자속 기준 제어를 사용하여 모터를 구동하기 위한 제어기 이득 구하기
이 예제에서는 PMSM(영구 자석 동기 모터)의 FOC(자속 기준 제어)에서 전류 제어 루프와 속도 제어 루프에 대한 최적 이론을 사용하여 PI 제어기 이득을 구하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 이 예제에서는 PI 제어기 이득을 구하기 위해 사용할 수 있는 다음 여러 가지 옵션을 제공합니다.
모터의 기본적인 전기 파라미터와 기계적 파라미터, 제어기의 샘플 시간, 전류 제어 루프와 저역통과 필터의 시정수를 지정한 다음, 특정 코드 섹션이나 Simulink 모델을 실행하여 제어기 이득을 구합니다.
모터와 인버터를 정의하는 작업 공간 변수를 정의한 다음, 이 예제에서 제공되는 Simulink 모델을 사용하여
mcb.calcFOCGains함수로 제어기 이득을 계산합니다. 이 방법은 모터 제어 애플리케이션이 특정 모터에 맞춰 설계된 경우에 유용하며, 제어기 컴파일 중에 이득 계산을 수행할 수 있습니다.모터와 인버터를 정의하는 작업 공간 변수를 정의한 다음, 이 예제에서 제공되는 Simulink 모델을 사용하여 FOC Default Controller Gains 블록으로 제어기 이득을 계산합니다. 이 방법은 모터 제어 애플리케이션이 매번 코드를 다시 컴파일하지 않고도 서로 다른 모터 설정으로 작동해야 하는 경우에 유용하며, 이득 계산을 제어기 코드에 통합할 수 있습니다.
mcb.calcFOCGains 함수 또는 FOC Default Controller Gains 블록을 사용하는 마지막 두 옵션에서는 피드백 루프의 지연과 계산에 사용할 단위계(SI 또는 Per-Unit)를 지정할 수 있습니다. 이 두 가지 옵션을 사용하면 모터 및 인버터 파라미터(작업 공간 변수)와 피드백 지연에 대한 새로운 값을 제공하여 Motor Control Blockset™의 다른 예제에서 언급된 모든 FOC 애플리케이션에 대한 제어기 이득을 계산할 수 있습니다.
필요한 MathWorks® 제품
Motor Control Blockset
Simulink®
Control System Toolbox™(전달 함수를 계산하는 데만 필요함)
폐루프 속도 제어 시스템의 전달 함수
다음 이미지는 자속 기준 제어를 사용하는 PMSM의 속도 제어에 대한 블록 다이어그램을 나타냅니다.
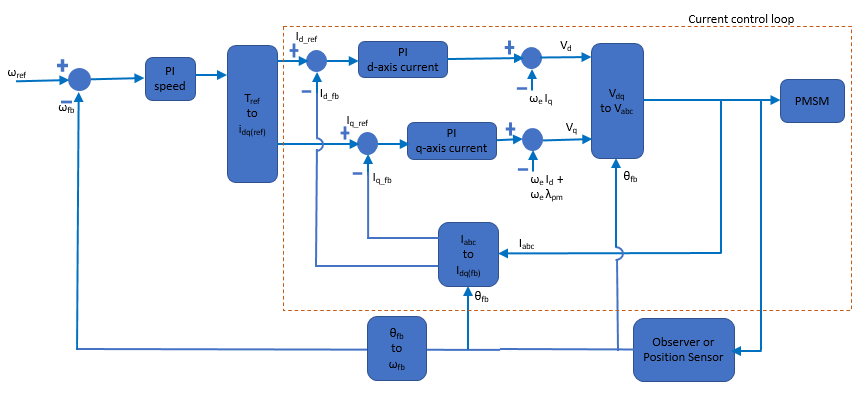
전류 제어 루프
다음 이미지는 전류 제어 루프의 폐루프 전달 함수를 나타냅니다.

참고: 위의 블록 다이어그램에서 전류 제어 루프의 실행 시간이 높은 값으로 설정된 경우, Sampling 전달 함수의 분모는 가 될 수 있습니다.
근사 블록 다이어그램
전달 함수를 사용한 전류 제어 루프의 근사 블록 다이어그램은 그 모습이 다음과 같습니다.

Id 제어기와 Iq 제어기의 Kp 및 Ki 값은 모두 모듈로(Modulus) 최적 이론을 사용하여 계산할 수 있습니다. 이 이론에 따라, 폐루프 시스템은 다음과 같은 전달 함수를 가집니다. 이는 와 동일합니다.
