Magnetic Flux Density in Electromagnet
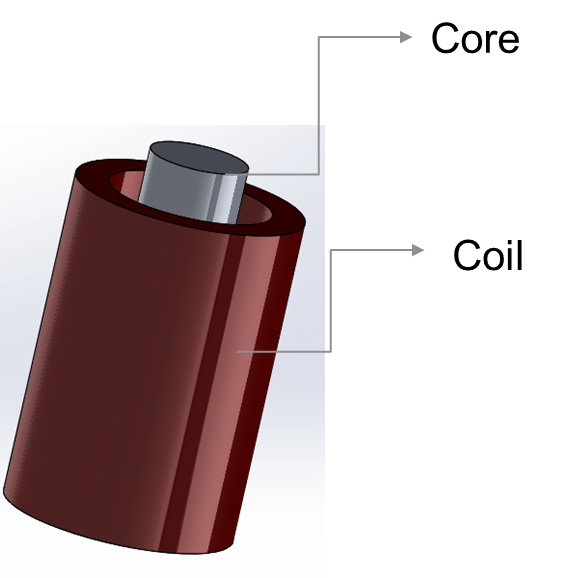
This example shows how to solve a 3-D magnetostatic problem for a solenoid with a finite length iron core. Using a ferromagnetic core with high permeability, such as an iron core, inside a solenoid increases magnetic field and flux density. In this example, you find the magnetic flux density for a geometry consisting of a coil with a finite length core in a cylindrical air domain.
The first part of the example solves the magnetostatic problem using a 3-D model. The second part solves the same problem using an axisymmetric 2-D model to speed up computations.
3-D Model of Coil with Core
Create geometries consisting of three cylinders: a solid circular cylinder models the core, an annular circular cylinder models the coil, and a larger circular cylinder models the air around the coil.
coreGm = multicylinder(0.03,0.1); coilGm = multicylinder([0.05 0.07],0.2,Void=[1 0]); airGm = multicylinder(1,2);
Position the core and coil so that the finite length core is located near the top of coil.
coreGm = translate(coreGm,[0 0 1.025]); coilGm = translate(coilGm,[0 0 0.9]);
Combine the geometries and plot the result.
gm = addCell(airGm,coreGm);
gm = addCell(gm,coilGm);
pdegplot(gm,FaceAlpha=0.2,CellLabels="on")
Zoom in to see the cell labels on the core and coil.
figure
pdegplot(gm,FaceAlpha=0.2,CellLabels="on")
axis([-0.1 0.1 -0.1 0.1 0.8 1.2])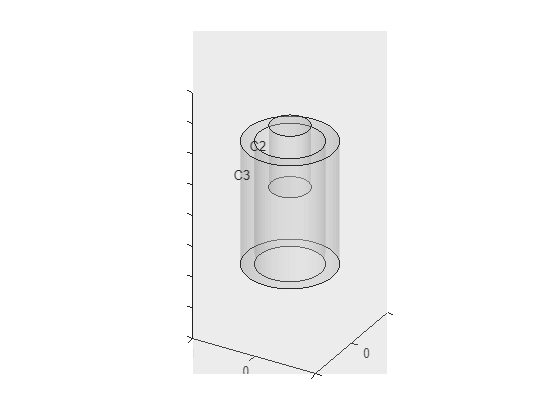
Create an femodel object for magnetostatic analysis and assign air geometry to the model.
model = femodel(AnalysisType="magnetostatic", ... Geometry=gm);
Specify the vacuum permeability value in the SI system of units.
model.VacuumPermeability = 1.2566370614E-6;
Specify a relative permeability of 1 for all domains.
model.MaterialProperties = ...
materialProperties(RelativePermeability=1);Now specify the large relative permeability of the core.
model.MaterialProperties(2) = ...
materialProperties(RelativePermeability=10000);Create a function that defines counterclockwise current density in the coil.
function f3D = windingCurrent3D(region,~) [TH,~,~] = cart2pol(region.x,region.y,region.z); f3D = -5E6*[sin(TH); -cos(TH); zeros(size(TH))]; end
Assign an excitation current using this function.
model.CellLoad(3) = ...
cellLoad(CurrentDensity=@windingCurrent3D);Assign the zero magnetic potential on the outer surface of the air domain. First, plot the geometry with face labels.
pdegplot(model.Geometry,FaceAlpha=0.5, ... FaceLabels="on")

Specify that the magnetic potential on faces forming the outer surface of the air domain is 0.
model.FaceBC(1:3) = faceBC(MagneticPotential=[0;0;0]);
Generate a mesh where only the core and coil regions are well refined and the air domain is relatively coarse to limit the size of the problem.
internalFaces = cellFaces(model.Geometry,2:3);
model = generateMesh(model,Hface={internalFaces,0.007});Solve the model.
