add
Add data to polar plot
Description
Examples
Create a helix antenna that has 28 mm radius, 1.2 mm width, and 4 turns. Calculate the directivity of the antenna at 1.8 GHz.
hx = helix(Radius=28e-3, Width=1.2e-3, Turns=4); H = pattern(hx,1.8e9,0,0:1:360);
Plot the polar pattern.
P = polarpattern(H);
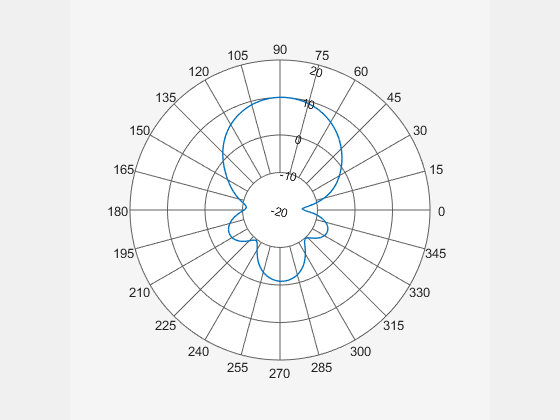
Create a dipole antenna and calculate the directivity at 270 MHz.
d = dipole; D = pattern(d,270e6,0,0:1:360);
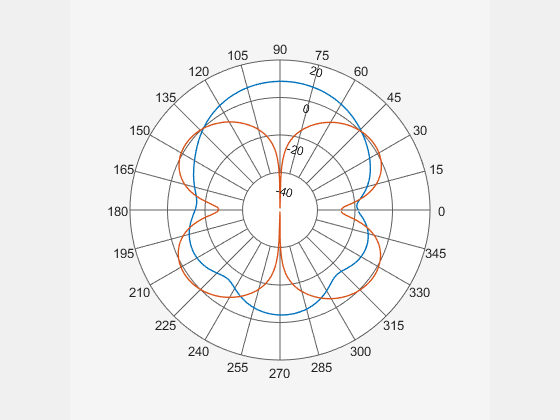
Add the directivity of the dipole to the existing polar plot of helix antenna.
add(P,D);
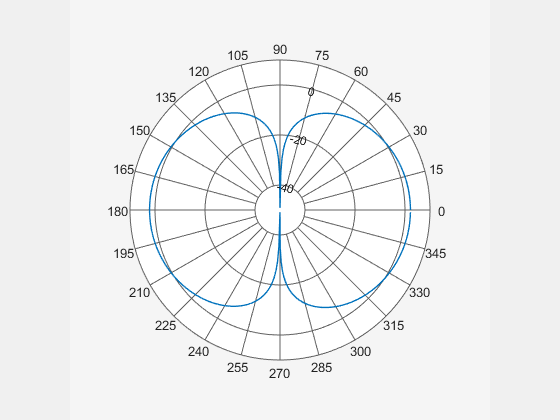
Create a dipole and plot the polar pattern of its directivity at a frequency of 75 MHz.
d = dipole; D = pattern(d,75e6,0,0:1:360); P = polarpattern(D);
Create a cavity antenna. Calculate the directivity of the antenna at 1 GHz. Write the directivity of the antenna to cavity.pln using the msiwrite function.
c = cavity; msiwrite(c,1e9,"cavity.pln", Name="Cavity Antenna Specifications");
Read the data from cavity.pln to Horizontal, Vertical, and Optional structures using the msiread function.
[Horizontal,Vertical,Optional] = msiread("cavity.pln")Horizontal = struct with fields:
PhysicalQuantity: 'Gain'
Magnitude: [360×1 double]
Units: 'dBi'
Azimuth: [360×1 double]
Elevation: 0
Frequency: 1.0000e+09
Slice: 'Elevation'
Vertical = struct with fields:
PhysicalQuantity: 'Gain'
Magnitude: [360×1 double]
Units: 'dBi'
Azimuth: 0
Elevation: [360×1 double]
Frequency: 1.0000e+09
Slice: 'Azimuth'
Optional = struct with fields:
name: 'Cavity Antenna Specifications'
frequency: 1.0000e+09
gain: [1×1 struct]
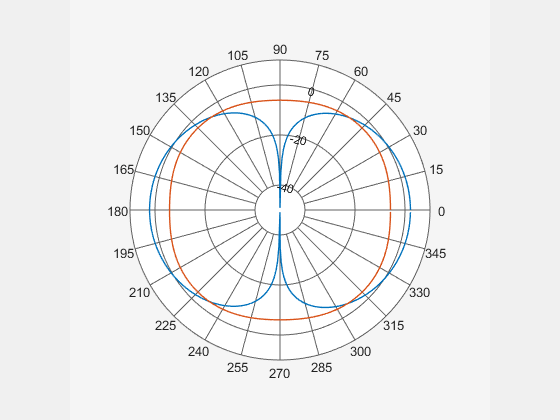
Add horizontal directivity data of the cavity antenna to the existing polar pattern of the dipole
add(P,Horizontal.Azimuth,Horizontal.Magnitude);
Input Arguments
Polar plot, specified as a scalar handle.
Example: polarpattern
Antenna or array data, specified as one of the following:
A real length-M vector, where M contains the magnitude values with angles assumed to be degrees.
A real M-by-N matrix, where M contains the magnitude values and N contains the independent data sets. Each column in the matrix has angles taken from the vector degrees. The set of each angle can vary for each column.
A real N-D array, where N is the number of dimensions. Arrays with dimensions
2and greater are independent data sets.A complex vector or matrix, where
datacontains Cartesian coordinates ((x,y) of each point. x contains the real part ofdataand y contains the imaginary part ofdata.
When data is in a logarithmic form such as dB, magnitude values
can be negative. In this case,polarpattern plots
the lowest magnitude values at the origin of the polar plot and highest
magnitude values at the maximum radius.
Example: pattern(dipole,70e6)
Set of angles, specified as a vector in degrees.
Set of magnitude values, specified as a vector or a matrix. For a matrix of magnitude values, each column is an independent set of magnitude values and corresponds to the same set of angles.
Version History
Introduced in R2016a
See Also
addCursor | animate | createLabels | findLobes | replace | showPeaksTable | showSpan
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)