beamwidth
Compute and display beamwidth of a subarray
Description
beamwidth(
plots the 2-D power pattern (in dB) of the subarray,freq)subarray for all azimuth
angles at a fixed elevation angle of zero degrees. The plot displays the half-power
beamwidth (in degrees) at the frequency specified in freq (in Hz) and
the angles (in degrees) in azimuth at which the magnitude of the power pattern decreases by
3 dB from the peak of the main beam.
beamwidth(
computes and plots the beamwidth with the specified parameter subarray,freq,Name=Value)Name set
to the specified Value. You can specify additional name-value pair
arguments in any order as (Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN).
Example: beamwidth(subarray,5e8,Cut="Elevation")
Examples
Plot the beamwidth of a rectangular lattice array composed of two uniform rectangular arrays. Consider the antenna elements of the array to be cosine antenna elements.
First, construct a phased.CosineAntennaElement object.
myAnt = phased.CosineAntennaElement
myAnt =
phased.CosineAntennaElement with properties:
FrequencyRange: [0 1.0000e+20]
CosinePower: [1.5000 1.5000]
Next, construct a 5-by-5 uniform rectangular array by creating a phased.URA object.
myArray = phased.URA([5 5],[0.5 0.5],Element=myAnt,...
ElementSpacing=[0.15 0.15])myArray =
phased.URA with properties:
Element: [1×1 phased.CosineAntennaElement]
Size: [5 5]
ElementSpacing: [0.1500 0.1500]
Lattice: 'Rectangular'
ArrayNormal: 'x'
Taper: 1
Use two of these 5-by-5 uniform rectangular arrays to construct a 5-by-10 rectangular lattice. Construct the lattice using the phased.ReplicatedSubarray object.
myRSA = phased.ReplicatedSubarray('Subarray',myArray,... Layout="Rectangular",GridSize=[1 2],... GridSpacing="Auto",SubarraySteering="Phase")
myRSA =
phased.ReplicatedSubarray with properties:
Subarray: [1×1 phased.URA]
Layout: 'Rectangular'
GridSize: [1 2]
GridSpacing: 'Auto'
SubarraySteering: 'Phase'
PhaseShifterFrequency: 300000000
NumPhaseShifterBits: 0
Now visualize the 10dB beamwidth of the obtained lattice across the azimuth plane (0 degrees elevation). The subarray is phase steered toward 24 degrees azimuth. Assume the operating frequency of the array to be 1 GHz.
stv = phased.SteeringVector('SensorArray',myRSA); beamwidth(myRSA,1e9,'dBDown',10,'SteerAngle',24,'Weights',stv(1e9,24))
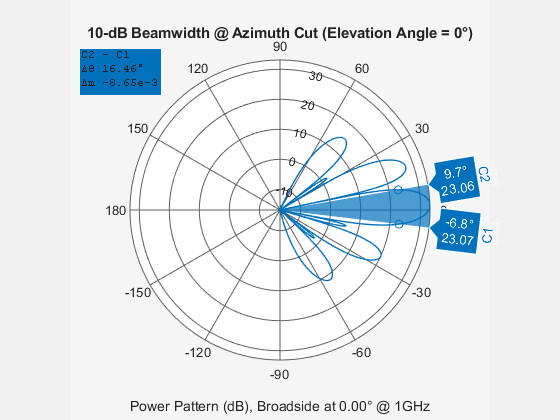
ans = 16.4600
Calculate the 3 dB beamwidth of a 10-element uniform linear array (ULA) composed of two 5-element ULAs across the azimuth plane and at 0 degrees elevation. By default, the antenna elements are isotropic. Assume the operating frequency of the array to be 500MHz.
myArray = phased.ULA(NumElements=5)
myArray =
phased.ULA with properties:
Element: [1×1 phased.IsotropicAntennaElement]
NumElements: 5
ElementSpacing: 0.5000
ArrayAxis: 'y'
Taper: 1
myRSA = phased.ReplicatedSubarray('Subarray',myArray,... GridSize=[1 2])
myRSA =
phased.ReplicatedSubarray with properties:
Subarray: [1×1 phased.ULA]
Layout: 'Rectangular'
GridSize: [1 2]
GridSpacing: 'Auto'
SubarraySteering: 'None'
[BW,Ang] = beamwidth(myRSA,5e8)
BW = 6.1200
Ang = 1×2
-3.0600 3.0600
Input Arguments
Subarray of sensor elements, specified as one of the following System objects:
Frequency used to calculate the beamwidth, specified as a scalar in Hz.
