영공 추적
아래의 예제에서는 항공 교통 관제와 일반 레이다 감시를 위해 영공 내의 타깃을 추적합니다.
추천 예제
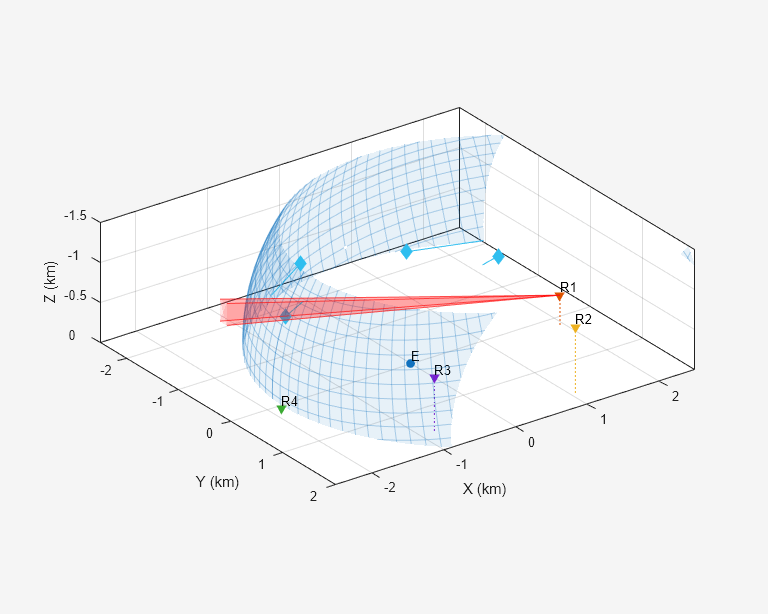
Track Targets Using Asynchronous Bistatic Radars
Builds upon the Tracking Using Bistatic Range Detections example and shows how to configure a multi-sensor multi-target tracker to track targets using asynchronous bistatic radars that report range and angles. Bistatic sensors are advantageous because the emitter part and the receiver part of the sensor are not collocated, which makes the receivers less detectable. Additionally, they allows many receivers to work with a single emitter. Therefore, bistatic sensors are becoming more common in various applications where it is beneficial to hide the receivers or reduce the amount of energy they consume.
- R2025a 이후
- 라이브 스크립트 열기
Use Truth Analysis to Track Maneuvering Targets
In this example, you will learn how to specify a tracker target specification for a maneuvering aircraft based on knowledge gained from analyzing recorded truth. You will then use this tracker target specification to define a multi-object tracker.
- R2025a 이후
- 라이브 스크립트 열기
Cooperative Bistatic Radar I/Q Simulation and Processing
Simulate I/Q for a cooperative bistatic system and perform subsequent signal processing for a single bistatic transmitter and receiver pair.
(Radar Toolbox)
- R2024b 이후
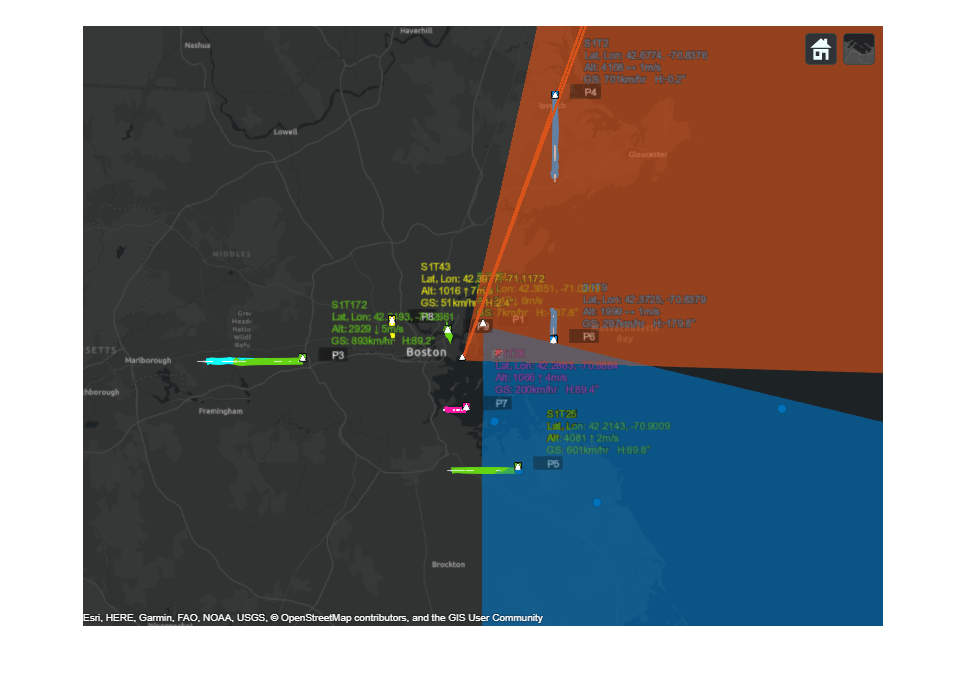
Track Heterogeneous Aircraft using Heterogeneous Sensors
Track heterogeneous aircraft using data collected by heterogeneous sensors. In the example, you track commercial passenger aircraft, general aviation aircraft, and helicopters flying in the airspace near the Logan International Airport in Boston, MA. You use active and passive radars and their outputs to track the aircraft using a JIPDATracker.
