이 페이지는 기계 번역을 사용하여 번역되었습니다. 영어 원문을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.
polyspace-access -unset-project-information
프로젝트별 정보 제거
설명
시스템 명령어 polyspace-access -unset-project-information는 Polyspace® Access 프로젝트에서 기존 배너를 제거합니다.
polyspace-access -unset-project-information 는 지정된 프로젝트에서 기존 프로젝트 배너를 제거합니다.<projectPath> -host <hostname> [login options] [output options]
예제
개별 프로젝트 또는 프로젝트 폴더에서 배너를 설정하거나 교체하거나 제거할 수 있습니다. 배너는 Polyspace Access 웹 인터페이스에서 프로젝트 또는 프로젝트 폴더를 볼 때 표시됩니다.
프로젝트 public/Bug_Finder_Example (Bug Finder)에 배너를 설정하세요.
polyspace-access -set-project-information "public/Bug_Finder_Example (Bug Finder)" ^
-banner "Must adhere to MISRA C++:2023" ^
-host myAccessServer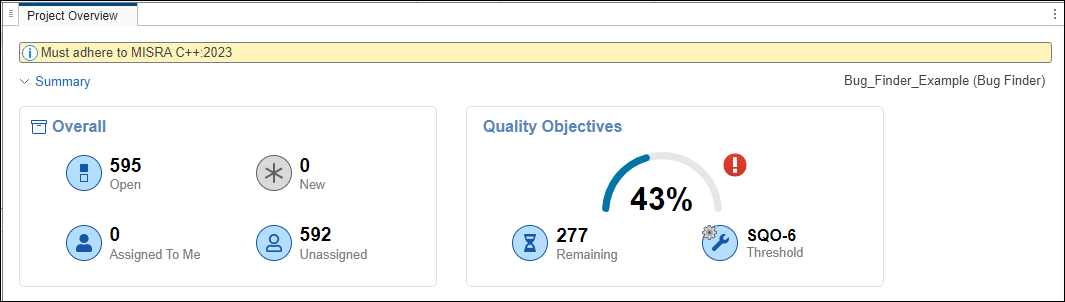
프로젝트 public/CP/Code_Prover_Example (Polyspace Code Prover)에서 배너를 제거하십시오.
polyspace-access -unset-project-information "public/CP/Code_Prover_Example (Polyspace Code Prover)" ^
-host myAccessServer입력 인수
프로젝트 관리 및 보기
프로젝트의 절대 경로로, 문자열로 지정됩니다. 경로 이름에 공백이 포함되어 있으면 큰따옴표를 사용하세요.
예: public/Folder/projectName
예: "public/Folder/Project with spaces"
연결 구성
Polyspace Access 인터페이스의 URL에 지정하는 Polyspace Access 머신 hostname, 예를 들어 https://. 사용할 호스트 이름을 확실히 모르시는 경우, 귀하의 Polyspace Access 관리자에게 문의하십시오. hostname:portNumber/metrics/index.html
-generate-migration-commands 및 -encrypt-password 명령어를 제외한 모든 polyspace-access 명령어에는 호스트 이름을 반드시 지정해야 합니다.
예: -host myAccessServer
Polyspace Access 인터페이스의 URL에서 지정하는 포트 번호(예: https://). 어떤 포트 번호를 사용해야 할지 확실하지 않으면 Polyspace Access 관리자에게 문의하세요.hostname:portNumber/metrics/index.html
Polyspace Access에 접근하는 데 사용되는 HTTP 프로토콜로, http 또는 https로 지정됩니다.
로그인 자격 증명을 저장하는 텍스트 파일의 전체 경로입니다. 스크립트에서 Polyspace Access 자격 증명이 필요한 명령어를 사용하지만 해당 스크립트에 자격 증명을 저장하고 싶지 않은 경우 이 옵션을 사용하십시오. 스크립트가 실행되는 동안 현재 실행 중인 프로세스를 검사하는 사람은 자격 증명을 볼 수 없습니다.
파일에는 자격 증명 세트를 하나만 저장할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, -login 및 -encrypted-password 항목을 별도의 줄에 저장할 수 있습니다.
-login jsmith -encrypted-password LAMMMEACDMKEFELKMNDCONEAPECEEKPL
-api-key 항목으로 자격 증명을 저장할 수도 있습니다:-api-key keyValue123
login.txt 파일에 대한 읽기 및 쓰기 권한을 제한하려면 다음 명령을 사용합니다.chmod go-rwx login.txt
로그인 정보와 암호화된 비밀번호를 제공하는 대신 로그인 자격 증명으로 사용하는 API 키입니다. 사용자에게 API 키를 할당하려면 User Manager 구성하기를 참조하거나 Polyspace Access 관리자에게 문의하세요.
Jenkins®와 같은 CI 툴을 사용하는 자동화 스크립트에서 Polyspace Access 로그인 자격 증명이 필요한 명령을 사용하는 경우 API 키를 사용하십시오. 사용자가 비밀번호를 업데이트하더라도, 해당 사용자와 연결된 API 키를 스크립트에서 업데이트할 필요는 없습니다.
API 키를 텍스트 파일에 저장하고, -credentials-file 옵션을 사용하여 해당 파일을 명령어에 전달하는 것이 좋습니다.
Polyspace Access와 상호작용할 때 사용하는 로그인 사용자 이름.
-login 및 -encryped-password 옵션을 함께 사용하십시오. 이 두 옵션을 함께 사용하지 않으면, -api-key를 사용하지 않는 한 명령줄에서 자격 증명을 입력하라는 메시지가 표시됩니다.
Polyspace Access과 상호작용할 때 사용하는 로그인 비밀번호입니다. <ENCRYPTED_PASSWORD>는 polyspace-access -encrypt-password
-login 및 -encryped-password 옵션을 함께 사용하십시오. 이 두 옵션을 함께 사용하지 않으면, -api-key 옵션을 사용하지 않는 한 명령줄에서 자격 증명을 입력하라는 메시지가 표시됩니다.
클라이언트 컴퓨터에서 Polyspace Access를 호스팅하는 서버 컴퓨터로 업로드할 때 polyspace-access 명령어가 실패하기 전까지 결과를 업로드하기 위해 재시도하는 횟수. 산발적인 네트워크 중단이 발생할 경우 업로드 명령을 다시 시도하려면 이 옵션을 지정합니다. 해당 명령은 재시도 사이에 10초간 기다립니다.
명령 출력의 전체 경로.
polyspace-access 명령어로 생성된 임시 파일을 저장하는 폴더 경로. 기본 폴더 경로는 사용 중인 플랫폼에 따라 다릅니다:
Windows —
C:\Users\%username%\AppData\Local\Temp\ps_results_serverLinux —
tmp/ps_results_server
명령 출력 로그를 저장하는 파일 경로입니다. 기본적으로 이 명령은 로그 파일을 생성하지 않습니다.
버전 내역
R2019a에 개발됨
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)