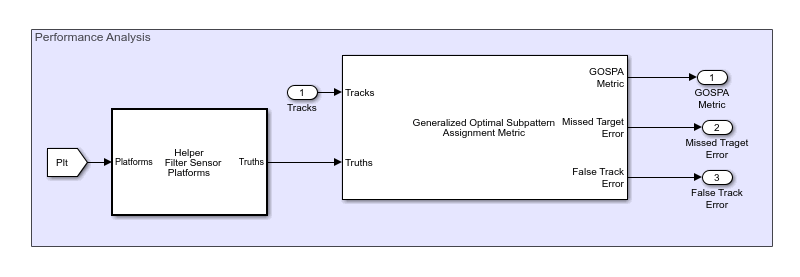
Generalized Optimal Subpattern Assignment Metric

Libraries:
Sensor Fusion and Tracking Toolbox /
Track Metrics
Description
The Generalized Optimal Subpattern Assignment Metric block evaluates the performance of a tracking algorithm by computing the generalized optimal subpattern assignment (GOSPA) metric between tracks and known truths. The metric is comprised of the switching error, localization error, missed target error, and false track error components. You can also select each individual error components as a block output.
Examples
Track-Level Fusion of Radar and Lidar Data in Simulink
Autonomous systems require precise estimation of their surroundings to support decision making, planning, and control. High-resolution sensors such as radar and lidar are frequently used in autonomous systems to assist in estimation of the surroundings. These sensors generally output tracks. Outputting tracks instead of detections and fusing the tracks together in a decentralized manner provide several benefits, including low false alarm rates, higher target estimation accuracy, a low bandwidth requirement, and low computational costs. This example shows you how to track objects from measurements of a radar and a lidar sensor and how to fuse them using a track-level fusion scheme in Simulink®. You process the radar measurements using a Gaussian Mixture Probability Hypothesis Density (GM-PHD) tracker and the lidar measurements using a Joint Probabilistic Data Association (JPDA) tracker. You further fuse these tracks using a track-level fusion scheme. The example closely follows the Track-Level Fusion of Radar and Lidar Data MATLAB® example.
- Since R2021a
- Open Model
Track Point Targets in Dense Clutter Using GM-PHD Tracker in Simulink
Radars generally receive echoes from all surfaces in the signal path. These unwanted back-scattered signals or echoes generated from physical objects are called clutter. In a densely cluttered environment, missed detections and false alarms make tracking objects a challenging task for conventional trackers such as Global Nearest-Neighbor (GNN) tracker. In such an environment a PHD tracker provides better estimation of objects as it can handle multiple detections per object per sensor without clustering them first. This example shows you how to track points targets in dense clutter using a Gaussian mixture probability hypothesis density (GM-PHD) tracker with a constant velocity model in Simulink. The example closely follows the Track Point Targets in Dense Clutter Using GM-PHD Tracker MATLAB® example.
- Since R2021a
- Open Model
Ports
Input
Track list, specified as a Simulink bus containing a MATLAB structure.
If you specify the Track bus parameter on the Port
Setting tab to objectTrack, the structure must
use this form:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
NumTracks | Number of tracks |
Tracks | Array of track structures |
Each track structure must contain TrackID and State
fields. Additionally, if you specify an NEES-based distance (posnees
or velnees) in the Distance type parameter, each
structure must contain a StateCovariance field.
| Field | Definition |
|---|---|
TrackID | Unique track identifier used to distinguish multiple tracks, specified as a nonnegative integer. |
State | Value of state vector at the update time, specified as an N-element vector, where N is the dimension of the state. |
StateCovariance | Uncertainty covariance matrix, specified as an N-by-N matrix, where N is the dimension of the state. |
If you specify an NEES-based distance (posnees or
velnees) in the Distance type parameter,
then the structure must contain a StateCovariance field.
If you specify the Track bus parameter to
custom, then you can use your own track bus format. In
this case, you must define a track extractor function using the Track
extractor function parameter. The function must use this
syntax:
tracks = trackExtractorFcn(trackInputFromBus)
trackInputFromBus is the input from the track bus and
tracks must return as an array of structures with
TrackID and State fields. Truth list, specified as a Simulink bus containing a MATLAB structure.