Example: 5e8
Data Types: double
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose
Name in quotes.
Example: beamwidth(subarray,5e8,Cut="Azimuth",CutAngle=45) plots the
beamwidth of the subarray that is operating at a frequency of 0.5 GHz, with the slice
direction set to "Azimuth", and the cut angle set to 45
degrees.
The slice direction in azimuth-elevation space along which the beamwidth is
computed, specified as the equal-sign-separated pair consisting of
Cut and "Azimuth" for the azimuth plane, and
Cut and "Elevation" for the elevation
plane.
Corresponding angle (in degrees) for the plane to get the required 2-D cut,
specified as the equal-sign-separated pair consisting of CutAngle
and a scalar. If Cut is specified as
"Azimuth", then CutAngle (Elevation) should
lie between [−90, 90] degrees. If Cut is specified as
"Elevation", then CutAngle (Azimuth) should
lie between [−180, 180] degrees.
Data Types: double
Power value (in dB) from the peak of the main lobe, specified as the
equal-sign-separated pair consisting of dBDown and a positive
scalar. The default value is 3 dB, which translates to half-power beamwidth. To
calculate the first-null beamwidth, specify the dBDown value as
Inf.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
Propagation speed, specified as the equal-sign-separated pair consisting of
PropagationSpeed and a positive scalar (in m/s).
Data Types: double
Weights applied to the array of sensor elements, specified as the
equal-sign-separated pair consisting of Weights and a
length-N column vector, where N is the number
of elements in the array.
Data Types: double
Subarray steering angle (in degrees), specified as the equal-sign-separated pair
consisting of 'SteerAngle' and a scalar or a length-2 column
vector. If the steering angle is a scalar, the value represents the azimuth angle and
the elevation angle is assumed to be 0. If the steering angle is a vector, the angle
is specified in the form of [AzimuthAngle; ElevationAngle].
Dependencies
This parameter is applicable when you set the
SubarraySteering property of subarray object
to either "Phase" or "Time".
Data Types: double
Weights applied to each element in the subarray, specified as the
equal-sign-separated pair consisting of ElementWeights and a
matrix or a cell array.
For a ReplicatedSubarray object,
ElementWeights must be a
NSE-by-N matrix, where NSE
is the number of elements in each individual subarray and N is the
number of subarrays. Each column in ElementWeights specifies the
weights for the elements in the corresponding subarray.
For a PartitionedArray object, if the individual subarrays have
the same number of elements, ElementWeights must be an
NSE-by-N matrix, where NSE
is the number of elements in each individual subarray and N is the
number of subarrays.
Each column in the WS property of the
subarray object specifies the weights for the elements in the
corresponding subarray. If subarrays in the PartitionedArray object
have different number of elements, ElementWeights can be one of
the following:
NSE-by-N matrix –– NSE indicates the number of elements in the largest subarray and N is the number of subarrays.
1-by-N cell array –– N is the number of subarrays and each cell contains a column vector whose length is the same as the number of elements of the corresponding subarray.
If WS is a matrix, the first K entries in
each column specify the weights for the elements in the corresponding subarray.
K is the number of elements in the corresponding subarray. If
WS is a cell array, each cell in the array is a column vector
specifying the weights for the elements in the corresponding subarray.
Dependencies
This parameter is applicable when you set the
SubarraySteering property of subarray object
to "Custom".
Data Types: double
Output Arguments
Angular beamwidth of the subarray, returned as a scalar in degrees.
Data Types: double
Angle values of the beamwidth, returned as a 1-by-2 vector. The two elements in the
vector [amin,
amax] define the beamwidth
bw as
amax−amin.
Version History
Introduced in R2020b
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
웹사이트 선택
번역된 콘텐츠를 보고 지역별 이벤트와 혜택을 살펴보려면 웹사이트를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에 따라 다음 웹사이트를 권장합니다:
또한 다음 목록에서 웹사이트를 선택하실 수도 있습니다.
사이트 성능 최적화 방법
최고의 사이트 성능을 위해 중국 사이트(중국어 또는 영어)를 선택하십시오. 현재 계신 지역에서는 다른 국가의 MathWorks 사이트 방문이 최적화되지 않았습니다.
미주
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
유럽
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)