phased.WidebandRadiator
Wideband signal radiator
Description
The phased.WidebandRadiator
System object™ implements a wideband signal radiator. A radiator converts signals into radiated
wavefields transmitted from arrays and individual sensor elements such as antennas, microphone
elements, and sonar transducers. The radiator output represents the fields at a reference
distance of one meter from the phase center of the element or array. The algorithm divides the
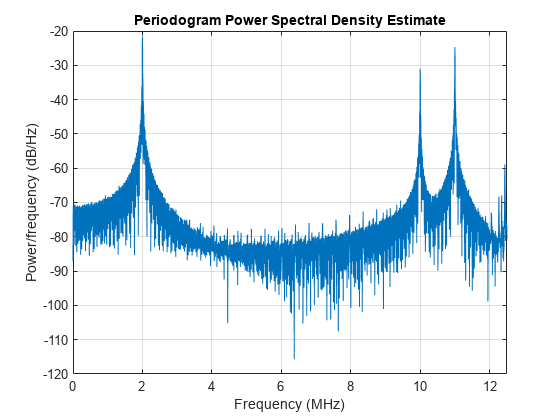
signal at each element into frequency subbands and applies a narrowband time-delay to each
signal using the phase-shift approximation. Then, the delayed subbands are coherently added to
create the output signal. You can then propagate the signals to the far field using, for
example, the phased.WidebandFreeSpace or phased.WidebandLOSChannel System objects. You can use this object to
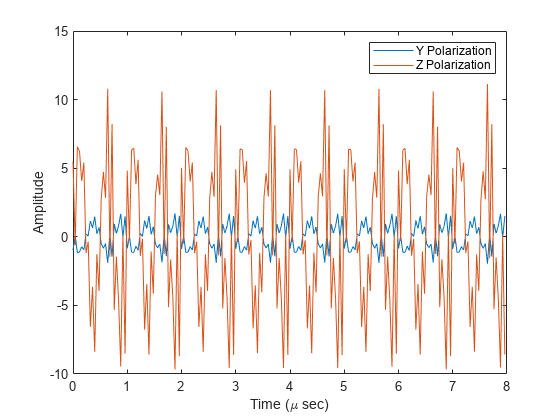
model radiated signals as polarized or non-polarized fields depending upon whether the element or array supports polarization and the value of the Polarization property. Using polarization, you can transmit a signal as a polarized electromagnetic field, or transmit two independent signals using dual polarizations.
model acoustic radiated fields by using nonpolarized microphone and sonar transducer array elements and by setting the Polarization to
'None'. You must also set the PropagationSpeed to a value appropriate for the medium.radiate fields from subarrays created by the
phased.ReplicatedSubarrayandphased.PartitionedArrayobjects. You can steer all subarrays in the same direction using the Steering angle argument,STEERANG, or steer each subarray in a different direction using the Subarray element weights argument,WS. The radiator distributes the signal powers equally among the elements of each subarray.
To radiate signals:
Create the
phased.WidebandRadiatorobject and set its properties.Call the object with arguments, as if it were a function.
To learn more about how System objects work, see What Are System Objects?
Creation
Description
radiator = phased.WidebandRadiatorradiator, with default property
values.
radiator = phased.WidebandRadiator(Name,Value)Name set to a
specified Value. You can specify additional name-value pair arguments
in any order as
(Name1,Value1,...,NameN,ValueN).
Enclose each property name in single quotes.
Example: radiator =
phased.WidebandRadiator('Sensor',phased.URA,'CarrierFrequency',300e6) sets the
sensor array to a uniform rectangular array (URA) with default URA property values. The
beamformer has a carrier frequency of 300 MHz.
Properties
Usage
Syntax
Description
Y = radiator(X,ANG,LAXES)LAXES.
This syntax applies when you set the Polarization
property to 'Combined'.
Y = radiator(___,W)W as array element or subarray weights. To use this
syntax, set the WeightsInputPort property to true.
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
Object Functions
To use an object function, specify the
System object as the first input argument. For
example, to release system resources of a System object named obj, use
this syntax:
release(obj)
Examples
More About
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2015b