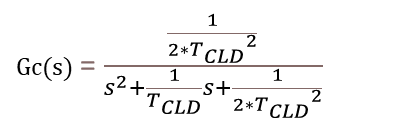
위 방정식과 다이어그램에서 각 항은 다음 값을 나타냅니다.
![]()
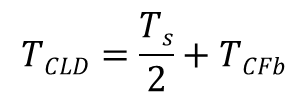
방정식은 다음 변수를 사용합니다.
전류 제어 루프에 있는 모든 지연의 합계 | |
전류 제어 루프의 피드백 경로에 있는 모든 지연의 합계 |
전류 필터가 없고 관측기 대신 센서가 사용되는 경우 입니다. 이 경우, 이는 다음 변수를 갖는 2차 시스템입니다.
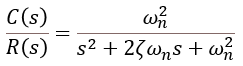
변수의 값은 다음과 같습니다.
(감쇠비):
(고유 주파수):
속도 제어 루프
다음 이미지는 속도 제어 루프의 폐루프 전달 함수를 나타냅니다.
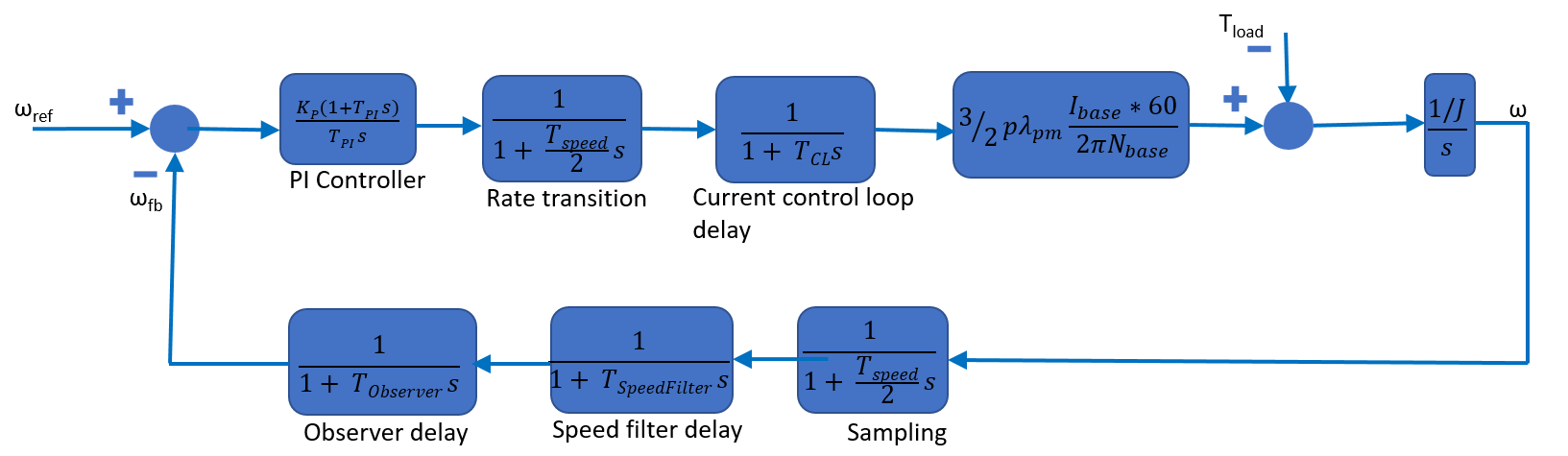
근사 블록 다이어그램
전달 함수를 사용한 속도 제어 루프의 근사 블록 다이어그램의 모습은 다음과 같습니다.

Id 제어기와 Iq 제어기의 Kp 및 Ki 값은 모두 모듈로(Modulus) 최적 이론을 사용하여 계산되며, 전류 제어 루프는 다음 1차 전달 함수로 구현할 수 있습니다.
속도 제어기의 Kp 및 Ki 값은 대칭 최적(Symmetric Optimum) 이론을 사용하여 계산할 수 있습니다. 이 이론에 따라, 폐루프 시스템은 다음과 같은 전달 함수를 가집니다.
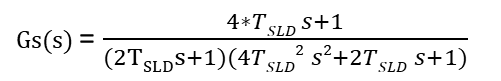
위 방정식과 다이어그램에서 각 항은 다음 값을 나타냅니다.
