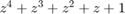BPSK Modulator Baseband
Modulate using BPSK method
Libraries:
Communications Toolbox /
Modulation /
Digital Baseband Modulation /
PSK
Communications Toolbox HDL Support /
Modulation /
PM
Description
The BPSK Modulator Baseband block modulates a signal by using the binary phase shift keying (BPSK)
method. The output is a baseband representation of the modulated signal. The input
signal must be a discrete-time binary-valued signal. If the input bit is 0 or 1, then
the modulated symbol is exp(jϕ) or -exp(jϕ), respectively. The Phase offset
(rad) parameter specifies the value of ϕ in radians.
Examples
Extended Examples
Ports
Input
Output
Parameters
Block Characteristics
More About
Algorithms
Phase modulation is a linear baseband modulation technique in which the message modulates the phase of a constant amplitude signal. Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK) is a two phase modulation scheme, where the 0’s and 1’s in a binary message are represented by two different phase states in the carrier signal
for where:
ϕn = πm + ϕ, m∈{0,1}.
ϕ is the initial phase offset.
Eb is the energy per bit.
Tb is the bit duration.
fc is the carrier frequency.
In MATLAB®, the baseband representation of a BPSK signal is
The BPSK signal has two phases: 0 and π.
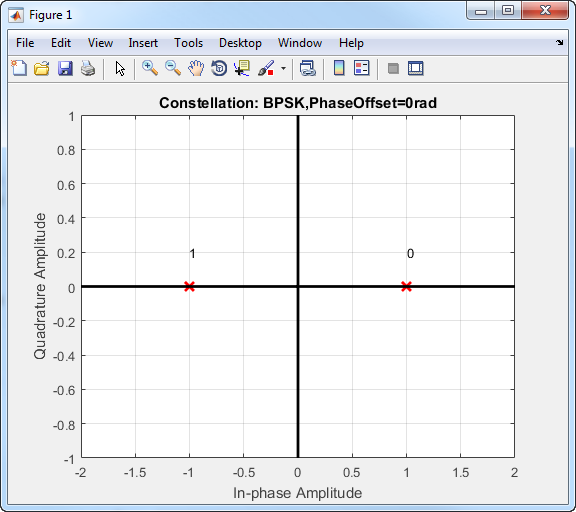
The probability of a bit error in an AWGN channel is
where N0 is the noise power spectral density.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced before R2006a
See Also
Blocks
- BPSK Demodulator Baseband | M-PSK Modulator Baseband | QPSK Modulator Baseband | DBPSK Modulator Baseband