If you specify the Truth bus parameter on the Port
Setting tab to
Platform, the structure
must use this form:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
NumPlatforms | Number of truth platforms |
Platforms | Array of truth platform structures |
Each platform structure has these fields:
| Field | Definition |
|---|---|
PlatformID | Unique identifier used to distinguish platforms, specified as a nonnegative integer. |
Position | Position of the platform, specified as an M-element vector, where M is the dimension of the position state. For example, M = 3 for 3-D position. |
Velocity | Velocity of the platform, specified as an M-element vector, where M is the dimension of the velocity state. For example, M = 3 for 3-D velocity. |
If you specify the Truth bus parameter as
Actor, the structure must
use this form:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
NumActors | Number of truth actors |
Actors | Array of truth actor structures |
Each actor structure has these fields:
| Field | Definition |
|---|---|
ActorID | Unique identifier used to distinguish actors, specified as a nonnegative integer. |
Position | Position of the actor, specified as an M-element vector, where M is the dimension of the position state. For example, M = 3 for 3-D position. |
Velocity | Velocity of the actor, specified as an M-element vector, where M is the dimension of the velocity state. For example, M = 3 for 3-D velocity. |
If you specify the Truth bus parameter to
custom, then you can define your own truth bus format. In this
case, you must define a truth extractor function using the Truth extractor
function parameter. The function must use this
syntax:
truths = truthExtractorFcn(truthInputFromBus)
truthInputFromBus is the input from the truth bus and
truths must return as an array of structures with
PlatformID, Position, and Velocity
fields.Known assignment, specified as an K-by-2 matrix of nonnegative
integers. K is the number of assignment pairs. The first column
elements are track IDs, and the second column elements are truth IDs. The IDs in the
same row are assigned to each other. If a track or truth is not assigned, specify
0 as the same row element.
The assignment must be a unique assignment between tracks and truths. Redundant or
false tracks should be treated as unassigned tracks by assigning them to the "0"
TruthID.
Dependencies
To enable this port, on the Port Setting tab, select Assignments.
Output
GOSPA metric including switching error component, returned as a nonnegative real scalar.
GOSPA metric without switching error component, returned as a nonnegative real scalar.
Example: 8.5
Dependencies
To enable this port, on the Port Setting tab, select GOSPA metric without switching error component.
Switching error component, returned as a nonnegative real scalar.
Example: 8.5
Dependencies
To enable this port, on the Port Setting tab, select Switching error.
Localization error component, returned as a nonnegative real scalar.
Example: 8.5
Dependencies
To enable this port, on the Port Setting tab, select Localization error.
Missed target error component, returned as a nonnegative real scalar.
Example: 8.5
Dependencies
To enable this port, on the Port Setting tab, select Missed target error.
False track error component, returned as a nonnegative real scalar.
Example: 8.5
Dependencies
To enable this port, on the Port Setting tab, select False track error.
Parameters
Properties
Threshold for cutoff distance between track and truth, specified as a real positive scalar. If the computed distance between a track and the assigned truth is higher than the threshold, the actual distance incorporated in the metric is reduced to the threshold.
Example: 40
Order of GOSPA metric, specified as a positive integer.
Example:
10
Alpha parameter of the GOSPA metric, specified as a positive scalar in the range [0, 2].
Example:
1
Distance type, specified as posnees, velnees,
posabserr, or velabserr. The distance type
specifies the physical quantity used for distance calculations:
posnees– Normalized estimation error squared (NEES) of track positionvelnees– NEES error of track velocityposabserr– Absolute error of track positionvelabserr– Absolute error of track velocitycustom– Custom distance error
If you specify it as custom, you must also specify the distance
function in the Custom distance function parameter.
Custom distance function, specified as a function handle. The function must support the following syntax:
d = myCustomFcn(Track,Truth)
Track is a structure for track information,
Truth is a structure of truth information, and d
is the distance between the truth and the track. See objectTrack for an example on how
to organize track information. Example:
@myCustomFcn
Dependencies
To enable this property, set the Distance type parameter to
custom.
Desired platform motion model, specified as constvel,
constacc, constturn, or
singer. This property selects the motion model used by the
Tracks input port.
