SI Engine Torque Structure Model
The spark-ignition (SI) engine implements a simplified version of the SI engine torque structure calculation used in a Bosch Engine Management System (EMS). For the torque structure estimation calculation, the block requires calibration tables for:
Inner torque — Maximum torque potential of the engine at a given speed and load
Friction torque — Torque losses due to friction
Optimal spark — Spark advance for optimal inner torque
Spark efficiency — Torque loss due to spark retard from optimal
Lambda efficiency — Torque loss due to lambda change from optimal
Pumping torque — Torque loss due to pumping
The tables available with Powertrain Blockset™ were developed with the Model-Based Calibration Toolbox™.
| Lookup Table | Used to Determine | Plot |
|---|---|---|
|
Inner torque, |
|
The inner torque lookup table, , is a function of engine speed and engine load, , where:
|
|
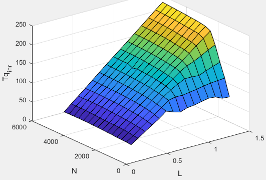
Friction torque, |
|
The friction torque lookup table, , is a function of engine speed and engine load, , where:
|
|
Pumping torque, ƒTpump |
|
The pumping torque lookup
table, ƒTpump, is a function of engine load and engine
speed,
|
|
Optimal spark, |
|
The optimal spark lookup table, , is a function of engine speed and engine load, , where:
|
|
Spark efficiency, |
|
The spark efficiency lookup table, , is a function of the spark retard from optimal where:
|
|
Lambda efficiency, |
|
The lambda efficiency lookup table, , is a function of lambda, , where:
|
The engine brake torque is a based on inner torque with lambda efficiency, spark retard efficiency multipliers, pumping torque, and a friction torque offset
To account for thermal effects, the torque structure model corrects the friction torque calculation as a function of coolant temperature.
The pumping torque is a function of engine speed and engine speed.
|
Optimal spark advance timing for maximum inner torque at stoichiometric air-fuel ratio (AFR) | |
|
Spark retard timing distance from optimal spark advance | |
|
Spark advance timing | |
|
Engine load at arbitrary cam phaser angles, corrected for final steady-state cam phaser angles | |
| N |
Engine speed |
|
Lambda multiplier on inner torque to account for the AFR effect | |
|
Lambda, AFR normalized to stoichiometric fuel AFR | |
|
Spark retard efficiency multiplier | |
|
Spark efficiency lookup table to account for torque loss due to spark retard from optimal | |
|
Friction torque lookup table to account for torque losses due to friction | |
|
Lambda efficiency lookup table to account for torque loss due to lambda change from optimal | |
|
Optimal spark lookup table, for maximum inner torque as a function of engine speed and load | |
|
Inner torque lookup table, for maximum torque potential of the engine at a given speed and load | |
|
Engine brake torque after accounting for spark advance, AFR, and friction effects | |
|
Friction torque offset to inner torque | |
|
Inner torque based on gross indicated mean effective pressure | |
| Tpump |
Pumping torque |
| Mfric |
Friction torque modifier |
| Tcoolant |
Coolant temperature |
References
[1] Gerhardt, J., Hönninger, H., and Bischof, H., A New Approach to Functional and Software Structure for Engine Management Systems – BOSCH ME7. SAE Technical Paper 980801, 1998.
See Also
SI Controller | SI Core Engine