![]()
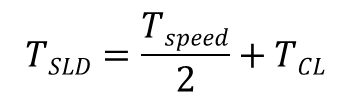
![]()
방정식은 다음 변수를 사용합니다.
속도 제어 루프 지연의 시정수 | |
속도 제어 중 피드백 루프 지연의 시정수 | |
전류 제어 루프에 있는 모든 지연의 합계 | |
전류 제어 루프의 피드백 경로에 있는 모든 지연의 합계 | |
전류 제어 루프 지연의 시정수 |
이론적 근사 전달 함수 Gs(s)와 함께 시스템의 계단 응답을 플로팅할 수 있습니다. 이득 계산은 시스템을 근사하여 수행되므로 두 플롯에 차이가 있을 수 있습니다.
기본적인 전기 파라미터 및 기계적 파라미터를 제공하여 제어기 이득 구하기
저항, 인덕턴스, 극쌍 개수, FluxPM, 제어기의 샘플 시간 등 기본 파라미터의 값을 제공하고, 아래 코드 섹션을 실행하여 전류 제어 루프와 속도 제어 루프의 Kp 및 Ki 값을 출력할 수 있습니다.
전류 제어 루프의 코드 실행하기
다음 코드 섹션에서 파라미터 값을 입력하고 Calculate Gain을 클릭하여 전류 제어 루프에 대한 제어기 이득을 구합니다.
%Electrical parameters of motor R =0.2; % Stator winding resistance per phase (ohm) L =
0.002; % d-axis winding inductance (henry) %Sample time of controller Ts_curr =
0.00005; % seconds %Time constant of low pass filter T_currfilter =
0.0001; % seconds %Run this section to obtain gains calculateCLGain; disp(PIGains);
Kp: 6.6667
Ki: 666.6667
속도 제어 루프의 코드 실행하기
다음 코드 섹션에서 파라미터 값을 입력하고 Calculate Gain을 클릭하여 속도 제어 루프에 대한 제어기 이득을 구합니다.
%Mechanical parameters of motor J =0.001; % Motor inertia (kg-m^2) p =
4; % Pole-pairs FluxPM =
1; % Permanent magnet flux linkage (weber) %Sample time of controller Ts_spd =
0.001; % seconds %Time constant of current control loop T_currloop = 1.5*Ts_curr + T_currfilter; % seconds %Time constant of low pass filter T_spdfilter =
0.001; % seconds %Run this section to obtain gains calculateSLGain; disp(PIGains);
Kp: 0.0383
Ki: 4.4039
전류 제어와 속도 제어에 대한 제어기 이득을 구하는 모델 시뮬레이션하기
또는 이 예제와 함께 제공된 ModelControlGainBlock 모델을 시뮬레이션할 수 있습니다. 이 모델에는 FOC Default Controller Gains 블록이 포함되어 있습니다. 이 블록에 대한 입력으로 기본 파라미터, 샘플 시간, 시정수 값 등을 제공하고 모델을 시뮬레이션하여 제어기 이득을 구합니다.

open_system('ModelControlGainBlock');
Motor Control Blockset 예제의 제어기 이득 구하기
Motor Control Blockset™을 사용하면 하드웨어 필터 지연이나 관측기(센서리스 FOC의 경우)로 인한 지연과 같은 시스템 내의 각종 지연을 개수 제한 없이 고려하여 최적 이론을 적용하고 제어기 이득을 계산할 수 있습니다. 이 섹션에 언급된 두 가지 방법 중 하나를 사용하여 제어 루프를 더 낮은 차수의 선형 시불변 시스템으로 근사할 수 있습니다. 두 방법 모두 전류 제어기 이득 계산에는 모듈로(Modulus) 최적 이론을 사용하고 속도 제어기 이득 계산에는 대칭(Symmetric) 최적 이론을 사용합니다.
작업 공간 변수 정의하기
함수나 블록을 사용하여 제어기 이득을 구하려면 먼저 일부 작업 공간 변수의 값을 지정해야 합니다. 이 예제에서 이러한 값은 mcb.calcFOCGains 함수와 FOC Default Controller Gains 블록에 대한 입력값입니다. 여기에는 모터 및 인버터 파라미터 값, per-unit 단위계 베이스 값, PWM 스위칭 시간 주기, 제어 시스템의 샘플 시간, 속도 제어기의 샘플 시간 및 필터 차단 주파수가 포함됩니다.
