initapekf
Constant velocity angle-parameterized EKF initialization
Syntax
Description
filter = initapekf(detection)
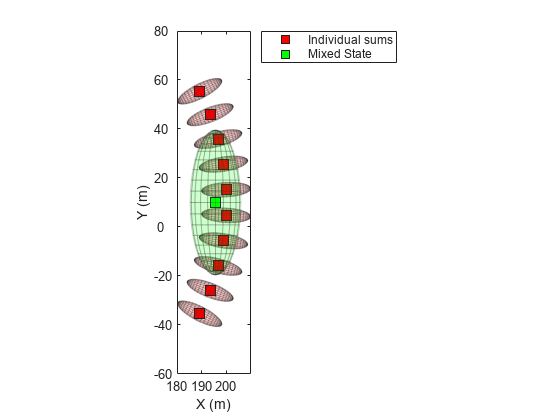
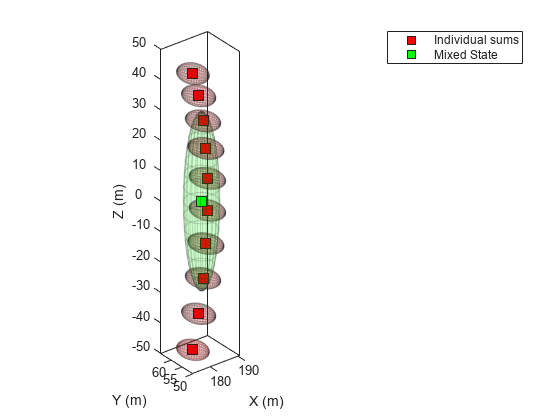
The angle-parameterized extended Kalman filter (APEKF) is a Gaussian-sum filter
(trackingGSF) with
multiple EKFs, each initialized at an estimated angular position of the target.
Angle-parametrization is a commonly used technique to initialize a filter from a range-only
detection.
filter = initapekf(detection,numFilters)
filter = initapekf(detection,numFilters,angleLimits)
Examples
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
Algorithms
The function can support the following types of measurements in the detection.
Range measurements –– Parameterization is done on the azimuth of the target, and the angular limits are [–180 180] by default.
Azimuth and range measurements –– Parameterization is done on the elevation of the target, and the angular limits are [–90 90] by default.
References
[1] Ristic, Branko, Sanjeev Arulampalam, and James McCarthy. "Target motion analysis using range-only measurements: algorithms, performance and application to ISAR data." Signal Processing 82, no. 2 (2002): 273-296.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2018b