3-D Multidomain Geometry from 2-D Geometry
This example shows how to create a 3-D multidomain geometry by extruding a 2-D geometry imported from STL data. The original 2-D geometry represents a cooled turbine blade section defined by a 2-D profile.
Before extruding the geometry, this example modifies the original 2-D profile as follows:
Translates the geometry to move the tip to the origin
Aligns the chord with the x-axis
Changes the dimensions from inches to millimeters
Import the geometry.
g = fegeometry("CooledBlade2D.STL");Plot the geometry with the face labels.
figure
pdegplot(g,FaceLabels="on")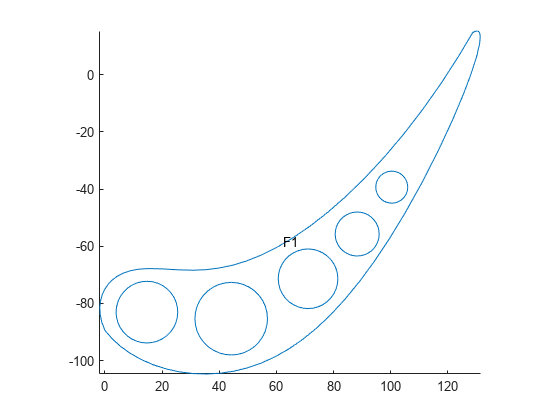
Translate the geometry to align the tip of the blade with the origin.
tip = [1.802091,-127.98192215]; g = translate(g,tip);
Rotate the geometry to align the chord with the x-axis.
angle = -36.26005; g = rotate(g,angle);
Scale the geometry to convert from inches to millimeters.
g = scale(g,[25.4 -25.4]);
Plot the resulting geometry with the face labels.
figure
pdegplot(g,FaceLabels="on")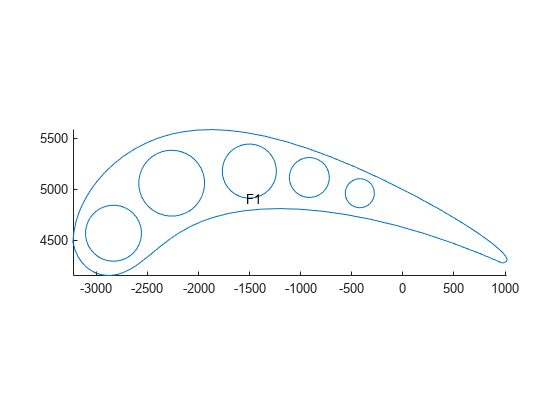
Fill the void regions with faces and plot the resulting geometry.
g = addFace(g,{3, 4, 5, 6, 7});
figure
pdegplot(g,FaceLabels="on")
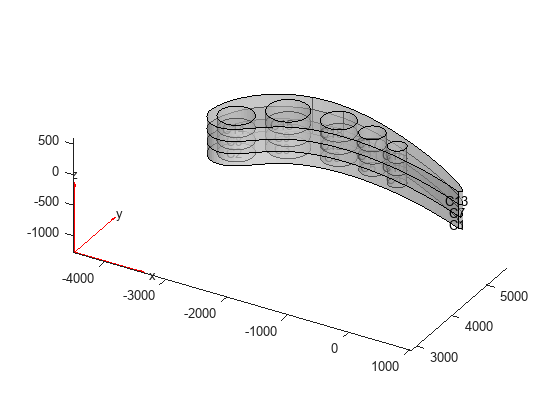
Extrude the geometry to create a stacked multilayer 3-D model of the blade. The thickness of each layer is 200 mm.
g = extrude(g,[200 200 200]);
Plot the geometry with the cell labels.
figure
pdegplot(g,CellLabels="on",FaceAlpha=0.5)