Magnetic Flux Density in H-Shaped Magnet
This example shows how to solve a 2-D magnetostatic model for a ferromagnetic frame with an H-shaped cavity. This setup generates a uniform magnetic field due to the presence of two coils.
Create a geometry that consists of a rectangular frame with an H-shaped cavity, four rectangles representing the two coils, and a unit square representing the air domain around the magnet. Specify all dimensions in millimeters, and use the value convfactor = 1000 to convert the dimensions to meters.
convfactor = 1000;
Create the H-shaped geometry to model the cavity.
xCoordsCavity = [-425 -125 -125 125 125 425 425 ... 125 125 -125 -125 -425]/convfactor; yCoordsCavity = [-400 -400 -100 -100 -400 -400 ... 400 400 100 100 400 400]/convfactor; RH = [2;12;xCoordsCavity';yCoordsCavity'];
Create the geometry to model the rectangular ferromagnetic frame.
RS = [3;4;[-525;525;525;-525;-500;-500;500;500]/convfactor]; zeroPad = zeros(numel(RH)-numel(RS),1); RS = [RS;zeroPad];
Create the geometries to model the coils.
RC1 = [3;4;[150;250;250;150;120;120;350;350]/convfactor;
zeroPad];
RC2 = [3;4;[-150;-250;-250;-150;120;120;350;350]/convfactor;
zeroPad];
RC3 = [3;4;[150;250;250;150;-120;-120;-350;-350]/convfactor;
zeroPad];
RC4 = [3;4;[-150;-250;-250;-150;-120;-120;-350;-350]/convfactor;
zeroPad];Create the geometry to model the air domain around the magnet.
RD = [3;4;[-1000;1000;1000;-1000;-1000; ...
-1000;1000;1000]/convfactor;zeroPad];Combine the shapes into one matrix.
gd = [RS,RH,RC1,RC2,RC3,RC4,RD];
Create a set formula and create the geometry.
ns = char('RS','RH','RC1','RC2','RC3','RC4','RD'); g = decsg(gd,'(RS+RH+RC1+RC2+RC3+RC4)+RD',ns');
Plot the geometry with the face labels.
figure
pdegplot(g,FaceLabels="on")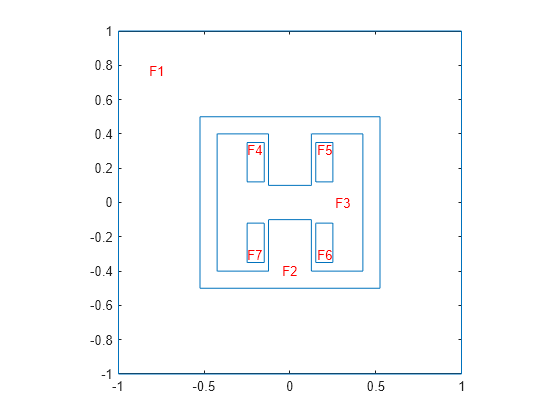
Plot the geometry with the edge labels.
figure
pdegplot(g,EdgeLabels="on")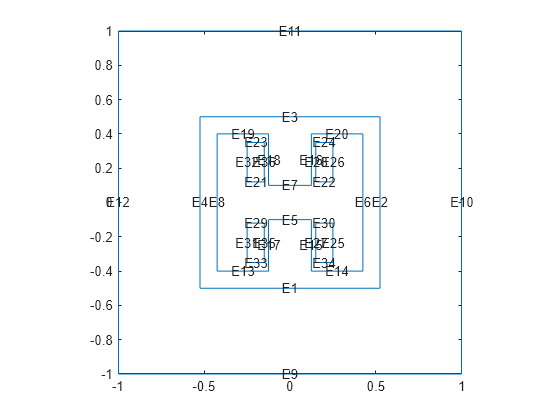
Create an femodel object for magnetostatic analysis and include the geometry in the model.
model = femodel(AnalysisType="magnetostatic", ... Geometry=g);
Generate a mesh with fine refinement in the ferromagnetic frame.
model = generateMesh(model,Hface={2,0.01},Hmax=0.1,Hgrad=2);
figure
pdemesh(model)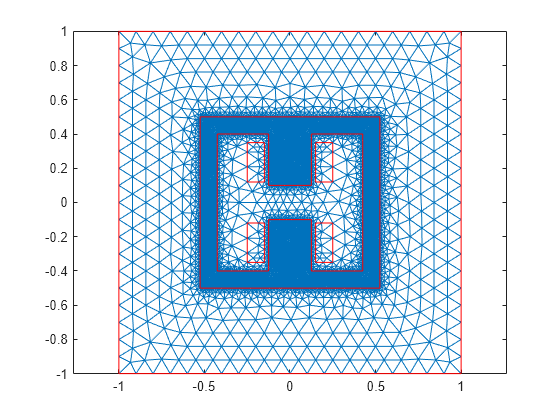
Specify the vacuum permeability value in the SI system of units.
model.VacuumPermeability = 1.25663706212e-6;
Specify a relative permeability of 1 for all domains.
model.MaterialProperties = ...
materialProperties(RelativePermeability=1);Now specify the large constant relative permeability of the ferromagnetic frame.
model.MaterialProperties(2) = ...
materialProperties(RelativePermeability=10000);Specify the current density values on the upper and lower coils.
model.FaceLoad([5,6]) = faceLoad(CurrentDensity=1E6); model.FaceLoad([4,7]) = faceLoad(CurrentDensity=-1E6);
Specify that the magnetic potential on the outer surface of the air domain is 0.
model.EdgeBC([5,6,13,14]) = edgeBC(MagneticPotential=0);
Solve the model.
R = solve(model)
R =
MagnetostaticResults with properties:
MagneticPotential: [32049x1 double]
MagneticField: [1x1 FEStruct]
MagneticFluxDensity: [1x1 FEStruct]
Mesh: [1x1 FEMesh]
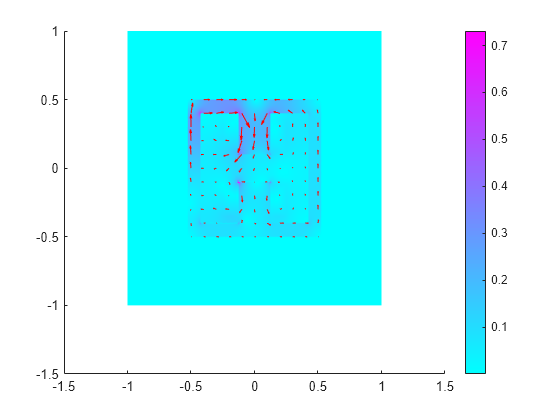
Plot the magnitude of the flux density.
Bmag = sqrt(R.MagneticFluxDensity.Bx.^2 + ... R.MagneticFluxDensity.By.^2); pdeplot(R.Mesh,XYData=Bmag, ... FlowData=[R.MagneticFluxDensity.Bx ... R.MagneticFluxDensity.By])
References
[1] Kozlowski, A., R. Rygal, and S. Zurek. "Large DC electromagnet for semi-industrial thermomagnetic processing of nanocrystalline ribbon." IEEE Transactions on Magnetics 50, issue 4 (April 2014): 1-4. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6798057.
