Server Overview
What Is a Server Instance?
A server instance is considered to be one unique
configuration of the MATLAB®
Production Server™ product. Each configuration has
its own server configuration file (main_config) and diagnostic files
(log, pid, and endpoint
files).
In addition, each server has its own auto_deploy folder, where you
upload the deployable archives (CTF files) that you want the server to host for
clients.
You can create any number of server instances using MATLAB Production Server software. Each server instance can host any number of deployable archives containing MATLAB code. You may find it helpful to create one server for all archives relating to a particular application. You can also create one server to host code strictly for testing, and so on.
The server also manages the
MATLAB Runtime
(MATLAB Compiler), which enables deployed MATLAB code to execute. The settings in main_config determine
how each server interacts with the MATLAB Runtime to process clients requests. You can set these parameters according to
your performance requirements and other variables in your IT environment.
How Does a Server Manage Work?
A server processes a transaction using these steps:
The client sends MATLAB function calls to the main server process.
The main server process passes the MATLAB function calls to one or more MATLAB Runtime workers.
The MATLAB Runtime workers execute the MATLAB functions deployed to the server.
The MATLAB Runtime workers pass the results of MATLAB function execution back to the main server process.
The main server process passes the results of MATLAB function execution back to the client for processing.
The server is the intermediary in the MATLAB Production Server environment. It simultaneously accepts connections from clients, and then dispatches MATLAB Runtime workers—MATLAB sessions—to process client requests to the MATLAB Runtime. By defining and adjusting the number of workers and threads available to a server, you tune capacity and throughput, respectively.
Workers (capacity management) (
num-workers) — The number of MATLAB Runtime workers available to a server.Each worker dispatches one MATLAB execution request to the MATLAB Runtime, interacting with one client at a time. By defining and tuning the number of workers available to a server, you set the number of concurrent MATLAB execution requests that can be processed simultaneously.
num-workersshould roughly correspond to the number of cores available on the local host.Threads (throughput management) (
num-threads) — The number of threads (units of processing) available to the main server process.MATLAB Production Server Data Flow from Client to Server and Back
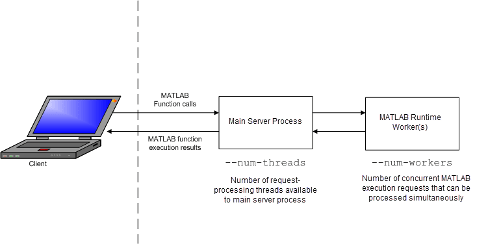
The server does not allocate a unique thread to each client connection. Rather, when data is available on a connection, the required processing is scheduled on a pool of threads.
--num-threadssets the size of that pool (the number of available request-processing threads) in the main server process. The threads in the pool do not execute MATLAB code directly. Instead, there is a single thread within each MATLAB Runtime worker process that executes MATLAB code on behalf of the client.