지상 감시
아래의 예제에서는 공항 및 산악 지형과 같은 지상 부근 영역의 타깃을 추적합니다.
추천 예제
Extended Object Tracking with Lidar for Airport Ground Surveillance
An apron is a defined area at the airport intended to accommodate aircraft for purposes of loading or unloading passengers, mail or cargo, fueling, parking or maintenance [1]. Airport aprons are usually highly dynamic and heterogeneous environments where apron personnel and vehicles operate in close proximity to each other. Due to such nature of the aprons, it presents a higher risk for ground handling accidents involving aircraft as well as ground personnel. Lidar-based surveillance systems at aprons have been proposed as an effective method to improve the situation picture and to serve as a measure to mitigate high risk at the aprons [2].
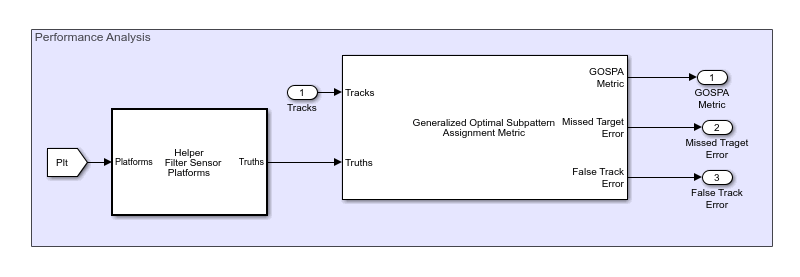
Simulate and Track Targets with Terrain Occlusions
Model a surveillance scenario in a mountainous region where terrain can occlude both ground and aerial vehicles from the surveillance radar. You define a tracking scenario with geo-referenced terrain data from a Digital Terrain Elevation Data (DTED) file, create trajectories following terrain, simulate the scenario, and track targets with a multi-object tracker.
- R2022a 이후
- 라이브 스크립트 열기
Track Point Targets in Dense Clutter Using GM-PHD Tracker
Track points targets in dense clutter using a Gaussian mixture probability hypothesis density (GM-PHD) tracker using a constant velocity model.
Track Point Targets in Dense Clutter Using GM-PHD Tracker in Simulink
Radars generally receive echoes from all surfaces in the signal path. These unwanted back-scattered signals or echoes generated from physical objects are called clutter. In a densely cluttered environment, missed detections and false alarms make tracking objects a challenging task for conventional trackers such as Global Nearest-Neighbor (GNN) tracker. In such an environment a PHD tracker provides better estimation of objects as it can handle multiple detections per object per sensor without clustering them first. This example shows you how to track points targets in dense clutter using a Gaussian mixture probability hypothesis density (GM-PHD) tracker with a constant velocity model in Simulink. The example closely follows the Track Point Targets in Dense Clutter Using GM-PHD Tracker MATLAB® example.
- R2021a 이후
- 모델 열기
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)