R = solve(model)
R =
MagnetostaticResults with properties:
MagneticPotential: [1×1 FEStruct]
MagneticField: [1×1 FEStruct]
MagneticFluxDensity: [1×1 FEStruct]
Mesh: [1×1 FEMesh]
Find the magnitude of the flux density.
Bmag = sqrt(R.MagneticFluxDensity.Bx.^2 + ... R.MagneticFluxDensity.By.^2 + ... R.MagneticFluxDensity.Bz.^2);
Find the mesh elements belonging to the core and the coil.
coreAndCoilElem = findElements(R.Mesh, ... "region", ... Cell=[2 3]);
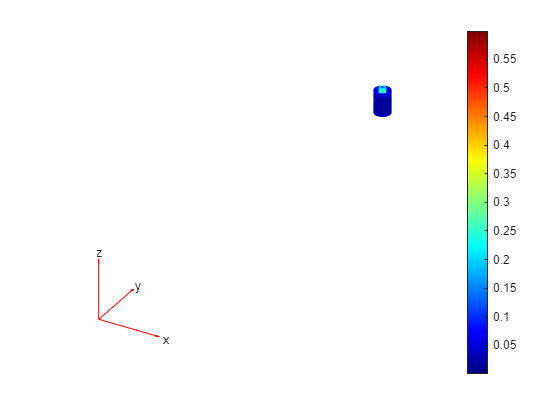
Plot the magnitude of the flux density on the core and coil.
pdeplot3D(R.Mesh.Nodes, ... R.Mesh.Elements(:,coreAndCoilElem), ... ColorMapData=Bmag)
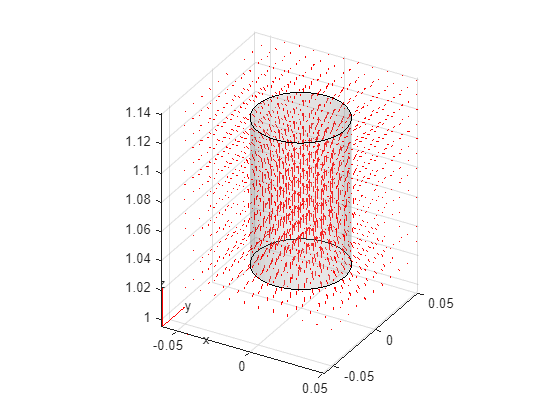
Interpolate the flux to a grid covering the portion of the geometry near the core.
x = -0.05:0.01:0.05; z = 1.02:0.01:1.14; y = x; [X,Y,Z] = meshgrid(x,y,z); intrpBcore = R.interpolateMagneticFlux(X,Y,Z);
Reshape intrpBcore.Bx, intrpBcore.By, and intrpBcore.Bz and plot the magnetic flux density as a vector plot.
Bx = reshape(intrpBcore.Bx,size(X)); By = reshape(intrpBcore.By,size(Y)); Bz = reshape(intrpBcore.Bz,size(Z)); quiver3(X,Y,Z,Bx,By,Bz,Color="r") hold on pdegplot(coreGm,FaceAlpha=0.2);
2-D Axisymmetric Model of Coil with Core
Now, simplify this 3-D problem to 2-D using the symmetry around the axis of rotation.
First, create the geometry. The axisymmetric section consists of two small rectangular regions (the core and coil) located within a large rectangular region (air).
