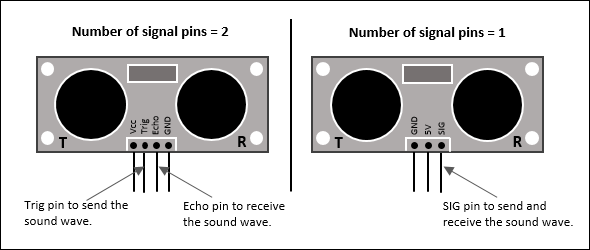
Ultrasonic Sensor
Add-On Required: This feature requires the Simulink Support Package for Raspberry Pi Hardware add-on.
Libraries:
Simulink Support Package for Raspberry Pi Hardware /
Sensors
Description
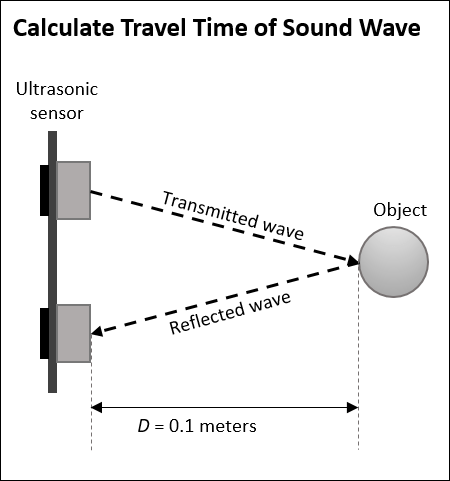
The Ultrasonic Sensor block outputs the distance between the ultrasonic
sensor connected to the hardware and the nearest object in front of the sensor. The
block outputs the distance as a double-precision value, in meters. If the object is
placed beyond the range of sensor detection, the block outputs 0.
If you simulate a model that contains the Ultrasonic Sensor block without connecting the hardware, the block outputs zeros. For more information, see Block Produces Zeros or Does Nothing in Simulation.
Ports
Output
Parameters
More About
Version History
Introduced in R2022b