%Run this section to define workspace variable %Select Motor SelectedMotor ='Teknic2310P'; pmsm = mcb.getPMSMParameters(SelectedMotor); %Select Inverter SelectedInverter =
'BoostXL-DRV8305'; inverter = mcb.getInverterParameters(SelectedInverter); %Get rated speed for motor and inverter pair pmsm.N_rated = mcb.getMotorBaseSpeed(pmsm,inverter); %Choose PWM frequency for controller PWMFrequency =
20000; % Hz %Defining sample time for current control loop and speed control loop Ts = 1/PWMFrequency; Ts_speed = 10/PWMFrequency; %Consider board resistance for calculating controller gain motor = pmsm; motor.Rs = pmsm.Rs + inverter.R_board; %Base for SI system PU_System.V_base = 1; % Volts PU_System.I_base = 1; % Amperes PU_System.N_base = 60/(2*pi); % RPM (= 1 rad/sec) PU_System.T_base = 1; % Nm % Two low pass filters are connected in series to measure the current signal in the loop % only to demonstrate how to use function, if the loop has certain delay component present % (either hardware or software). % Value of cutoff frequency is chosen randomly. CutOffFrq1 = 100; % Hz CutOffFrq2 = 100; % Hz
mcb.calcFOCGains 함수
모터 제어 애플리케이션이 특정 모터에 맞춰 설계된 경우 제어기 코드 컴파일 중에 이득 계산을 수행할 수 있습니다. 이 시나리오에서는 mcb.calcFOCGains 함수를 사용하여 제어기 이득을 확인할 수 있습니다. 이 예제에서는 이 함수를 사용하여 PMSM의 FOC에서 전류 제어 루프와 속도 제어 루프에 대한 제어기 이득을 구하는 방법을 자세히 설명합니다.
mcb.calcFOCGains를 사용하여 토크 또는 전류 제어 루프의 이득 구하기
% Command to obtain gain
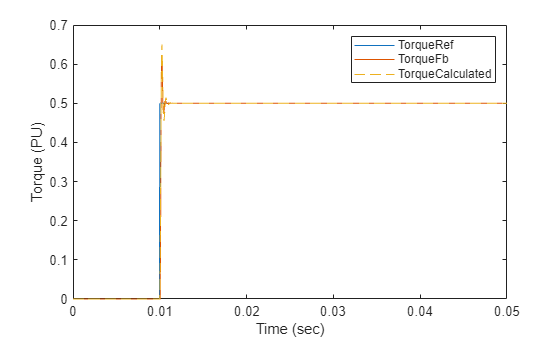
PI_params = mcb.calcFOCGains(motor,Ts,Ts_speed);모델을 시뮬레이션하고 이론적 근사 전달 함수 Gc(s)와 함께 시스템의 계단 응답을 플로팅합니다. 이득 계산은 시스템을 근사하여 수행되므로 두 플롯에 차이가 있을 수 있습니다.
% Run this section to simulate model and plot torque step responses of the modeled torque % control loop (TorqueFb) and the approximated transfer function (TorqueCalculated) T = Ts; % Total delay (Here, T = T_CLD from the equation) plotStepResponse('ModelForTorqueControl','UsingScript','SI','WithoutDelay');

mcb.calcFOCGains를 사용한 Per-Unit 단위계 기반의 제어기 이득
이 섹션에서는 함수에서 사용된 초기값을 대신 per-unit 값으로 바꿉니다.
%Run this section to define base values for PU system
PU_System.V_base = inverter.V_dc/sqrt(3);
PU_System.I_base = pmsm.I_rated;
PU_System.N_base = pmsm.N_rated;
PU_System.T_base = pmsm.T_rated;% Use input argument 'Base' to provide base values defined for system
PI_params = mcb.calcFOCGains(pmsm,Ts,Ts_speed,Base=PU_System);% Run this section to simulate model and plot torque step responses of modeled torque % control loop (TorqueFb) and the approximated transfer function (TorqueCalculated) plotStepResponse('ModelForTorqueControl','UsingScript','PU','WithoutDelay');
지연 요소가 1개일 때 mcb.calcFOCGains를 사용한 SI 단위계 기반의 제어기 이득
이 섹션에서는 피드백 경로에 지연 요소를 추가하고 전류 제어 루프의 제어에 대한 제어 이득을 구합니다.