The motion models expect the State field of the track structure
to have a column vector containing these values:
constvel— Position is in elements [1 3 5], and velocity is in elements [2 4 6].constacc— Position is in elements [1 4 7], velocity is in elements [2 5 8], and acceleration is in elements [3 6 9].constturn— Position is in elements [1 3 6], velocity is in elements [2 4 7], and yaw rate is in element 5.singer— Position is in elements [1 4 7], velocity is in elements [2 5 8], and acceleration is in elements [3 6 9].
The StateCovariance field of the track structure input
must have position, velocity, and turn-rate covariances in the rows and columns
corresponding to the position, velocity, and turn-rate of the State
field of the track structure.
Penalty for assignment switching, specified as a nonnegative real scalar.
Example:
2
Select a simulation type from these options:
Interpreted execution— Simulate the model using the MATLAB interpreter. This option shortens startup time. InInterpreted executionmode, you can debug the source code of the block.Code generation— Simulate the model using generated C code. The first time you run a simulation, Simulink generates C code for the block. The C code is reused for subsequent simulations as long as the model does not change. This option requires additional startup time.
Port Setting
Select this parameter to enable the input of know assignments through the Assignments input port.
Select this parameter to enable the output of the GOSPA metric without the switching error component through the GOSPA Metric Without Switching output port.
Select this parameter to enable the output of the switching error component through the Switching Error output port.
Select this parameter to enable the output of the localization error component through the Localization Error output port.
Select this parameter to enable the output of the missed target error component through the Missed Target Error output port.
Select this parameter to enable the output of the false track error component through the False Track Error output port.
Track bus selection, specified as objectTrack or
custom. See the description of the Tracks
input port for more details about each selection.
Truth bus selection, specified as Platform,
Actor, or custom. See the
description of the Truths input port for more details about each
selection.
Track extractor function, specified as a function handle. The function must support this syntax:
tracks = trackExtractorFcn(trackInputFromBus)
trackInputFromBus is the input from the track bus and
tracks must return as an array of structures with
TrackID and State fields. If you specify an
NEES-based distance (posnees or velnees) in the
Distance type parameter, then the structure must contain a
StateCovariance field.Example: @myCustomFcn
Dependencies
To enable this property, set the Track bus parameter to custom.
Truth extractor function, specified as a function handle. The function must support this syntax:
truths = truthExtractorFcn(truthInputFromBus)
truthInputFromBus is the input from the track bus and
truths must return as an array of structures with
PlatformID, Position, and
Velocity as field names.Example:
@myCustomFcn
Dependencies
To enable this property, set the Truth bus parameter to
custom.
Algorithms
At time tk, a list of truths is:
At time tk, a tracker obtains a list of tracks:
In general, the GOSPA metric including the switching component (SGOSPA) is:
where p is the order of the metric, SC is the switching component, and GOSPA is the basic GOSPA metric.
Assuming m ≤ n, GOSPA is:
where dc is the cutoff-based distance and yπ(i) represents the track assigned to truth xi. The cutoff-based distance dc is defined as:
where c is the cutoff distance threshold, and db(x,y) is the base distance between track x and truth y calculated by the distance function. The cutoff based distance dc is the smaller value of db and c. α is the alpha parameter.
The switching component SC is:
where SP is the switching penalty and ns is the number of switches. When a track switches assignment from one truth to another truth, the number of switching is counted as 1. When a track switches from assigned to unassigned or switches from unassigned to assigned, the number of switching is counted as 0.5. For example, as shown in the table, Tracks 1 and 2 both switched to different truths, whereas Track 3 switched from assigned to unassigned. Therefore, the total number of switching is 2.5.
Track Switching Scenario
| Previous | Current | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tracks | Truths | Tracks | Truths |
| 1 | 3 | 1 | 7 |
| 2 | 5 | 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 7 | 3 | 0 |
When α = 2, the GOSPA metric can reduce to three components:
The localization component (loc) is calculated as:
where h is the number of nontrivial assignments. A trivial assignment is when a track is assigned to no truth. The missed target component is calculated as:
where nmiss is the number of missed targets. The false track component is calculated as:
where nfalse is the number of false tracks.
If m > n, simply exchange m and n in the formulation to obtain the GOSPA metric.
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using Simulink® Coder™.
Version History
Introduced in R2021aAs of R2023a, the Simulink buses created by this block no longer show in MATLAB workspace.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)