Use the Raspberry Pi I2C Interface to Connect to a Device
This example shows how to create a connection to an I2C device, write data to the device, and read data from the device.
Warning
Excessive voltage and current can damage the Raspberry Pi® hardware. Observe the manufacturer’s precautions for handling the Raspberry Pi hardware and connecting it to other devices. For more information, see https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/.
Create a connection to the Raspberry Pi hardware using raspi.
mypi = raspi
mypi =
raspi with properties:
DeviceAddress: 'raspberrypi-computername'
Port: 18725
BoardName: 'Raspberry Pi Model B Rev 2'
AvailableLEDs: {'led0'}
AvailableDigitalPins: [4 7 8 9 10 11 14 15 17 18 22 23 24 25 27 30 31]
AvailableSPIChannels: {}
AvailableI2CBuses: {'i2c-0' 'i2c-1'}
I2CBusSpeed: 100000
Supported peripheralsNote
If you encounter errors after running the above command, try using additional arguments
(as listed in raspi) or refer to Troubleshoot Connecting Issues to Raspberry Pi Hardware.
The default I2C bus speed is 100000 bits per second.
You can redisplay the AvailableI2CBuses and
I2CBusSpeed properties.
mypi.AvailableI2CBuses mypi.I2CBusSpeed
ans =
'i2c-0' 'i2c-1'
ans =
100000Show the location of the I2C pins on the GPIO header.
showPins(mypi)
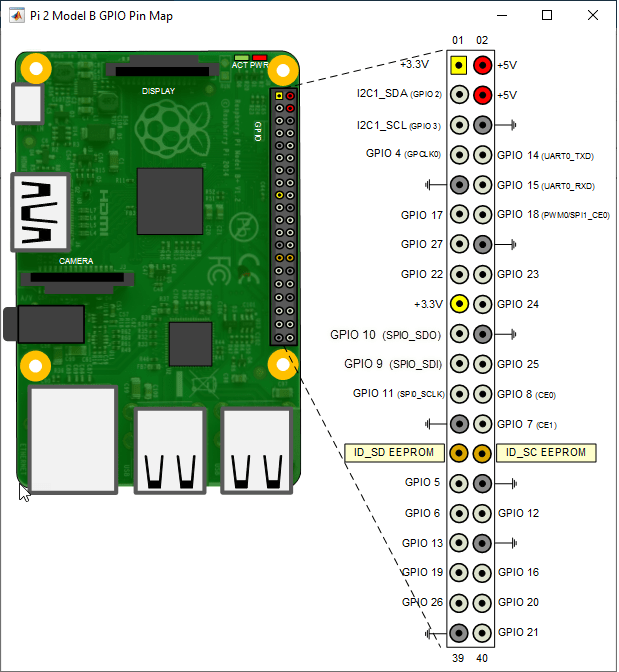
The pin map shows that, for this model and revision of the board, the
i2c-1 bus is available on the GPIO header pins I2C1_SDA (GPIO
2) and I2C1_SCL (GPIO 3).
Raspberry Pi hardware uses +3.3V. Do not connect Raspberry Pi hardware directly to devices that deliver higher voltages.
Before continuing, research the manufacturer’s product information to determine which settings the I2C device supports. Then, connect the Raspberry Pi board to the I2C device.
For example, with the MCP4725 12-bit DAC, connect:
I2C1_SDA (GPIO2)pin on the Raspberry Pi board to the SDA pin on the DAC.I2C1_SCL (GPIO3)pin on the Raspberry Pi board to the SCL pin on the DAC.GNDon the Raspberry Pi board to theGNDpin on the DAC.+3.3Von the Raspberry Pi board to theVDDpin on the DAC.VOUTpin on the DAC to the positive lead on the voltmeter.GNDto the negative lead on the voltmeter.
Get the addresses of I2C devices that are attached to the I2C bus,
'i2c-1'.
scanI2CBus(mypi,'i2c-1')
ans =
'0x62'Create a connection to the I2C DAC at '0x62' and assign that connection
to a handle, i2cdac.
i2cdac = i2cdev(mypi,'i2c-1','0x62')
i2cdac =
i2cdev with properties:
Bus: 'i2c-1'
Address: '0x62'Write a value to the I2C device.
write(i2cdac,4092)
To read a value from an I2C sensor, physically connect the sensor, use
scanI2CBus to get the address, use i2cdev to
create a connection to the device. Then, use read to get the
value.
addr = scanI2CBus(mypi,'i2c-1') i2csensor = i2cdev(mypi,'i2c-1',char(addr)) read(i2csensor,1)
If you are not using I2C, disable I2C using the Hardware Setup Screen to make additional GPIO pins available.
Note
Before disabling I2C, clear the i2cdev object, if created. For
example, clear (i2csensor).
When you use I2C again, enable I2C using the Hardware Setup screen. You can also change the I2C bus speed using the Hardware Setup screen.
mypi.I2CBusSpeed
ans =
40000