%Run this section to consider delay in the loop %Select cutoff frequency CutOffFrq =100; % Hz %Create delay component to represent filter Delay.Gain = 1; Delay.TimeConstant = 1/(2*pi*CutOffFrq);
%Input argument 'CLFeedbackPathDelay' is used to define a delay element in %feedback path of the current control loop (CL) PI_params = mcb.calcFOCGains(pmsm,Ts,Ts_speed,CLFeedbackPathDelay=Delay);
아래 코드에서 T는 Gc(s)에 대한 전달 함수에 표현된 것과 같이 입니다.
% Run this section to simulate model and plot torque step responses of modeled torque % control loop (TorqueFb) and the approximated transfer function (TorqueCalculated) T = Ts + Delay.TimeConstant; % Total delay (Here T is T_CLD) plotStepResponse('ModelForTorqueControl','UsingScript','SI','WithDelay');
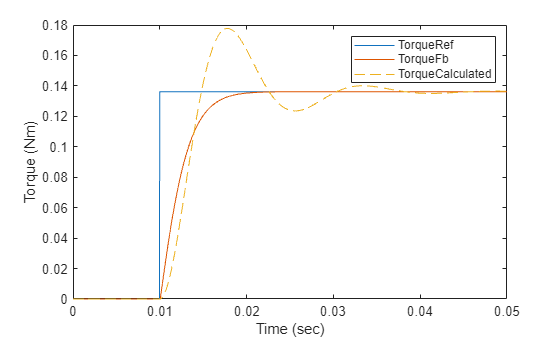
참고: 계산된 토크와 시뮬레이션 결과 간의 동특성 차이는 전달 함수의 근사 때문에 생기는 것입니다.
지연 요소가 2개일 때 mcb.calcFOCGains를 사용한 SI 단위계 기반의 제어기 이득
이 섹션에서는 피드백 경로에 여러 지연 요소(예: 하드웨어 저역통과 필터, 소프트웨어 저역통과 필터 또는 관측기)를 추가하고 전류 제어 루프에 대한 제어 이득을 구합니다.
% Run this section to add two delay in series for the loop % Select cutoff frequency for first filter CutOffFrq =500; % Hz % Create delay component to represent filter Delay1.Gain = 1; Delay1.TimeConstant = 1/(2*pi*CutOffFrq); % Select cutoff frequency for second filter CutOffFrq =
500; % Hz % Create delay component to represent filter Delay2.Gain = 1; Delay2.TimeConstant = 1/(2*pi*CutOffFrq); TotalDelay.Gain = [Delay1.Gain Delay2.Gain]; TotalDelay.TimeConstant = [Delay1.TimeConstant Delay2.TimeConstant];
% Input argument 'CLFeedbackPathDelay' to define all delay elements in % feedback path of the current control loop (CL) PI_params = mcb.calcFOCGains(pmsm,Ts,Ts_speed,CLFeedbackPathDelay=TotalDelay);
아래 코드에서 T는 Gc(s)에 대한 전달 함수에 표현된 것과 같이 입니다.
% Run this section to simulate model and plot torque step responses of modeled torque % control loop (TorqueFb) and the approximated transfer function (TorqueCalculated) T = Ts + Delay1.TimeConstant + Delay2.TimeConstant; % Total delay (Here T is T_CLD) plotStepResponse('ModelForTorqueControl','UsingScript','SI','WithTwoDelays');
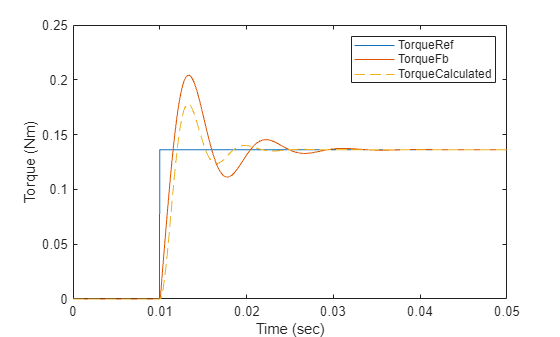
참고: 계산된 토크와 시뮬레이션 결과 간의 동특성 차이는 전달 함수의 근사 때문에 생기는 것입니다.
FOC Default Controller Gains 블록
모터 제어 애플리케이션이 매번 코드를 다시 컴파일하지 않고도 서로 다른 모터 설정으로 작동해야 하는 경우 이득 계산을 제어기 코드에 통합해야 합니다. 이 시나리오에서는 런타임 중에 FOC Default Controller Gains 블록을 사용하여 제어기 이득을 확인할 수 있습니다. 이 예제의 Simulink 모델은 이 블록을 사용하여 PMSM의 FOC에서 전류 제어 루프와 속도 제어 루프의 제어기 이득을 구합니다.
