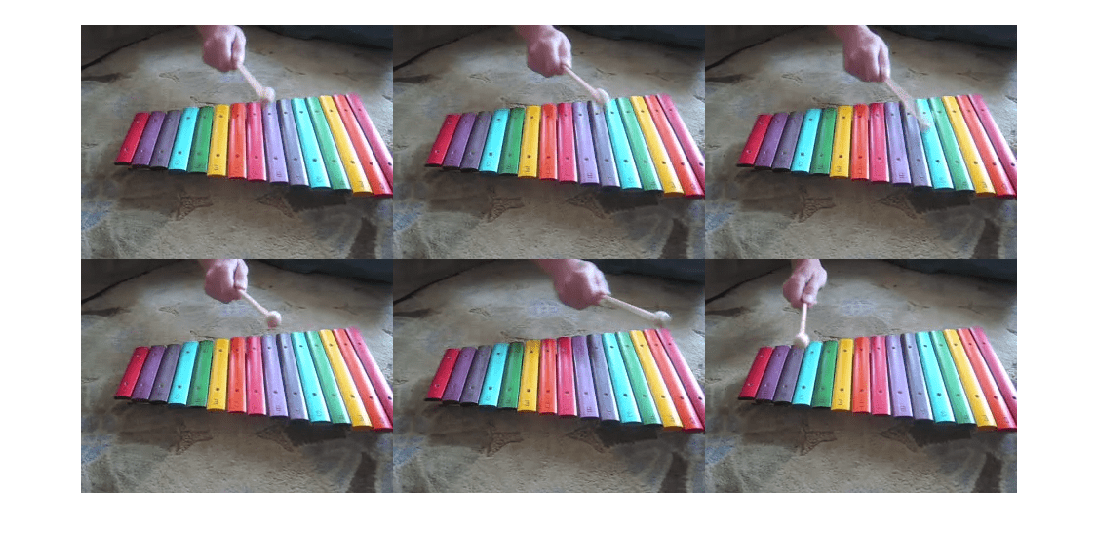
정교하게 세분한 서브셋을 사용하여 arrds로부터 지정된 인덱스에 있는 6개의 서로 인접하지 않은 프레임을 추출합니다.
subds = subset(arrds,[67 79 82 69 89 33]); imshow(imtile(subds.readall()))

입력 인수
입력 데이터저장소입니다. datastore 함수를 사용하여 데이터에서 datastore 객체를 만들 수 있습니다.
파티션 개수로, 양의 정수로 지정됩니다.
partition 함수에 지정한 파티션 개수가 데이터저장소에 있는 파일 개수의 약수가 아닐 경우, partition 함수는 나머지 각 관측값을 기존 파티션에 첫 번째 파티션부터 추가합니다.
남은 관측값이 포함된 기존 파티션의 개수는 데이터저장소에 있는 파일 개수를 파티션 개수로 나누어서 얻는 나머지와 같습니다. 예를 들어, 3개 파티션으로 나누려는 datastore 객체에 23개 파일이 있는 경우 partition이 생성하는 처음 두 개 파티션은 8개의 파일을 포함하고 마지막 파티션은 7개 파일을 포함합니다.
예: 3
데이터형: double
인덱스로, 양의 정수로 지정됩니다.
예: 1
데이터형: double
파일 이름으로, 문자형 벡터 또는 string형 스칼라로 지정됩니다.
filename의 값은 데이터저장소의 Files 속성에 포함된 파일 이름과 정확하게 일치해야 합니다. 파일 이름이 정확하게 일치하는지 확인하려면 ds.Files{N}을 사용하여 filename을 지정하십시오. 여기서 N은 Files 속성에 있는 파일의 인덱스입니다. 예를 들어, ds.Files{3}은 데이터저장소 ds의 세 번째 파일을 지정합니다.
예: ds.Files{3}
예: 'file1.csv'
예: '../dir/data/file1.csv'
예: 'hdfs://myserver:7867/data/file1.txt'
데이터형: char
출력 인수
출력 데이터저장소입니다. 출력 데이터저장소는 입력 데이터저장소 ds와 형식이 같습니다.
확장 기능
사용법 관련 참고 및 제한 사항:
스레드 기반 환경에서는 다음과 같은 데이터저장소에만
partition함수를 사용할 수 있습니다.ImageDatastore객체ImageDatastore객체로부터combine또는transform을 사용하여 생성한CombinedDatastore,SequentialDatastore또는TransformedDatastore객체
Parallel Computing Toolbox™가 있는 경우
partition함수를 다른 데이터저장소에도 사용할 수 있습니다. 이렇게 하려면backgroundPool또는ThreadPool을 사용하는 대신 프로세스를 지원하는 병렬 풀을 사용하는 함수를 실행하십시오(ProcessPool또는ClusterPool사용).
자세한 내용은 스레드 기반 환경에서 MATLAB 함수 실행하기 항목을 참조하십시오.
버전 내역
R2015a에 개발됨
참고 항목
datastore | numpartitions | subset
도움말 항목
- Partition a Datastore in Parallel (Parallel Computing Toolbox)
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)