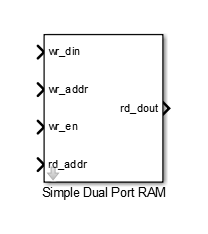
Simple Dual Port RAM
(To be removed) Dual port RAM with single output port
Simple Dual Port RAM will be removed in a future release. Use the Simple Dual Port RAM System instead.
Libraries:
HDL Coder /
HDL RAMs
Description
The Simple Dual Port RAM block models RAM that supports simultaneous read and write operations, and has a single output port for read data. You can use this block to generate HDL code that maps to RAM in most FPGAs.
The Simple Dual Port RAM is similar to the Dual Port RAM, but the Dual Port RAM has both a write data output port and a read data output port.
Read-During-Write Behavior
During a write operation, if a read operation occurs at the same address, old data appears at the output.
Ports
Input
Data that you write into the RAM memory location when wr_en is
true. The data inherits the width and data type from the input signal.
wr_din can be a double,
single, integer, or a fixed-point
(fi) object, and can be real or complex.
Data type: scalar fixed point, integer, or complex
Data Types: int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | fixed point
Write address.
Address that you write the data into when wr_en is true. This
value can be either fixed-point(fi) or integer,
must be unsigned, and have a fraction length of 0.
Data Types: uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | fixed point
When wr_en is true, the RAM writes the data into the memory
location that you specify.
Data Types: Boolean
Address that you read the data from. This value can be either
fixed-point(fi) or integer, must be unsigned,
and have a fraction length of 0.
Data Types: uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | fixed point
Output
Output data from read address, rd_addr.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point | enumerated | bus
Parameters
Minimum bit width is 2, and maximum bit width is 29.
Programmatic Use
Block parameter:
ram_size |
| Type: string scalar | character vector |
Value: A minimum value of
2 and maximum value of 29 |
Default:
'8' |
Algorithms
HDL code generated for RAM blocks has:
A latency of one clock cycle for read data output.
No reset signal, because some synthesis tools do not infer a RAM from HDL code if it includes a reset.
Code generation for a RAM block creates a separate file,
blockname.ext. blockname is derived
from the name of the RAM block. ext is the target language file
name extension.
Code generated to initialize a RAM is intended for simulation only. Synthesis tools can ignore this code.
The HDL block property, RAMArchitecture, enables or suppresses
generation of clock enable logic for all RAM blocks in a
subsystem. You can set RAMArchitecture to the following values:
WithClockEnable(default): Generates RAM using HDL templates that include a clock enable signal, and an empty RAM wrapper.WithoutClockEnable: Generates RAM without clock enables, and a RAM wrapper that implements the clock enable logic.
Some synthesis tools do not infer RAM with a clock enable. If your synthesis tool does
not support RAM structures with a clock enable, and cannot map your generated HDL code to
FPGA RAM resources, set RAMArchitecture to
WithoutClockEnable.
To learn how to generate RAM without clock enables for your design, see the Getting Started with RAM and ROM example. To open the example, at the command prompt, enter:
openExample('hdlcoder/GettingStartedWithRAMAndROMInSimulinkExample');
If you use RAM blocks to perform concurrent read and write operations, verify the read-during-write behavior in hardware. The read-during-write behavior of the RAM blocks in Simulink® matches that of the generated behavioral HDL code. However, if a synthesis tool does not follow the same behavior during RAM inference, it causes the read-during-write behavior in hardware to differ from the behavior of the Simulink model or generated HDL code.
Your synthesis tool might not map the generated code to RAM for the following reasons:
Small RAM size: your synthesis tool uses registers to implement a small RAM for better performance.
A clock enable signal is present. You can suppress generation of a clock enable signal in RAM blocks, as described in Implement RAM With or Without Clock Enable.
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using Simulink® Coder™.
HDL Coder™ provides additional configuration options that affect HDL implementation and synthesized logic.
This block has one default HDL architecture.
| General | |
|---|---|
| ConstrainedOutputPipeline | Number of registers to place at
the outputs by moving existing delays within your design. Distributed
pipelining does not redistribute these registers. The default is
|
| InputPipeline | Number of input pipeline stages
to insert in the generated code. Distributed pipelining and constrained
output pipelining can move these registers. The default is
|
| OutputPipeline | Number of output pipeline stages
to insert in the generated code. Distributed pipelining and constrained
output pipelining can move these registers. The default is
|
| RAMDirective | Specify whether to map RAM blocks in your design to distributed RAMs, block RAMs, or UltraRAM memory on the target FPGA. See also RAMDirective. |
This block supports code generation for complex signals.
The Simple Dual Port RAM
System block implementation uses a MATLAB System block that uses
the hdl.RAM
System object™. Use this block to perform simultaneous read and write operations. It has a
single output port to read data. In the Block Parameters dialog box of the block, you can
specify an initial value for the RAM.
Use this block to replace the Simple Dual Port RAM block in your model. You obtain faster simulation results when using this block in your model.
Version History
Introduced in R2014aThe Simple Dual Port RAM is no longer recommended. This block will be removed in a future release. Instead, use the Simple Dual Port RAM System block. For more information, see Simple Dual Port RAM System.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)