FOC Default Controller Gains 블록을 사용하여 토크 또는 전류 제어의 제어기 이득 구하기
%Run this section to open the model openModel('ModelForTorqueControl','UsingBlock','SI','WithoutDelay');
모델의 Controller/Controller Gain 서브시스템에는 FOC Default Controller Gains 블록이 포함되어 있습니다. 모델을 시뮬레이션하여 Controller 서브시스템의 Field-Oriented Current Controller 블록에 대한 입력인 제어기 이득을 구할 수 있습니다.
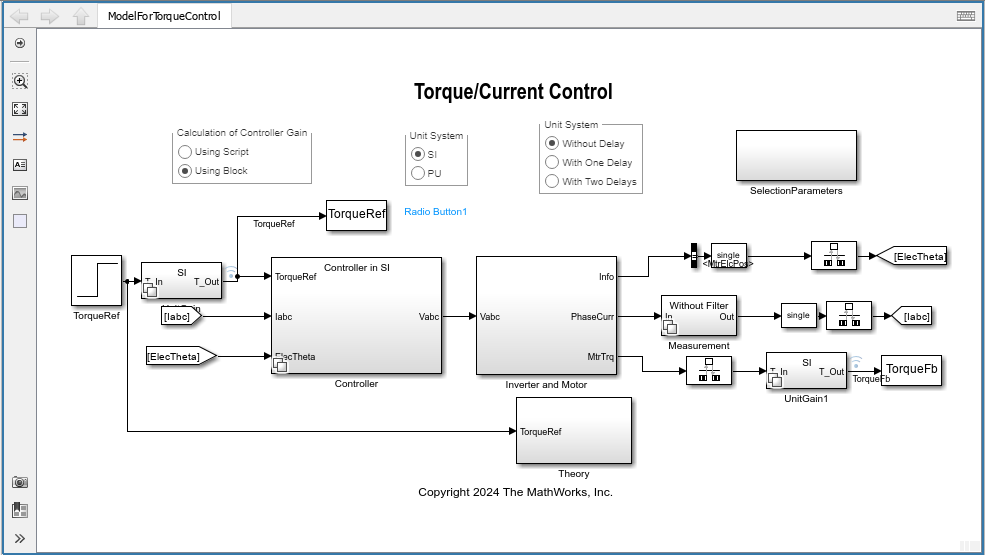
FOC Default Controller Gains 블록을 사용한 Per-Unit 단위계 기반의 제어기 이득
이 섹션에서는 블록에서 사용된 초기값을 대신 per-unit 값으로 바꿉니다.
%Run this section to open the model openModel('ModelForTorqueControl','UsingBlock','PU','WithoutDelay');
모델을 시뮬레이션하여 Controller 서브시스템의 Field-Oriented Current Controller 블록에 대한 입력인 제어기 이득을 구합니다.

지연 요소가 1개일 때 FOC Default Controller Gains 블록을 사용한 SI 단위계 기반의 제어기 이득
%Run this section to open the model openModel('ModelForTorqueControl','UsingBlock','SI','WithDelay');
모델을 시뮬레이션하여 Controller 서브시스템의 Field-Oriented Current Controller 블록에 대한 입력인 제어기 이득을 구합니다.
지연 요소가 2개일 때 FOC Default Controller Gains 블록을 사용한 SI 단위계 기반의 제어기 이득
%Run this section to open the model openModel('ModelForTorqueControl','UsingBlock','SI','WithTwoDelays');
응답이 느릴 경우의 토크 제어에 대한 이득 구하기
시스템에 알 수 없는 지연 컴포넌트가 있는 경우, 제어기 이득을 계산하기 위해 감속 인자를 사용할 수 있습니다.
%Run this section to add slow down factor in torque control loop %Select slow down factor Factor =0.25; PI_params = mcb.calcFOCGains(pmsm,Ts,Ts_speed,DCurrLoopFactor=Factor,QCurrLoopFactor=Factor);
%Run this section to simulate model and plot torque step responses of modeled torque %control loop (TorqueFb) and the approximated transfer function (TorqueCalculated) T = Ts + 1/(2*pi*CutOffFrq1); plotStepResponse('ModelForTorqueControl','UsingScript','SI','WithDelay');
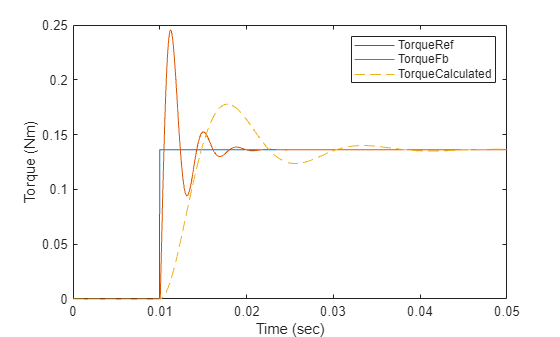
참고: 계산된 토크와 시뮬레이션 결과 간의 동특성 차이는 전달 함수의 근사 때문에 생기는 것입니다.