- R2024b 이후
- 라이브 스크립트 열기
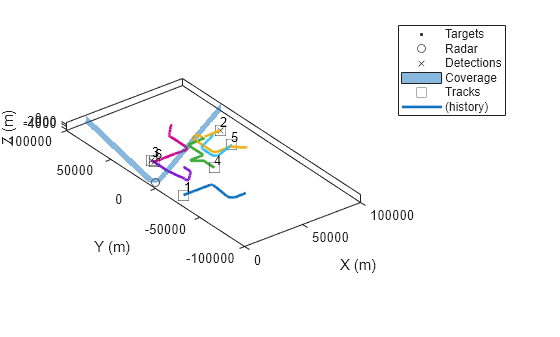
Air Traffic Control
Generate an air traffic control scenario, simulate radar detections from an airport surveillance radar (ASR), and configure a global nearest neighbor (GNN) tracker to track the simulated targets using the radar detections. This enables you to evaluate different target scenarios, radar requirements, and tracker configurations without needing access to costly aircraft or equipment. This example covers the entire synthetic data workflow.
Simulate and Track En-Route Aircraft in Earth-Centered Scenarios
Use an Earth-Centered trackingScenario and a geoTrajectory object to model a flight trajectory that spans thousands of kilometers. You use two different models to generate synthetic detections of the airplane: a monostatic radar and ADS-B reports. You use a multi-object tracker to estimate the plane trajectory, compare the tracking performance, and explore the impact that ADS-B provides on the overall tracking quality.
Simulate, Detect, and Track Anomalies in a Landing Approach
The example shows how to automatically detect deviations and anomalies in aircraft making final approaches to an airport runway. In this example, you will model an ideal landing approach trajectory and generate variants from it, simulate radar tracks, and issue warnings as soon as the tracks deviate from safe landing rules.
Multiplatform Radar Detection Fusion
Fuse radar detections from a multiplatform radar network. The network includes two airborne and one ground-based long-range radar platforms. See the Multiplatform Radar Detection Generation example for details. A central tracker processes the detections from all platforms at a fixed update interval. This enables you to evaluate the network's performance against target types, platform maneuvers, as well as platform configurations and locations..
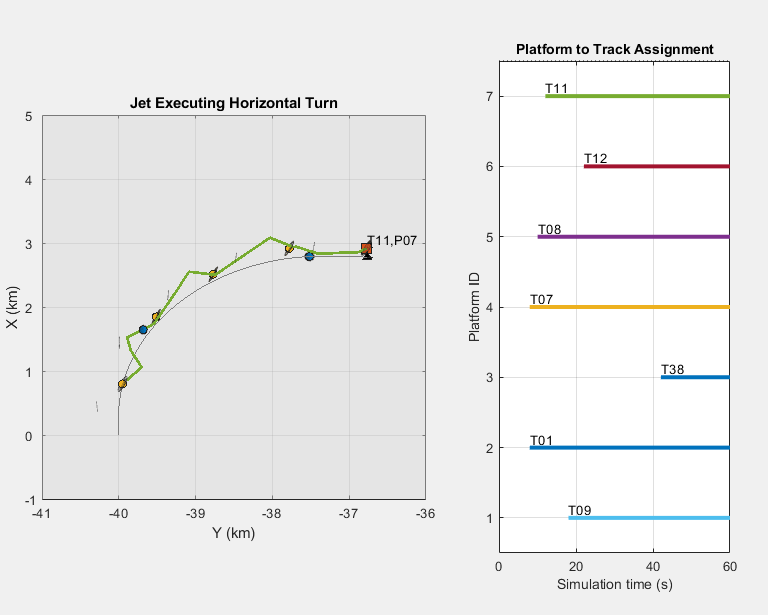
Adaptive Tracking of Maneuvering Targets with Managed Radar
Use radar resource management to efficiently track multiple maneuvering targets. Tracking maneuvering targets requires the radar to revisit the targets more frequently than tracking non-maneuvering targets. An interacting multiple model (IMM) filter estimates when the target is maneuvering. This estimate helps to manage the radar revisit time and therefore enhances the tracking. This example uses the Radar Toolbox™ for the radar model and Sensor Fusion and Tracking Toolbox™ for the tracking.
Air Traffic Control in Simulink
Create a tracking system for an air traffic control center using a global nearest neighbor (GNN) tracker in Simulink.
- R2022b 이후
- 라이브 스크립트 열기
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)