Configure Class Interface
In this step of the tutorial, you configure the C++ class interface. A customized C++ class interface enables the generated classes to meet specific code standards or interface requirements so that the generated code can compile and integrate into larger architectures requiring minimal post-generation customization.
To customize the class interface of model CppClassWorkflowKeyIgnition:
Change the class name to
engine_status.Set the class namespace to
en1.Configure the inports of the model as public with a set method for access.
Configure the outports of the model as public with an aggregate structure-based get method to access all output ports.
Update the names of the initialize and terminate entry-point methods.
Configure Model Class Name and Namespace
If the model
CppClassWorkflowKeyIgnitionis not open, open the model.openExample("CppClassWorkflowKeyIgnition.slx")On the C++ Code tab, click Code Interface and select Class Name & Namespace.
Edit the C++ Class Name field to
engine_status.Enter
en1in the C++ Class Namespace field.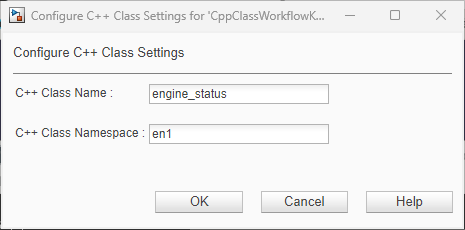
Click OK. Validation is performed interactively with field warnings that alert you if you enter an invalid name or namespace.
Save the model, and then click Build to build and regenerate the code.
In the Code view, search for
engine_statusto view the change in the generated code.
Configure Visibility and Access of Class Members
Open the Code Mappings editor.
To open the Code Mappings editor, on the C++ Code tab, click Code Interface and select Code Mappings.
Click the Data tab to open the Data pane.
The Code Mappings spreadsheet displays visibility and access information for each category of model element.
Configure Inports.
In the Data Visibility column, select
public.In the Member Access Method column, select
Inlined method.
Configure Outports.
In the Data Visibility column, select
public.In the Member Access Method column, select
Structure-based method.
Save the model, and click Build to build and regenerate the code.
In the model
CppClassWorkflowKeyIgnition, click the Inport blockkeyState.Place your cursor over the ellipsis menu above the block and click Navigate To Code.
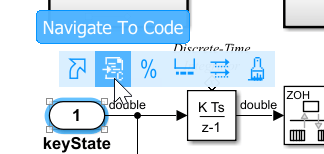
The Code view highlights code that corresponds to the block.
In the Code view, click the search arrows to locate the public declaration and definition of the set method
setkeyStatefor the root inportkeyState.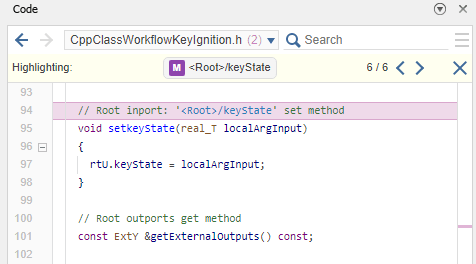
The get method for the aggregated root outports,
getExternalOutputs, is declared directly beneath the inport set method.Place your cursor over the identifier
ExtYin thegetExternalOutputsmethod declaration.A traceability dialog box displays definitions that correspond to the code.

In the traceability dialog box, click
struct ExtYto locate the structure.// External outputs (root outports fed by signals with default storage) struct ExtY { real_T engineState; // '<Root>/engineState' real_T cycleTime; // '<Root>/cycleTime' };In the search bar, type
getExternalOutputsand press Enter to locate the method definition inCppClassWorkflowKeyIgnition.cpp.
Configure Model Functions
Configure the class method names. When you generate C++ code from a model, model entry-point functions appear as class methods in the generated code. To integrate with external code or interface requirements, you can customize the name of the generated methods.
In the Code Mappings editor, click the Functions tab to view the class methods.
Configure the Initialize function name.
In the Method Name column, click and edit the spreadsheet to change the name to
initIntegrator.Configure the Terminate function name.
In the Method Name column, click and edit the spreadsheet to change the name to
terminateIntegrator.Verify the updated names in the Method Preview column.

Save the model, and then click Build to build and regenerate code.
In the Code view, search for the updated method names for the entry-point functions to view the generated code.
Next, simulate and verify the generated C++ code.