mcb.calcFOCGains를 사용하여 속도 제어 루프에 대한 이득 구하기
%Run this section to obtain gain for speed control loop %Base for SI system PU_System.V_base = 1; % V PU_System.I_base = 1; % A PU_System.N_base = 60/(2*pi); % RPM (= 1 rad/sec) %Define coefficient for IIR filter present for measured speed SpdCoeff =0.05; PI_params = mcb.calcFOCGains(motor,Ts,Ts_speed,SpdLPFltCoeff=SpdCoeff);
%Run this section to simulate model and plot torque step responses of the modeled %speed control loop (SpeedFb) and the approximated transfer function (SpeedCalculated) T = 1.5*Ts + Ts_speed + Ts*(1-SpdCoeff)/SpdCoeff; % Here T = T_SLD plotStepResponse('ModelForSpeedControl','UsingScript','SI','WithoutDelay');

참고: 계산된 속도와 시뮬레이션 결과 간의 동특성 차이는 전달 함수의 근사 때문에 생기는 것입니다.
mcb.calcFOCGains를 사용하여 Per-Unit 단위계 기반의 속도 제어에 대한 이득을 구하고 응답 플로팅하기
이 섹션에서는 함수에서 사용된 초기값을 대신 per-unit 값으로 바꿉니다.
%Run this section to define base values for PU system
PU_System.V_base = inverter.V_dc/sqrt(3);
PU_System.I_base = pmsm.I_rated;
PU_System.N_base = pmsm.N_rated;
PU_System.T_base = pmsm.T_rated;%Use input argument 'Base' to provide base values defined for system
PI_params = mcb.calcFOCGains(pmsm,Ts,Ts_speed,SpdLPFltCoeff=SpdCoeff,Base=PU_System);%Run this section to simulate model and plot torque step responses of modeled %speed control loop (SpeedFb) and the approximated transfer function (SpeedCalculated) T = 1.5*Ts + Ts_speed + Ts*(1-SpdCoeff)/SpdCoeff; plotStepResponse('ModelForSpeedControl','UsingScript','PU','WithoutDelay')
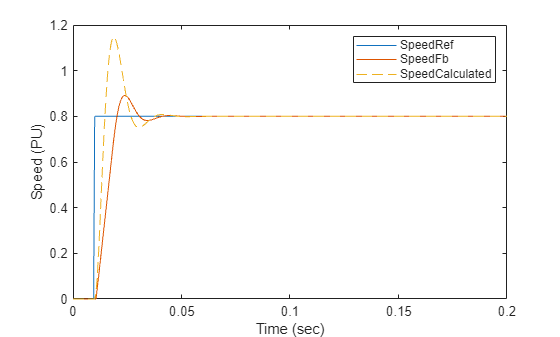
참고: 전달 함수의 근사로 인해 이론과 시뮬레이션 간에 동특성 차이가 있습니다.
FOC Default Controller Gains 블록을 사용하여 속도 제어 루프에 대한 이득 구하기
%Run this section to open the model openModel('ModelForSpeedControl','UsingBlock','SI','WithoutDelay');
모델의 Controller/Controller Gain 서브시스템에는 FOC Default Controller Gains 블록이 포함되어 있습니다. 모델을 시뮬레이션하여 Controller 서브시스템의 Field-Oriented Current Controller 블록에 대한 입력인 제어기 이득을 구합니다.
FOC Default Controller Gains 블록을 사용하여 속도 제어에 대한 Per-Unit 단위계 기반의 이득 구하기
이 섹션에서는 블록에서 사용된 초기값을 대신 per-unit 값으로 바꿉니다.
%Run this section to open the model openModel('ModelForSpeedControl','UsingBlock','PU','WithoutDelay');
모델을 시뮬레이션하여 Controller 서브시스템의 Field-Oriented Current Controller 블록에 대한 입력인 제어기 이득을 구합니다.

