Projector Controller Testing Using verify and Real-Time Tests
This example demonstrates testing a projector control system using model simulation and real-time execution on a target computer. The tests verify the controller by using test sequence scenarios that exercise the top-level controller model. The controller uses a push button input and a temperature sensor input, and outputs signals controlling the fan, fan speed, and projector lamp.
Set up the test file, model, and internal harness names for the example.
testFile = 'sltestProjectorCtrlTests.mldatx'; model = 'sltestProjectorController'; testharness = 'Test_Scenarios';
Open the model.
open_system(model)
View the Test Harness
Open the Test_Scenarios test harness.
sltest.harness.open(model,testharness);
The test harness uses a Test Sequence block to define the test scenarios and a Test Assessment block to verify the results.

In the test harness, open the Test Sequence block to view the scenarios, which are defined in tabs.

Open the Test Assessment block to view the verify statements.

Open the Test File and Configure the Real-Time Target Computer
Open the test file in the Test Manager by entering:
open(testFile)
The test file contains a test suite with two test cases, each of which tests the four test scenarios. The Simulation_Tests test case simulates the model, and the HIL_Tests test case runs the tests on a real-time target computer.
Before running the example:
Configure your target computer using the Simulink Real-Time Explorer.
Connect to your target computer.
If your target computer is not the default target, update Target Computer in the HIL_Tests test case's System Under Test section.
For more information on real-time configuration see System Configuration (Simulink Real-Time).
Run the Model Simulation Tests
Run the Simulation_Tests test case. After simulation completes, click the Results and Artifacts pane in the Test Manager.
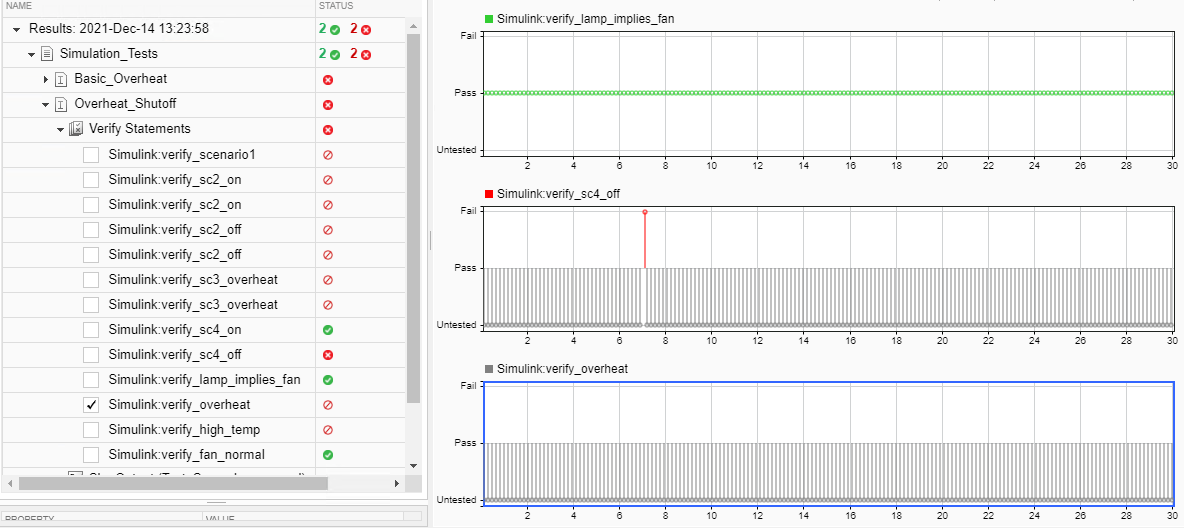
Expand the Simulation_Tests results and the four scenarios. Select one of the Verify Statement check boxes to view the results in the Data Inspector tab. The results in the Verify Statements section demonstrate fail, pass, and untested results:
In all scenarios except Basic_Overheat, the controller does not operate in high-temperature or overheat mode, so the
verify_overheatandverify_high_tempstatements of the associatedverifystatements are untested.In all scenarios, the controller passes the test that if the lamp is on, the fan is also on:
verify_lamp_implies_fan.In the Overheat_Shutoff scenario, the controller passes the test that the system stays off if the on_off button is pressed when the temperature is above a limit:
verify_sc4_on. For other scenarios,verify_sc4_onis untested.In only the Overheat_Shutoff scenario, the controller fails the test that the system shuts off if the on_off button is pressed when the temperature is above a limit:
verify_sc4_off. Resolving this failure requires modifying theOnOff Checksubsystem in the main model.
For more information, see Verify Model Simulation by Using when Decomposition.
In the Overheat_Shutoff scenario, in the Inspect pane, select the verify_sc4_off, verify_lamp_implies_fan, and verify_overheat results.
Execute the Real-Time Tests and Review the Results
The real-time test case (HIL_Tests) verifies that real-time execution results match model simulation results, and that the verify statements pass.
In the Test Manager, run the real-time test case (HIL_Tests).
The results of the Simulation_Tests and HIL_Tests show matching pass, fail, and untested statuses.
In the Overheat_Shutoff scenario, in the Inspect pane, select verify_sc4_off, verify_lamp_implies_fan, and verify_overheat to visualize the results. The Verify Statements section shows similar results to the model simulation.

close_system(testharness,0) close_system(model,0) sltest.testmanager.clear; sltest.testmanager.clearResults; sltest.testmanager.close clear testFile testHarness model;
See Also
Test Sequence | Test Assessment