Matrix Sum (Obsolete)
Sum matrix elements along rows, columns, or entire input
Library
Math Functions / Matrices and Linear Algebra / Matrix Operations
dspobslib
Description
The Matrix Sum block sums the elements of an M-by-N input matrix u along its rows, its columns, or over all its elements.
When the Sum over parameter is set to Rows,
the block sums across the elements of each row and outputs the resulting
M-by-1 matrix. A length-N 1-D vector input is treated as a
1-by-N matrix.
When the Sum over parameter is set to
Columns, the block sums down the elements of each column and outputs
the resulting 1-by-N matrix. A length-M 1-D vector input is
treated as a M-by-1 matrix.
When the Sum over parameter is set to Entire
input, the block sums all the elements of the input together and outputs the
resulting scalar.
The output of the Matrix Sum block has the same frame status as the input. This block accepts real and complex fixed-point and floating-point inputs except for complex unsigned fixed-point inputs.
Fixed-Point Data Types
The following diagram shows the data types used within the Matrix Sum block for fixed-point signals.

You can set the accumulator and output data types in the block dialog as discussed in Dialog Box below.
Dialog Box
The Main pane of the Matrix Sum block dialog appears as follows.
- Sum over
Indicate whether to sum the elements of each row, each column, or of the entire input.
The Fixed-point pane of the Matrix Sum block dialog appears as follows.
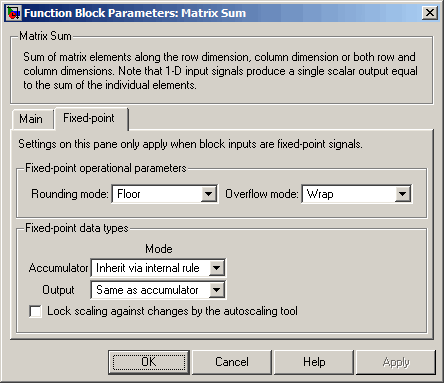
- Rounding mode
Select the rounding mode for fixed-point operations.
- Overflow mode
Select the overflow mode for fixed-point operations.
- Accumulator

As depicted above, the elements of the block input are cast to the accumulator data type before they are added together. The output of the adder remains in the accumulator data type as each element of the input is added to it. Use this parameter to specify how you would like to designate this accumulator word and fraction lengths:
When you select
Inherit via internal rule, the accumulator word length and fraction length are calculated automatically. For information about how the accumulator word and fraction lengths are calculated when an internal rule is used, see Inherit via Internal Rule.When you select
Same as input, these characteristics match those of the input to the block.When you select
Binary point scaling, you can enter the word length and the fraction length of the accumulator, in bits.When you select
Slope and bias scaling, you can enter the word length, in bits, and the slope of the accumulator. This block requires power-of-two slope and a bias of zero.
- Output
Choose how you specify the output word length and fraction length:
When you select
Same as accumulator, these characteristics match those of the accumulator.When you select
Same as input, these characteristics match those of the input to the block.When you select
Binary point scaling, you can enter the word length and the fraction length of the output, in bits.When you select
Slope and bias scaling, you can enter the word length, in bits, and the slope of the output. This block requires power-of-two slope and a bias of zero.
- Lock scaling against changes by the autoscaling tool
Select this parameter to prevent any fixed-point scaling you specify in this block mask from being overridden by the autoscaling feature of the Fixed-Point Tool. See the
fxptdlg(Fixed-Point Designer) reference page for more information.
Supported Data Types
Port | Supported Data Types |
|---|---|
Input |
|
Output |
|
See Also
| Matrix Product | DSP System Toolbox |
| Matrix Multiply (Simulink) | DSP System Toolbox |
sum | MATLAB |
Version History
Introduced in R2008b