응답이 느릴 경우의 속도 제어에 대한 이득 구하기
시스템에 알 수 없는 지연 컴포넌트가 있는 경우, 제어기 이득을 계산하기 위해 감속 인자를 사용할 수 있습니다.
%Run this section to add slow down factor for speed control loop % Select slow down factor Factor =0.5; PI_params = mcb.calcFOCGains(pmsm,Ts,Ts_speed,SpdLPFltCoeff=0.1,SpdLoopFactor=Factor,Base=PU_System);
%Run this section to simulate model and plot torque step responses of modeled %speed control loop (SpeedFb) and the approximated transfer function (SpeedCalculated) T = 1.5*Ts + Ts_speed + Ts*(1-SpdCoeff)/SpdCoeff; plotStepResponse('ModelForSpeedControl','UsingScript','PU','WithoutDelay');
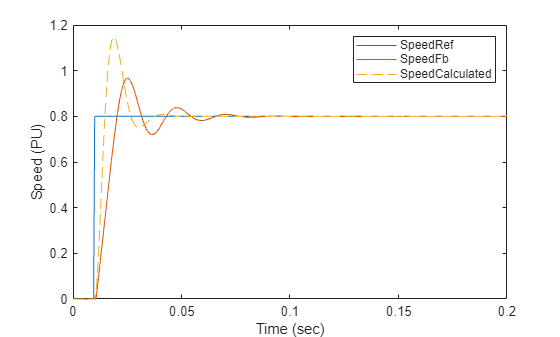
참고: 계산된 속도와 시뮬레이션 결과 간의 동특성 차이는 전달 함수의 근사 때문에 생기는 것입니다.
OLTF 및 CLTF와 관련한 mcb.calcFOCGains의 고급 기능
mcb.calcFOCGains 함수는 3개의 루프(D축 전류, Q축 전류, 속도) 각각에 대한 OLTF(개루프 전달 함수)와 CLTF(폐루프 전달 함수)도 출력합니다.
참고: mcb.calcFOCGains 함수를 사용하여 전달 함수를 계산하려면 Control System Toolbox™ 라이선스가 필요합니다.
예를 들면 다음과 같습니다.
[PI_params,OLTF,CLTF] = mcb.calcFOCGains(motor,Ts,Ts_speed);
% Open loop transfer function for D-axis current control loop
DCurrOpenLoopTF = tf(OLTF.DCurrLoop.Numerator,OLTF.DCurrLoop.Denominator)DCurrOpenLoopTF =
2.745
-------------------------------
2.745e-08 s^2 + 0.0005989 s + 1
Continuous-time transfer function.
Model Properties
% Open loop transfer function for Q-axis current control loop
QCurrOpenLoopTF = tf(OLTF.QCurrLoop.Numerator,OLTF.QCurrLoop.Denominator)QCurrOpenLoopTF =
2.745
-------------------------------
2.745e-08 s^2 + 0.0005989 s + 1
Continuous-time transfer function.
Model Properties
% Open loop transfer function for speed control loop
SpeedOpenLoopTF = tf(OLTF.SpdLoop.Numerator,OLTF.SpdLoop.Denominator)SpeedOpenLoopTF =
5434
----------------
0.000575 s^2 + s
Continuous-time transfer function.
Model Properties
% Closed loop transfer function for D-axis current control loop
DCurrCloseLoopTF = tf(CLTF.DCurrLoop.Numerator,CLTF.DCurrLoop.Denominator)DCurrCloseLoopTF =
2e08
--------------------
s^2 + 20000 s + 2e08
Continuous-time transfer function.
Model Properties
% Closed loop transfer function for Q-axis current control loop
QCurrCloseLoopTF = tf(CLTF.QCurrLoop.Numerator,CLTF.QCurrLoop.Denominator)QCurrCloseLoopTF =
2e08
--------------------
s^2 + 20000 s + 2e08
Continuous-time transfer function.
Model Properties
% Closed loop transfer function for speed control loop
SpeedCloseLoopTF = tf(CLTF.SpdLoop.Numerator,CLTF.SpdLoop.Denominator)SpeedCloseLoopTF =
0.0023 s + 1
--------------------------------------------
1.521e-09 s^3 + 2.645e-06 s^2 + 0.0023 s + 1
Continuous-time transfer function.
Model Properties
위 전달 함수 객체에 대한 제어 분석을 수행하는 방법에 대한 자세한 내용은 Control System Toolbox 시작하기 항목을 참조하십시오.