Torque Converter
Torque converter coupling between two drive shafts
Libraries:
Simscape /
Driveline /
Couplings & Drives
Description
The Torque Converter block represents an automotive torque converter that comprises an impeller, a turbine, and a stator. The impeller and the turbine make up the fluid coupling, and the stator increases torque by redirecting the flow returning to the impeller. As the shaft turns the impeller, centrifugal force flings the fluid outward toward the turbine blades, which causes the turbine to spin as the fluid proceeds to the center and out toward the stator. Use the block to connect an engine to an automatic transmission. Connect port I to the engine and port T to the transmission.

By default, the block constrains , the torque at port T, and , the torque at port I, to one another for a given time step.
You can optionally include the effect of torque transmission time lag that is caused by
internal fluid flow and compressibility. To include transmission lag, set Model
transmission lag to Specify time constant and initial
value. The block introduces the lag and finds the steady state torque at port
I such that
The instantaneous function of the capacity factor K determines the steady-state value of τI. The block operates in drive mode when power flows from port I to port T. The block operates in coast mode when power flows in reverse. You can simulate the coast mode transition continuously or by using mode charts. The block uses the capacity factor for the torque converter to calculate torque from angular speed.
Two Mode Coast Transition
When you set Coast mode modeling to Two
mode, the block uses separate modes for coasting or driving. The block
computes the torque from angular speed such that
where K* is the Drive mode capacity factor vector parameter and ω is the angular speed for either port I or port T. The capacity factor is a function of the speed ratio. When in drive mode, the block defines the speed ratio as
where ωT and ωI represent the speeds at ports T and I, respectively. When in coast mode, the block defines the speed ratio as
Because of the different speed ratio definitions, the block also uses a
separate capacity factor for the coast mode, , which is the Coast mode capacity factor vector
parameter. The Mode transition parameter determines the speed at
which the block changes modes. The graphic illustrates the two modes.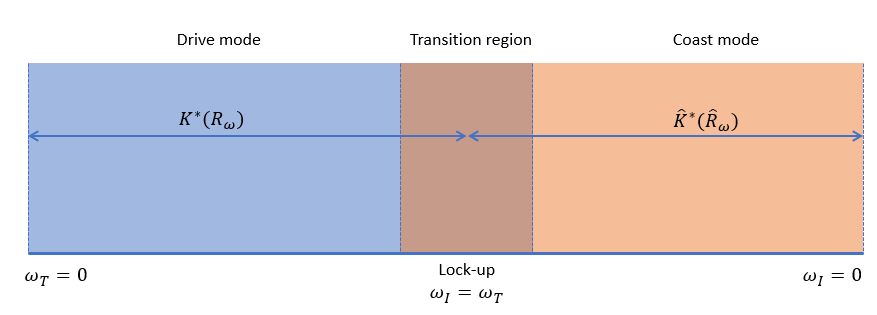
Continuous Coast Transition
When you set Coast mode modeling to
Continuous, the block smoothly transitions between drive and
coast mode. You can also add dynamics. The block simulation is less accurate when operating
near the transition region.
The block defines the speed ratio as and the torque ratio as . The Capacity factor parameterization parameter controls how the block defines the capacity factor. When you select:
Ratio of speed to square root of impeller torque, the block uses .Ratio of impeller torque to square of speed, the block uses .
To improve fidelity, you can include lag due to the transmission in your
simulation. When you set Model transmission lag to
Specify time constant and initial value, the block adds a
constant time delay to the torque transfer.
When you set Coast mode modeling to
Continuous:
The impeller shaft must always rotate in a positive direction. Simulation is not valid for < 0.
If you drive the Torque Converter block by using a torque source, such as the Generic Engine block, you must include an inertia in the source to represent the engine, shaft inertia, or other source components. To ensure that the impeller starts by rotating in a positive direction, set the initial speed for this inertia to a positive value.
Examples
Ports
Conserving
Parameters
References
[1] Society of Automotive Engineers. "Hydrodynamic Drive Test Code (Surface Vehicle Recommended Practice)." SAE J643. (December 2018) https://doi.org/10.4271/J643_201812