R1 = [3,4,0.0,1,1,0.0,0,0,2,2]'; R2 = [3,4,0,0.03,0.03,0,1.025,1.025,1.125,1.125]'; R3 = [3,4,0.05,0.07,0.07,0.05,0.90,0.90,1.10,1.10]'; ns = char('R1','R2','R3'); sf = 'R1+R2+R3'; gdm = [R1, R2, R3]; g = decsg(gdm,sf,ns');
Plot the geometry with the face labels.
pdegplot(g,FaceLabels="on")
Zoom in to see the face labels on the core and coil.
figure
pdegplot(g,FaceLabels="on")
axis([0 0.1 0.8 1.2])
Create an femodel object for magnetostatic axisymmetric analysis and include the geometry.
model = femodel(AnalysisType="magnetostatic", ... Geometry=g); model.PlanarType = "axisymmetric";
Specify the vacuum permeability value in the SI system of units.
model.VacuumPermeability = 1.2566370614E-6;
Specify a relative permeability of 1 for all domains.
model.MaterialProperties = ...
materialProperties(RelativePermeability=1);Now specify the large relative permeability of the core.
model.MaterialProperties(3) = ...
materialProperties(RelativePermeability=10000);Specify the current density in the coil. For an axisymmetric model, use the constant current value.
model.FaceLoad(2) = ...
faceLoad(CurrentDensity=5E6);Assign zero magnetic potential on the outer edges of the air domain as the boundary condition. First, plot the geometry with edge labels.
pdegplot(model.Geometry,FaceAlpha=0.2, ... EdgeLabels="on")
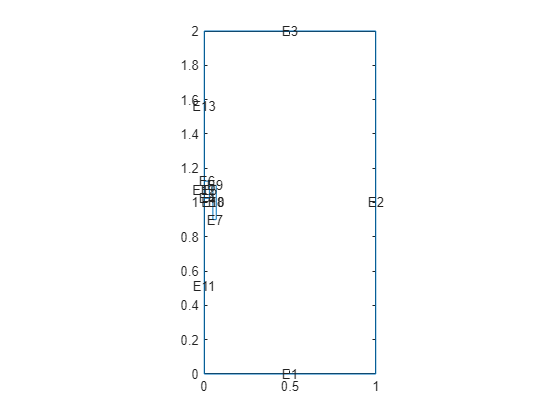
Specify that the magnetic potential on the outer edges of the air domain is 0.
model.EdgeBC([2 8]) = edgeBC(MagneticPotential=0);
Generate a mesh where only the core and coil regions are well refined and the air domain is relatively coarse to limit the size of the problem.
internalEdges = faceEdges(model.Geometry,2:3);
model = generateMesh(model,Hedge={internalEdges,0.007});Solve the model.
R = solve(model);
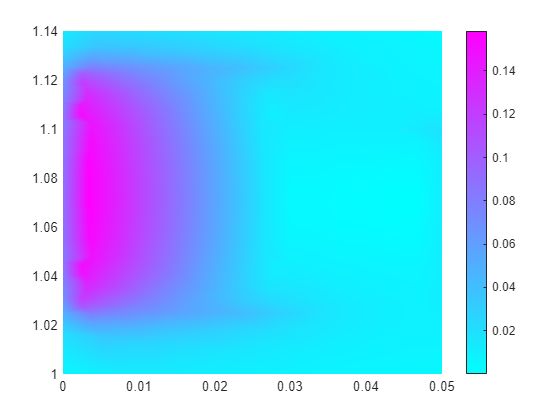
Find the magnitude of the flux density.
Bmag = sqrt(R.MagneticFluxDensity.Bx.^2 + ...
R.MagneticFluxDensity.By.^2);Plot the magnitude of the flux density on the core and coil.
pdeplot(R.Mesh,XYData=Bmag) xlim([0,0.05]); ylim([1.0,1.14])
Interpolate the flux to a grid covering the portion of the geometry near the core.
x = 0:0.01:0.05; y = 1.02:0.01:1.14; [X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y); intrpBcore = R.interpolateMagneticFlux(X,Y);
Reshape intrpBcore.Bx and intrpBcore.By and plot the magnetic flux density as a vector plot.
Bx = reshape(intrpBcore.Bx,size(X)); By = reshape(intrpBcore.By,size(Y)); quiver(X,Y,Bx,By,Color="r") hold on pdegplot(model.Geometry); xlim([0,0.07]); ylim([1.0,1.14])

References
[1] Thierry Lubin, Kévin Berger, Abderrezak Rezzoug. "Inductance and Force Calculation for Axisymmetric Coil Systems Including an Iron Core of Finite Length." Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, EMW Publishing 41 (2012): 377-396. https://hal.science/hal-00711310.